Abstract
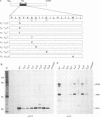
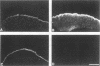
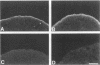
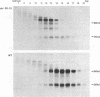
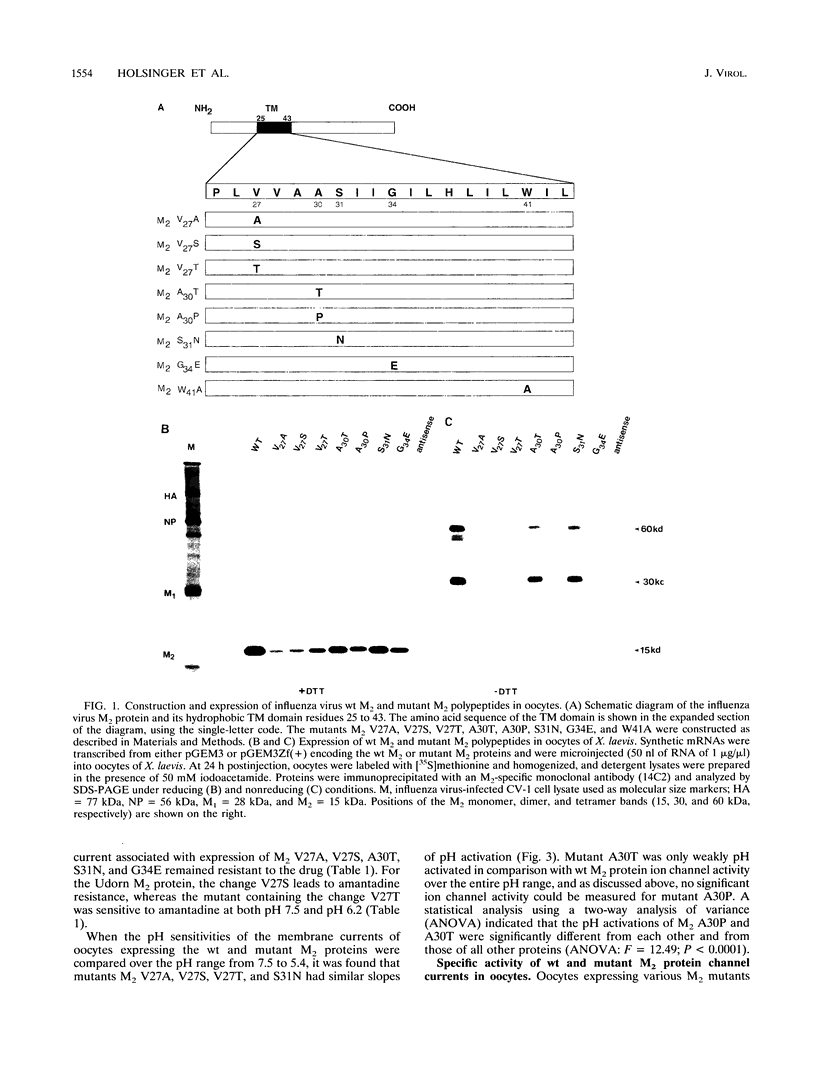
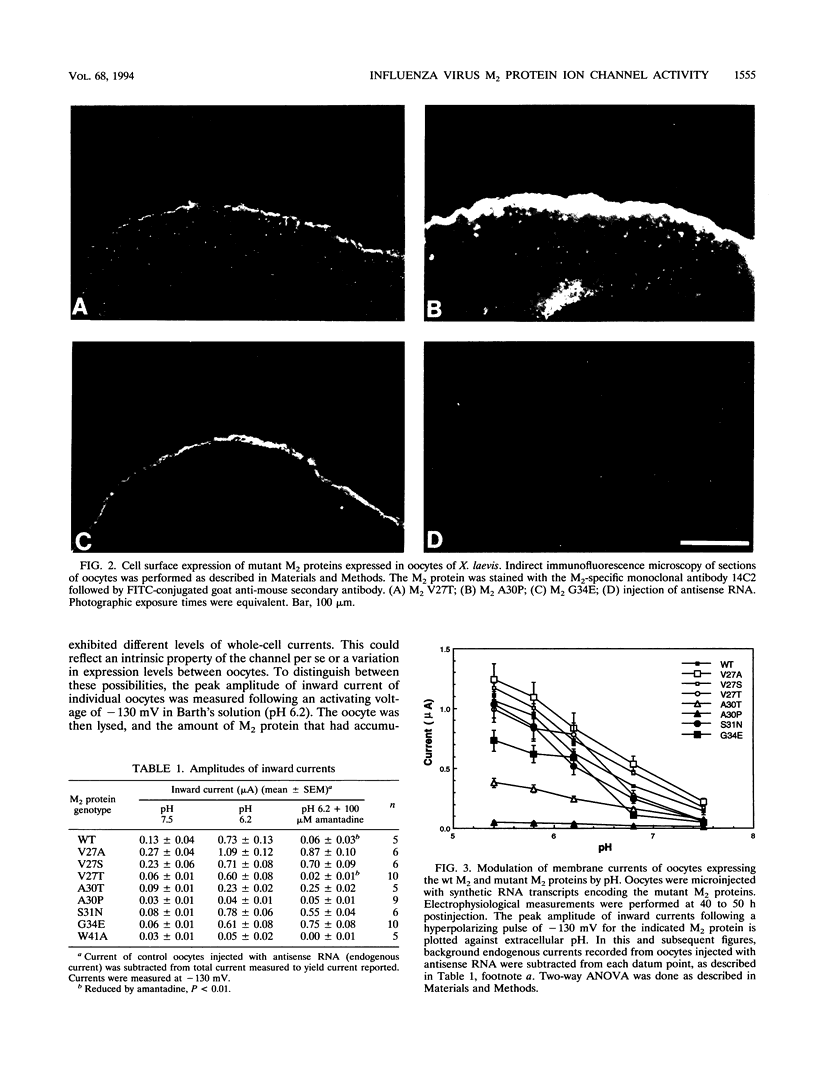
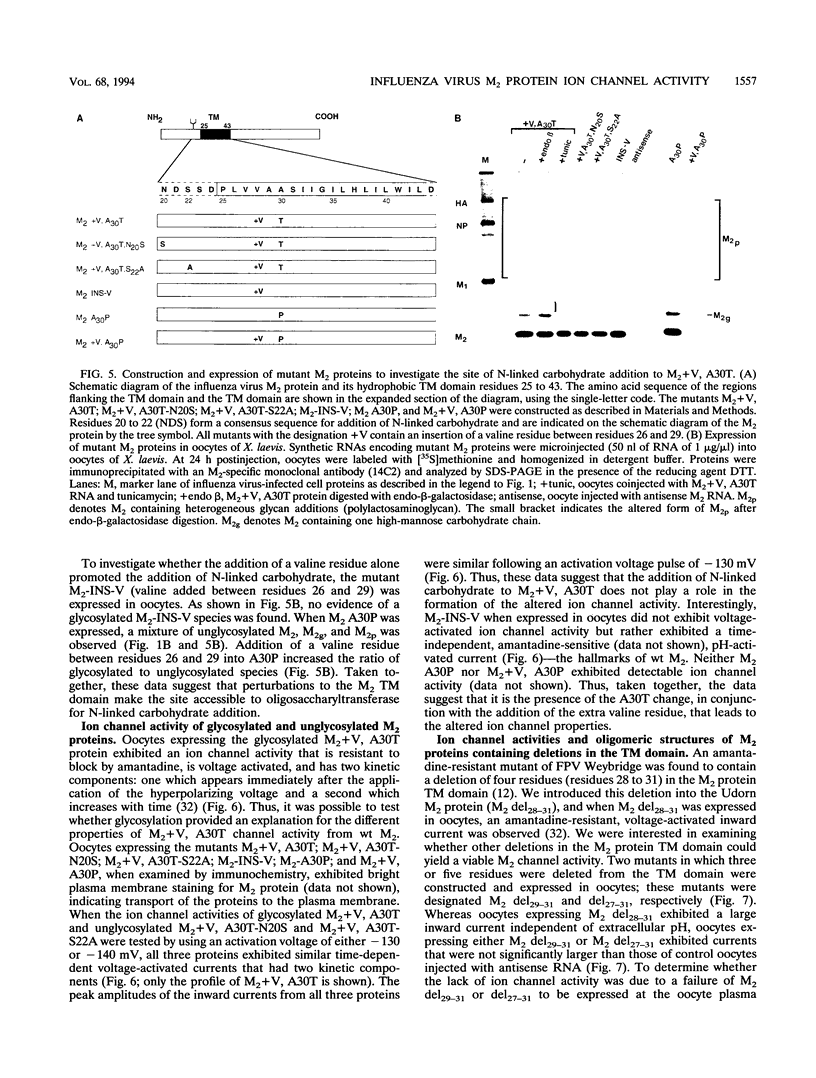
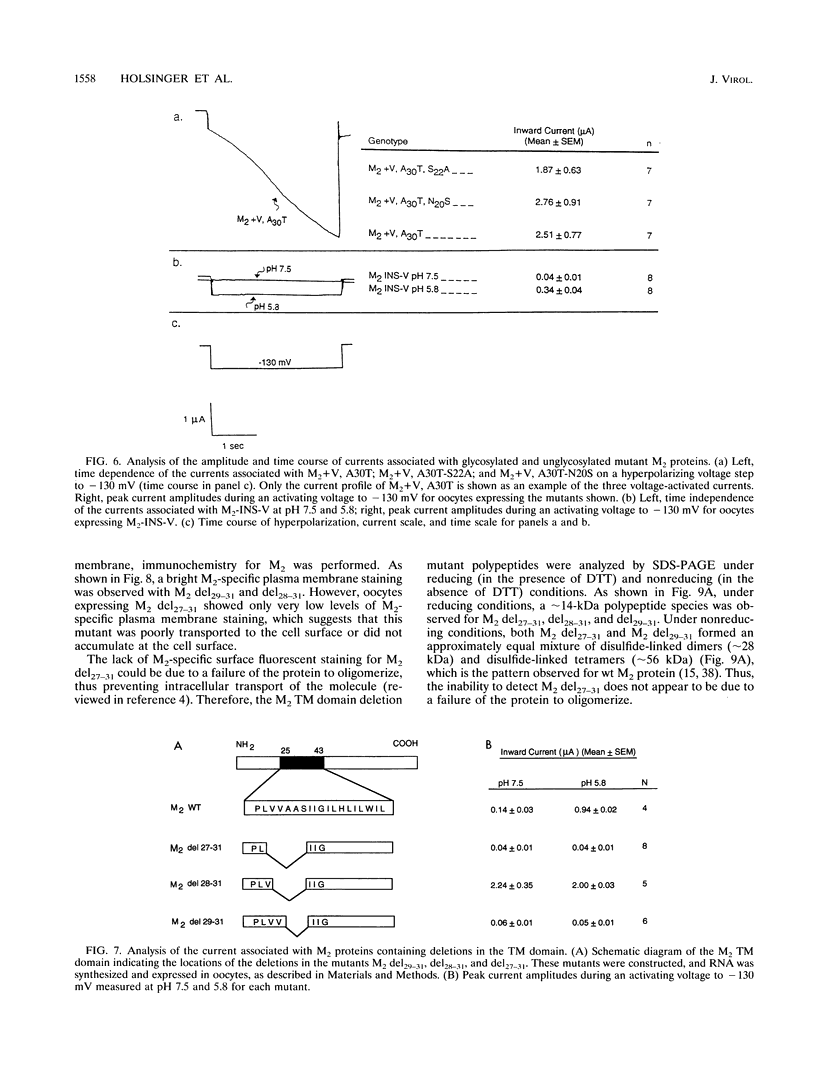
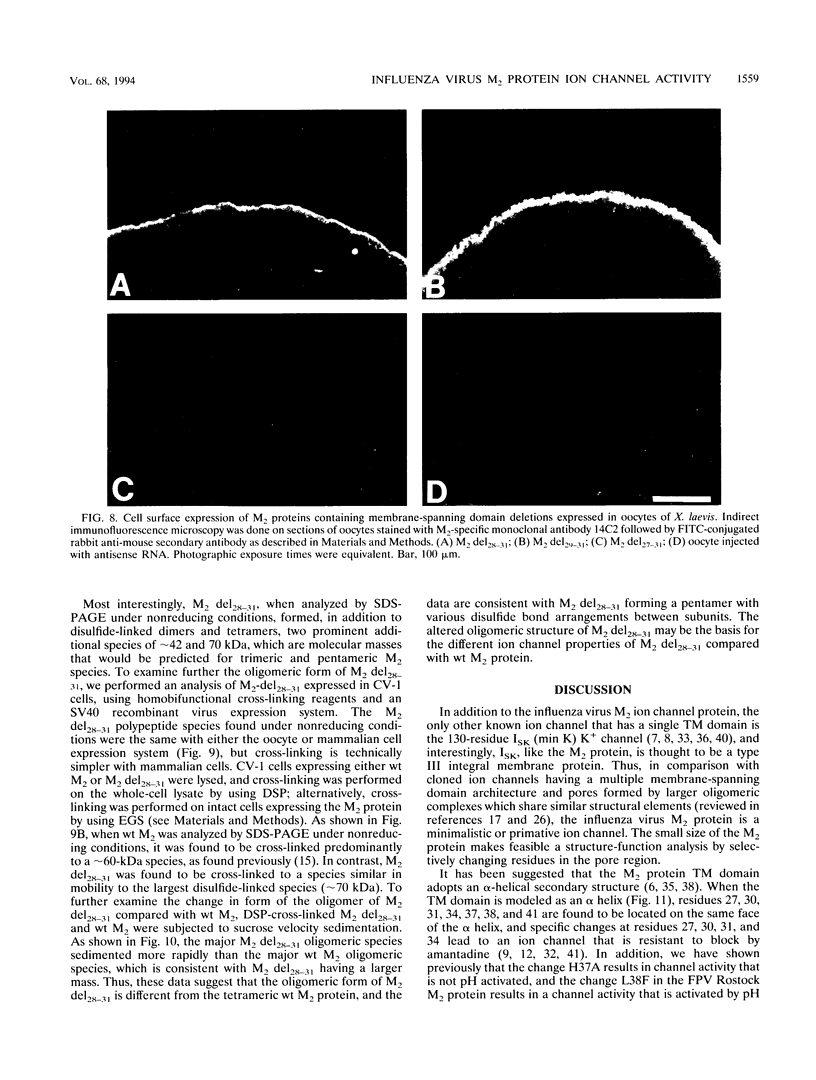
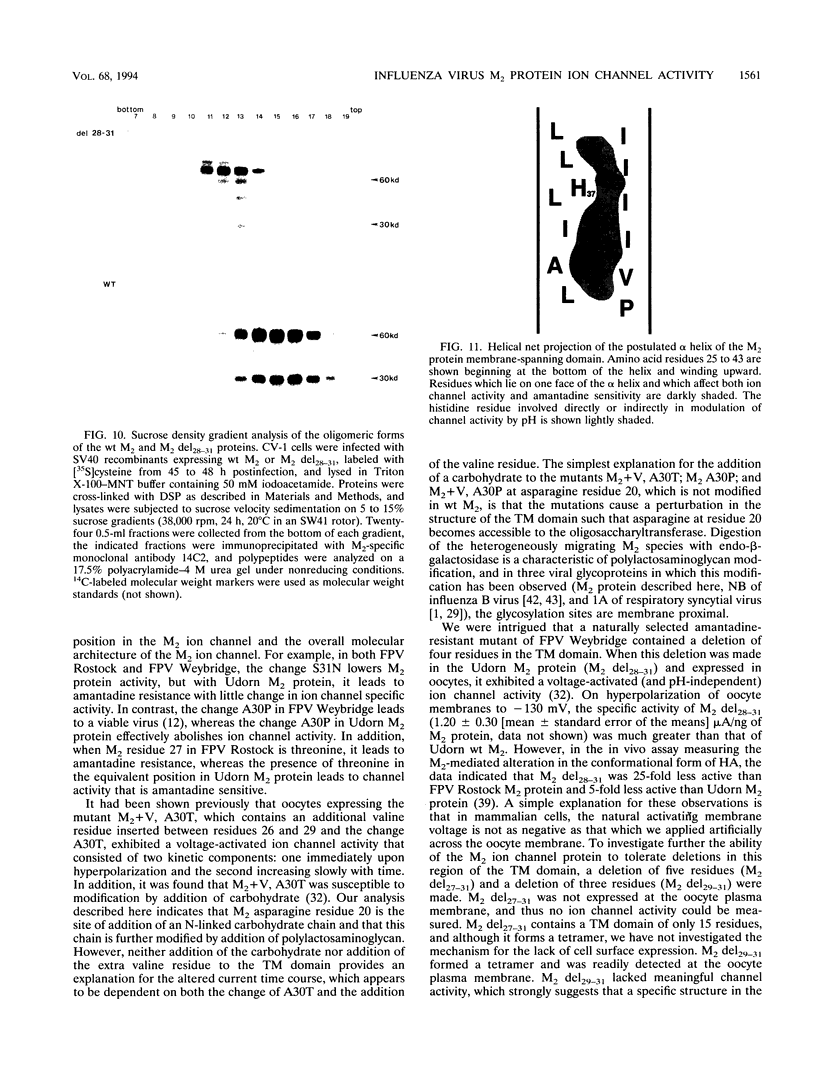
A structure-function analysis of the influenza A virus M2 ion channel protein was performed. The M2 protein of human influenza virus A/Udorn/72 and mutants containing changes on one face of the putative alpha helix of the M2 transmembrane (TM) domain, several of which lead to amantadine resistance when found in virus, were expressed in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. The membrane currents of oocytes expressing mutant M2 ion channels were measured at both normal and low pH, and the amantadine-resistant mutant containing the change of alanine at residue 30 to threonine was found to have a significantly attenuated low pH activation response. The specific activity of the channel current of the amantadine-resistant mutants was investigated by measuring the membrane current of individual oocytes followed by quantification of the amount of M2 protein expressed in these single oocytes by immunoblotting analysis. The data indicate that changing residues on this face of the putative alpha helix of the M2 TM domain alters properties of the M2 ion channel. Some of the M2 proteins containing changes in the TM domain were found to be modified by addition of an N-linked carbohydrate chain at an asparagine residue that is membrane proximal and which is not modified in the wild-type M2 protein. These N-linked carbohydrate chains were further modified by addition of polylactosaminoglycan. A glycosylated M2 mutant protein (M2 + V, A30T) exhibited an ion channel activity with a voltage-activated, time-dependent kinetic component. Prevention of carbohydrate addition did not affect the altered channel activity. The ability of the M2 protein to tolerate deletions in the TM domain was examined by expressing three mutants (del29-31, del28-31, and del27-31) containing deletions of three, four, and five residues in the TM domain. No ion channel activity was detected from expression of M2 del29-31 and del27-31, whereas expression of M2 del28-31 resulted in an ion channel activity that was activated by hyperpolarization (and not low pH) and was resistant to amantadine block. Examination of the oligomeric form of M2 del28-31 indicated that the oligomer is different from wild-type M2, and the data were consistent with M2 del28-31 forming a pentamer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K., King A. M., Lerch R. A., Wertz G. W. Polylactosaminoglycan modification of the respiratory syncytial virus small hydrophobic (SH) protein: a conserved feature among human and bovine respiratory syncytial viruses. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):417–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F., Bayley P. M., Nermut M. V., Hirst E. M., Sugrue R. J., Hay A. J. Evidence that the amantadine-induced, M2-mediated conversion of influenza A virus hemagglutinin to the low pH conformation occurs in an acidic trans Golgi compartment. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90730-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F., Thompson C. A., Grambas S., Hay A. J. Regulation of pH by the M2 protein of influenza A viruses. Virus Res. 1992 Mar;22(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90056-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Lamb R. A., Rose J. K., Helenius A. Folding and assembly of viral membrane proteins. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):545–562. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff K. C., Ashley R. H. The transmembrane domain of influenza A M2 protein forms amantadine-sensitive proton channels in planar lipid bilayers. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91239-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff K. C., Kelly S. M., Price N. C., Bradshaw J. P. The secondary structure of influenza A M2 transmembrane domain. A circular dichroism study. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 26;311(3):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folander K., Smith J. S., Antanavage J., Bennett C., Stein R. B., Swanson R. Cloning and expression of the delayed-rectifier IsK channel from neonatal rat heart and diethylstilbestrol-primed rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. A., Miller C. Site-specific mutations in a minimal voltage-dependent K+ channel alter ion selectivity and open-channel block. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambas S., Bennett M. S., Hay A. J. Influence of amantadine resistance mutations on the pH regulatory function of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):541–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90229-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambas S., Hay A. J. Maturation of influenza A virus hemagglutinin--estimates of the pH encountered during transport and its regulation by the M2 protein. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91187-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Wolstenholme A. J., Skehel J. J., Smith M. H. The molecular basis of the specific anti-influenza action of amantadine. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3021–3024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., MacKinnon R. The aromatic binding site for tetraethylammonium ion on potassium channels. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90276-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A. Unpacking the incoming influenza virus. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):577–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 integral membrane protein is a homotetramer stabilized by formation of disulfide bonds. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):32–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90115-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull J. D., Gilmore R., Lamb R. A. Integration of a small integral membrane protein, M2, of influenza virus into the endoplasmic reticulum: analysis of the internal signal-anchor domain of a protein with an ectoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1489–1498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Voltage-sensitive ion channels. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumpf R. A., Dougherty D. A. A mechanism for ion selectivity in potassium channels: computational studies of cation-pi interactions. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1708–1710. doi: 10.1126/science.8378771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Identification of a second protein (M2) encoded by RNA segment 7 of influenza virus. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J., Choppin P. W. Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J. Spliced and unspliced messenger RNAs synthesized from cloned influenza virus M DNA in an SV40 vector: expression of the influenza virus membrane protein (M1). Virology. 1982 Dec;123(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Zebedee S. L., Richardson C. D. Influenza virus M2 protein is an integral membrane protein expressed on the infected-cell surface. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):627–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Hughes H. Hunting for the pore of voltage-gated channels. Curr Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Randall R. E., Lamb R. A. Intracellular maturation and transport of the SV5 type II glycoprotein hemagglutinin-neuraminidase: specific and transient association with GRP78-BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum and extensive internalization from the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3273–3289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Cramer A., Vey M., Ohuchi R., Garten W., Klenk H. D. Rescue of vector-expressed fowl plague virus hemagglutinin in biologically active form by acidotropic agents and coexpressed M2 protein. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):920–926. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.920-926.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Collins P. L. The 1A protein of respiratory syncytial virus is an integral membrane protein present as multiple, structurally distinct species. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2019–2029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2019-2029.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Ability of the hydrophobic fusion-related external domain of a paramyxovirus F protein to act as a membrane anchor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. RNA editing by G-nucleotide insertion in mumps virus P-gene mRNA transcripts. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4137–4145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4137-4145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto L. H., Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90452-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., Snay K. J., Trimmer J. S., MacLusky N. J., Naftolin F., Kaczmarek L. K., Boyle M. B. Estrogen induction of a small, putative K+ channel mRNA in rat uterus. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):807–812. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90207-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom M. S., Kerr I. D. Influenza virus M2 protein: a molecular modelling study of the ion channel. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):65–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Tanabe Y., Shigemoto R., Iwai M., Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Immunohistochemical study of a rat membrane protein which induces a selective potassium permeation: its localization in the apical membrane portion of epithelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jan;113(1):39–47. doi: 10.1007/BF01869604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue R. J., Bahadur G., Zambon M. C., Hall-Smith M., Douglas A. R., Hay A. J. Specific structural alteration of the influenza haemagglutinin by amantadine. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3469–3476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue R. J., Hay A. J. Structural characteristics of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses: evidence that it forms a tetrameric channel. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90075-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 protein ion channel activity stabilizes the native form of fowl plague virus hemagglutinin during intracellular transport. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):911–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.911-919.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takumi T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning of a membrane protein that induces a slow voltage-gated potassium current. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.3194754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Takeuchi K., Pinto L. H., Lamb R. A. Ion channel activity of influenza A virus M2 protein: characterization of the amantadine block. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5585–5594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5585-5594.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Lamb R. A. Determination of the orientation of an integral membrane protein and sites of glycosylation by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: influenza B virus NB glycoprotein lacks a cleavable signal sequence and has an extracellular NH2-terminal region. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4317–4328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. A., Lamb R. A. Polylactosaminoglycan modification of a small integral membrane glycoprotein, influenza B virus NB. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1186–1196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2762-2772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Richardson C. D., Lamb R. A. Characterization of the influenza virus M2 integral membrane protein and expression at the infected-cell surface from cloned cDNA. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):502–511. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.502-511.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]