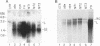Abstract
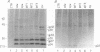
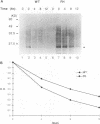
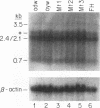
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) mutants unable to synthesize HBV e antigen have been described in association with fulminant hepatitis. We have cloned and sequenced the entire viral genome of an HBV strain associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. This strain contained, in addition to two G-to-A mutations in the precore region (nucleotides 1898 and 1901), numerous other mutations in conserved nucleotide positions resulting in significant amino acid substitutions in HBV gene products. We introduced either or both of the two G-to-A mutations into wild-type HBV by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis and generated replication-competent constructs of these mutants as well as the fulminant strain. Viral antigen synthesis, transcription, and replication were analyzed after transfection into human hepatoma cells. All viral constructs produced and secreted similar levels of envelope proteins (HBV surface antigen). Analysis of cellular lysate for core-specific immunoreactivity demonstrated a much higher level of core-associated antigens in cells transfected with the fulminant strain. While cells transfected with mutant and wild-type HBV DNAs synthesized similar levels of viral RNAs, the fulminant strain directed the synthesis of a much higher level of core-associated replicative intermediates (as well as virion particles) than the wild type and mutants with either or both of the precore mutations. Increase in the encapsidation of pregenomic RNA into core particles likely the basis for the enhanced replication associated with the fulminant strain. Our study suggests that an HBV mutant with enhanced viral replication may be important in the pathogenesis of fulminant hepatic failure, and mutations other than the precore mutations may be responsible for this variant behavior.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernuau J., Rueff B., Benhamou J. P. Fulminant and subfulminant liver failure: definitions and causes. Semin Liver Dis. 1986 May;6(2):97–106. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Pumpen P., Gren E. Subtype ayw variant of hepatitis B virus. DNA primary structure analysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80771-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Galun E., Liang T. J., von Weizsäcker F., Wands J. R. Naturally occurring missense mutation in the polymerase gene terminating hepatitis B virus replication. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1836–1842. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1836-1842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Zhang Z. S., Galun E., von Weizsäcker F., Garner B., Liang T. J., Wands J. R. Hepatitis B virus X protein is not central to the viral life cycle in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1223–1227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1223-1227.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Carman W. F., Thomas H. C. The clinical significance of molecular variation within the hepatitis B virus genome. Hepatology. 1992 Jan;15(1):144–148. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto M. R., Stemler M., Bonino F., Schodel F., Oliveri F., Rizzetto M., Verme G., Will H. A new hepatitis B virus strain in patients with severe anti-HBe positive chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1990 Mar;10(2):258–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(90)90062-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruss V., Ganem D. The role of envelope proteins in hepatitis B virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1059–1063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Jacyna M. R., Hadziyannis S., Karayiannis P., McGarvey M. J., Makris A., Thomas H. C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):588–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Thomas H. C. Genetic variation in hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. S., Kew M. C., Hornbuckle W. E., Tennant B. C., Cote P. J., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. The precore gene of the woodchuck hepatitis virus genome is not essential for viral replication in the natural host. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5682–5684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5682-5684.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L. Naturally occurring point mutation in the C terminus of the polymerase gene prevents duck hepatitis B virus RNA packaging. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1282–1287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1282-1287.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Vogel R., Ye W., Blume M., Lee S., Hung P. The core gene of hepatitis B virus; subtype adw2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8188–8188. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. W., Hu C. P., Su T. S., Lo S. C., Chu M. H., Schaller H., Chang C. M. Encapsidation of truncated human hepatitis B virus genomes through trans-complementation of the core protein and polymerase. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):355–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90005-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., Buras J., McLachlan A., Popper H., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Kirchhoff F., Czajak S. C., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C. Protective effects of a live attenuated SIV vaccine with a deletion in the nef gene. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1938–1941. doi: 10.1126/science.1470917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehata T., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Variations in codons 84-101 in the core nucleotide sequence correlate with hepatocellular injury in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):332–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI115581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa K., Huang J. K., Wands J. R., Obata H., Liang T. J. Association of hepatitis B viral precore mutations with fulminant hepatitis B in Japan. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):460–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90799-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Nomura M., Gotanda T., Sano T., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Takahashi K., Toyama S., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Demonstration of two distinct antigenic determinants on hepatitis B e antigen by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):69–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen R. S., Nathanson N., Endres M. J., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Virulence of La Crosse virus is under polygenic control. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.1-7.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Koike K. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA of subtype adr and its conserved gene organization. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka Y., Takase K., Kojima M., Shimizu M., Inoue K., Yoshiba M., Tanaka S., Akahane Y., Okamoto H., Tsuda F. Fulminant hepatitis B: induction by hepatitis B virus mutants defective in the precore region and incapable of encoding e antigen. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90286-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau J. Y., Bain V. G., Davies S. E., O'Grady J. G., Alberti A., Alexander G. J., Williams R. High-level expression of hepatitis B viral antigens in fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):956–962. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine J., Hirsch R., Ganem D. A system for studying the selective encapsidation of hepadnavirus RNA. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4257–4263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4257-4263.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T. J., Hasegawa K., Rimon N., Wands J. R., Ben-Porath E. A hepatitis B virus mutant associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1705–1709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T. J., Isselbacher K. J., Wands J. R. Rapid identification of low level hepatitis B-related viral genome in serum. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1367–1371. doi: 10.1172/JCI114308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo G. X., Chao M., Hsieh S. Y., Sureau C., Nishikura K., Taylor J. A specific base transition occurs on replicating hepatitis delta virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1021–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1021-1027.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naoumov N. V., Schneider R., Grötzinger T., Jung M. C., Miska S., Pape G. R., Will H. Precore mutant hepatitis B virus infection and liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Feb;102(2):538–543. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov N. V., Mondelli M., Alexander G. J., Tedder R. S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Relationship between expression of hepatitis B virus antigens in isolated hepatocytes and autologous lymphocyte cytotoxicity in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Shimozaki M., Hoshi Y., Iizuka H., Gotanda T., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned hepatitis B virus genome, subtype ayr: comparison with genomes of the other three subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2305–2314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Yotsumoto S., Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Miyazaki Y., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B viruses with precore region defects prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to the antibody against e antigen. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1298-1303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata M., Ehata T., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Mutations in the precore region of hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with fulminant and severe hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1699–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Tucker W., Schaller H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: domain structure and RNase H activity. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.613-620.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Kim K., Hyun S. W., Kim Y. S. The nucleotide sequence and reading frames of a mutant hepatitis B virus subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2124–2124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere Y., Ahmed R., Southern P. J., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Genetic mapping of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus pathogenicity: virulence in guinea pigs is associated with the L RNA segment. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):704–709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.704-709.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roingeard P., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Leturcq D., Goudeau A., Essex M. Hepatitis B virus core antigen (HBc Ag) accumulation in an HBV nonproducer clone of HepG2-transfected cells is associated with cytopathic effect. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saracco G., Macagno S., Rosina F., Rizzetto M. Serologic markers with fulminant hepatitis in persons positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. A worldwide epidemiologic and clinical survey. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Mar;108(3):380–383. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-3-380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Huang M. J., Yu M. S. Morphogenetic and regulatory effects of mutations in the envelope proteins of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1310-1317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Tsurimoto T., Matsubara K. Three envelope proteins of hepatitis B virus: large S, middle S, and major S proteins needed for the formation of Dane particles. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3521–3529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3521-3529.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Zurawski V. R., Jr High affinity monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) produced by somatic cell hybrids. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):225–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Koike K. Identification of a promoter region for 3.6-kilobase mRNA of hepatitis B virus and specific cellular binding protein. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2914–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2914-2920.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoakum G. H., Korba B. E., Lechner J. F., Tokiwa T., Gazdar A. F., Seeley T., Siegel M., Leeman L., Autrup H., Harris C. C. High-frequency transfection and cytopathology of the hepatitis B virus core antigen gene in human cells. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):385–389. doi: 10.1126/science.6194563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]