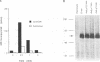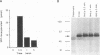Abstract
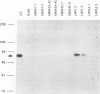
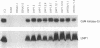
CaM kinase-Gr is a multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase which is enriched in neurons and T lymphocytes. The kinase is absent from primary human B lymphocytes but is expressed in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed B-lymphoblastoid cell lines, suggesting that expression of the kinase can be upregulated by an EBV gene product(s). We investigated the basis of CaM kinase-Gr expression in EBV-transformed cells and the mechanisms that regulate its activity therein by using an EBV-negative Burkitt lymphoma cell line, BJAB, and BJAB cells converted to expression of individual EBV proteins by single-gene transfer. CaM kinase-Gr expression was upregulated in BJAB cells by EBV latent-infection membrane protein 1 (LMP1) but not by LMP2A or by nuclear proteins EBNA1, EBNA2, EBNA3A, and EBNA3C. In LMP1-converted BJAB cells, the kinase was functional and was dramatically activated upon cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin M. Overlapping cDNA clones that encode human CaM kinase-Gr were sequenced, revealing 81% amino acid identity between the rat and human proteins. Transfection of BJAB cells with an expression construct for the human enzyme resulted in a functional kinase which was shown by epitope tagging to localize primarily to cytoplasmic and perinuclear structures. Induction of CaM kinase-Gr expression by LMP1 provides the first example of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase upregulated by a viral protein. In view of the key role played by LMP1 in B-lymphocyte immortalization by EBV, these findings implicate CaM kinase-Gr as a potential mediator of B-lymphocyte growth transformation.
Full text
PDF


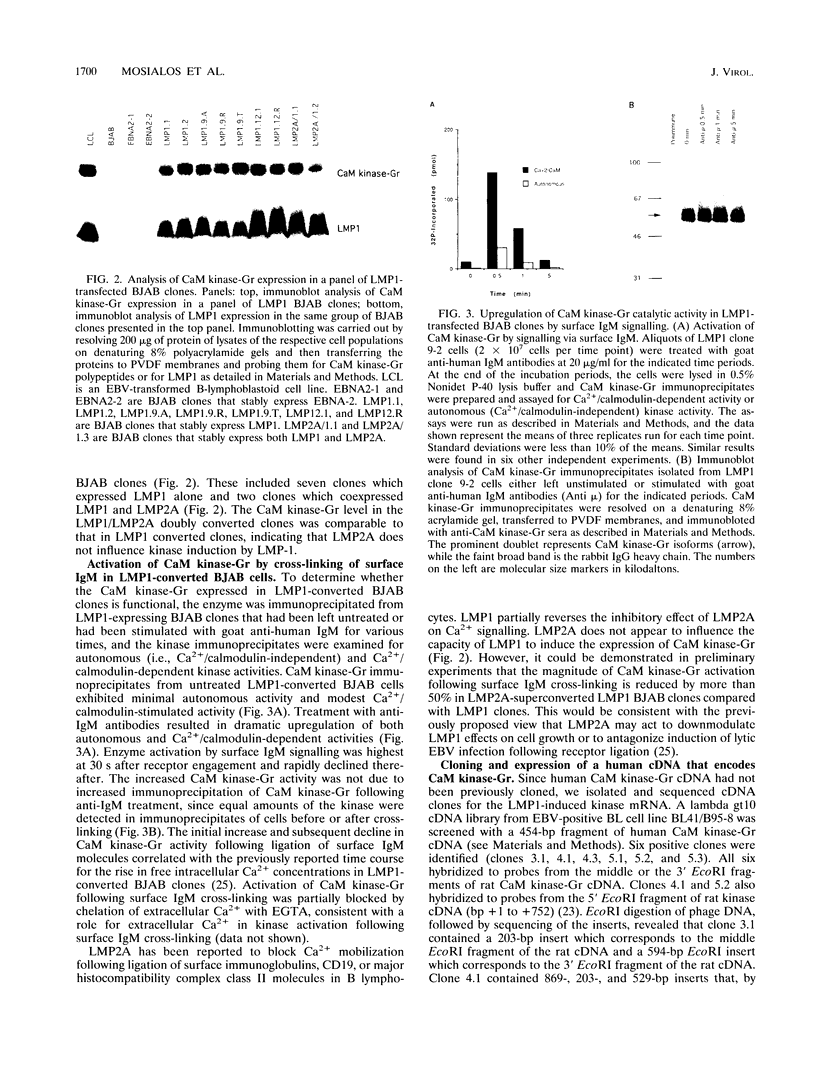

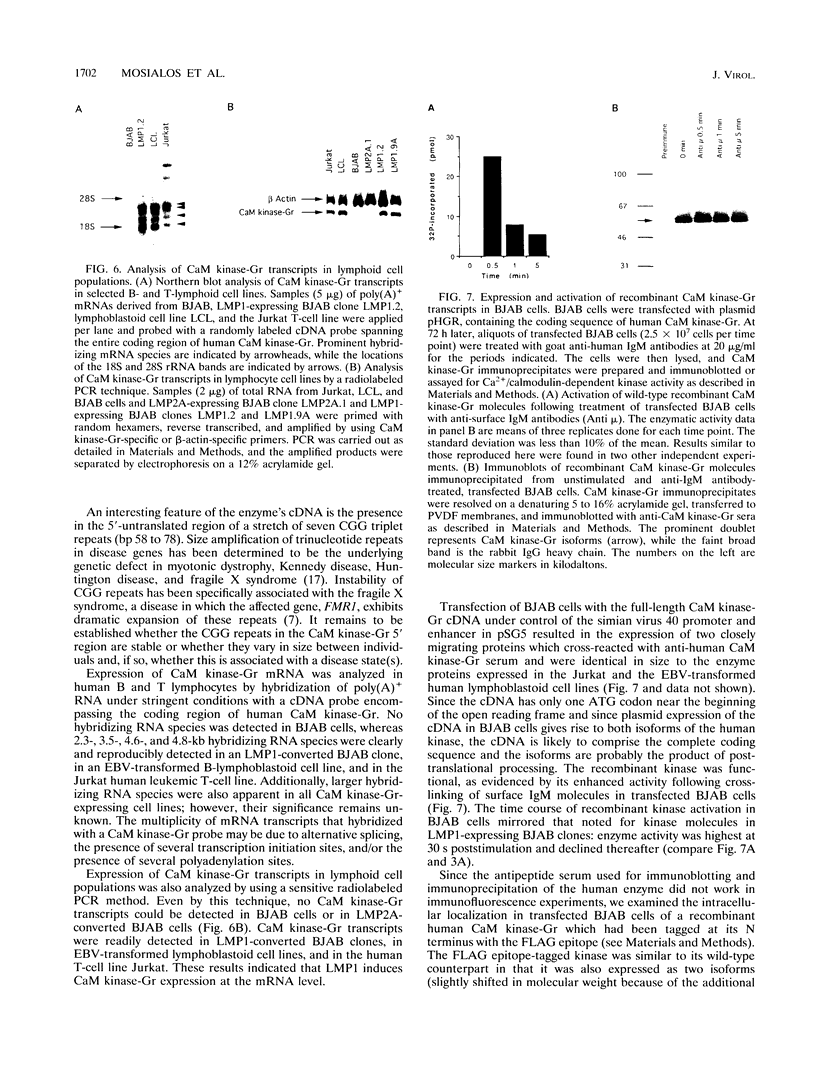



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkenbach M., Josefsen K., Yalamanchili R., Lenoir G., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2209–2220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2209-2220.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruzalegui F. H., Means A. R. Biochemical characterization of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV expressed in insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26171–26178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C. Anionic regions in nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1479–1482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangakis M. V., Chatila T., Wood E. R., Sahyoun N. Expression of a neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, CaM kinase-Gr, in rat thymus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17592–17596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangakis M. V., Ohmstede C. A., Sahyoun N. A brain-specific Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaM kinase-Gr) is regulated by autophosphorylation. Relevance to neuronal Ca2+ signaling. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11309–11316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanissian S. H., Frangakis M., Bland M. M., Jawahar S., Chatila T. A. Expression of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, CaM kinase-Gr, in human T lymphocytes. Regulation of kinase activity by T cell receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20055–20063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Ohmstede C. A., Fisher R. S., Sahyoun N. Nuclear and axonal localization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type Gr in rat cerebellar cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2850–2853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. A., Glod J., Wilson-Shaw D., Hahn W. E., Sikela J. M. cDNA sequence and differential expression of the mouse Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV gene. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80919-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl D. P., Caskey C. T. Trinucleotide repeats and genome variation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Jun;3(3):404–407. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laherty C. D., Hu H. M., Opipari A. W., Wang F., Dixit V. M. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24157–24160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorca T., Cruzalegui F. H., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Méry J., Means A., Dorée M. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II mediates inactivation of MPF and CSF upon fertilization of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):270–273. doi: 10.1038/366270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald O. B., Merrill B. M., Bland M. M., Taylor L. C., Sahyoun N. Site and consequences of the autophosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type "Gr". J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10054–10059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. R., Cruzalegui F., LeMagueresse B., Needleman D. S., Slaughter G. R., Ono T. A novel Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and a male germ cell-specific calmodulin-binding protein are derived from the same gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3960–3971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. L., Longnecker R., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A blocks calcium mobilization in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3087-3094.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyano O., Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. Purification and characterization of a brain-specific multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase from rat cerebellum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1198–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Klein G. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characteristics of human B-lymphoid cell lines and their relevance for the etiology of Burkitt's lymphoma. Adv Cancer Res. 1982;37:319–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60886-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmstede C. A., Bland M. M., Merrill B. M., Sahyoun N. Relationship of genes encoding Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Gr and calspermin: a gene within a gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmstede C. A., Jensen K. F., Sahyoun N. E. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase enriched in cerebellar granule cells. Identification of a novel neuronal calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5866–5875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Slaughter G. R., Cook R. G., Means A. R. Molecular cloning sequence and distribution of rat calspermin, a high affinity calmodulin-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2081–2087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne M. E., Fong Y. L., Ono T., Colbran R. J., Kemp B. E., Soderling T. R., Means A. R. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Characterization of distinct calmodulin binding and inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7190–7195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rooney C. M., Edwards C. F., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus status and tumour cell phenotype in sporadic Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1986 Mar 15;37(3):367–373. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910370307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahyoun N., McDonald O. B., Farrell F., Lapetina E. G. Phosphorylation of a Ras-related GTP-binding protein, Rap-1b, by a neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, CaM kinase Gr. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2643–2647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Silverman L. B., Castigli E., Ahern D., Laudano A. P., Terhorst C., Geha R. S., Chatila T. A. Developmental regulation of transmembrane signaling via the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Lou L. L. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: domain structure and regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):62–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H. The multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini F., Chatila T., Geha R. S. Engagement of MHC class I molecules induces cell adhesion via both LFA-1-dependent and LFA-1-independent pathways. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2045–2049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]