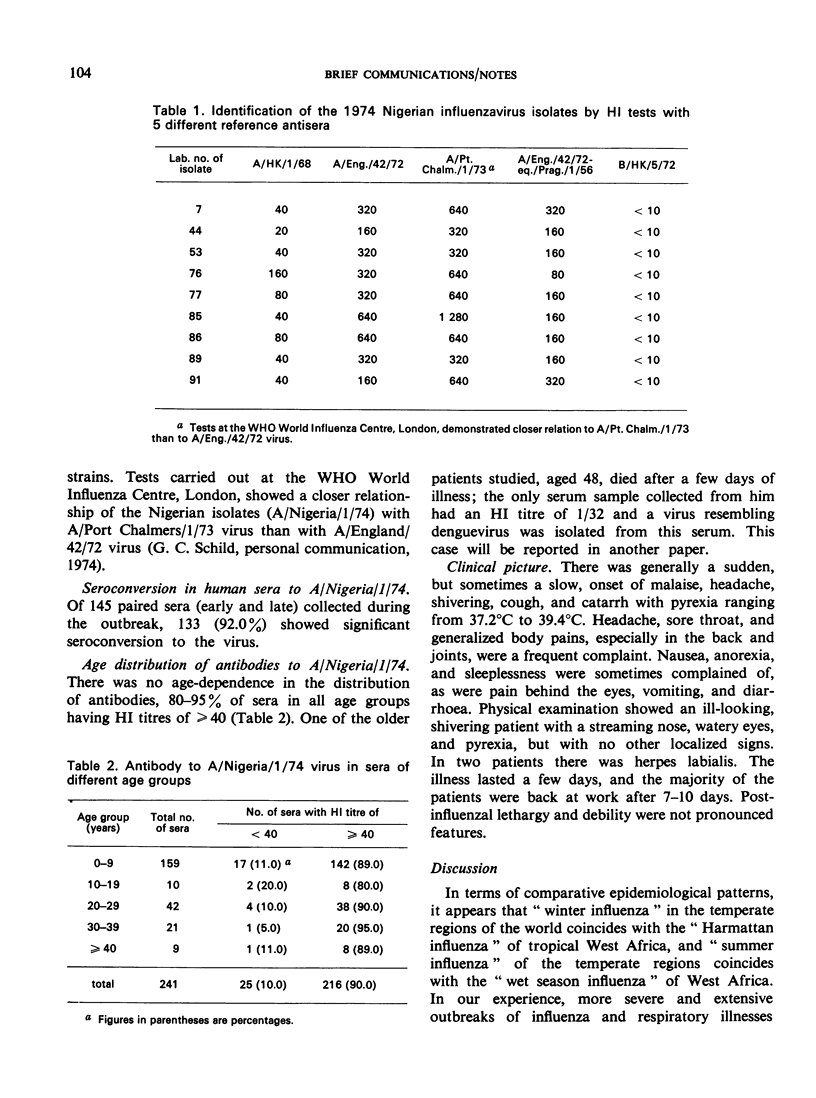
Abstract
Altogether 13 strains of virus were isolated during the 1974 influenza epidemic in Nigeria. These A/Nigeria/1/74 strains were shown by haemagglutination-inhibition tests to be closely related to the A/Port Chalmers/1/73 virus. Antibody to the epidemic strains developed rapidly in the population and 80-95% of all age groups tested possessed high antibody levels; of 145 paired sera tested, 133 (92%) showed sero-conversion to A/Nigeria/1/74 virus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- David-West T. S. Biophysical and immunological studies on the differential effect of guanidine hydrochloride on type A and type B influenza viruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Feb;72(1):31–39. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. S., Chakraverty P., Schild G. C., Coleman M. T., Dowdle W. R. Prevalence of antibody to current influenza viruses and effect of vaccination on antibody response. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 23;4(5842):701–703. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5842.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


