Abstract
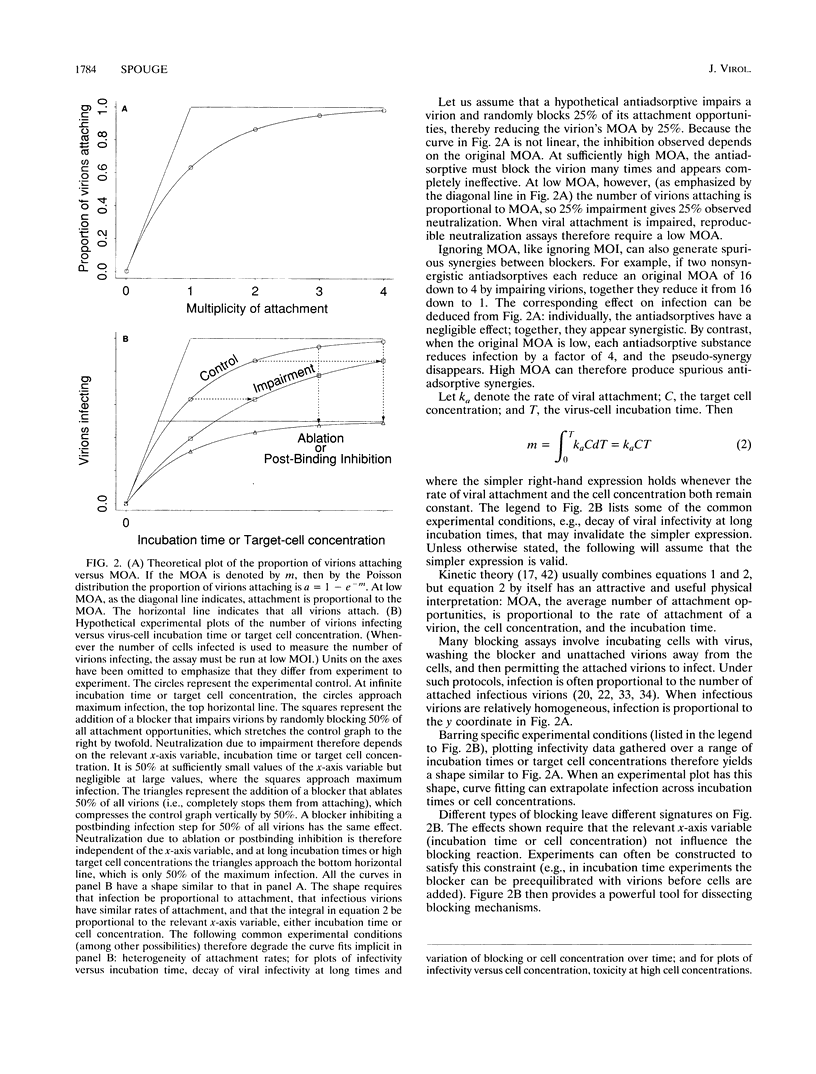
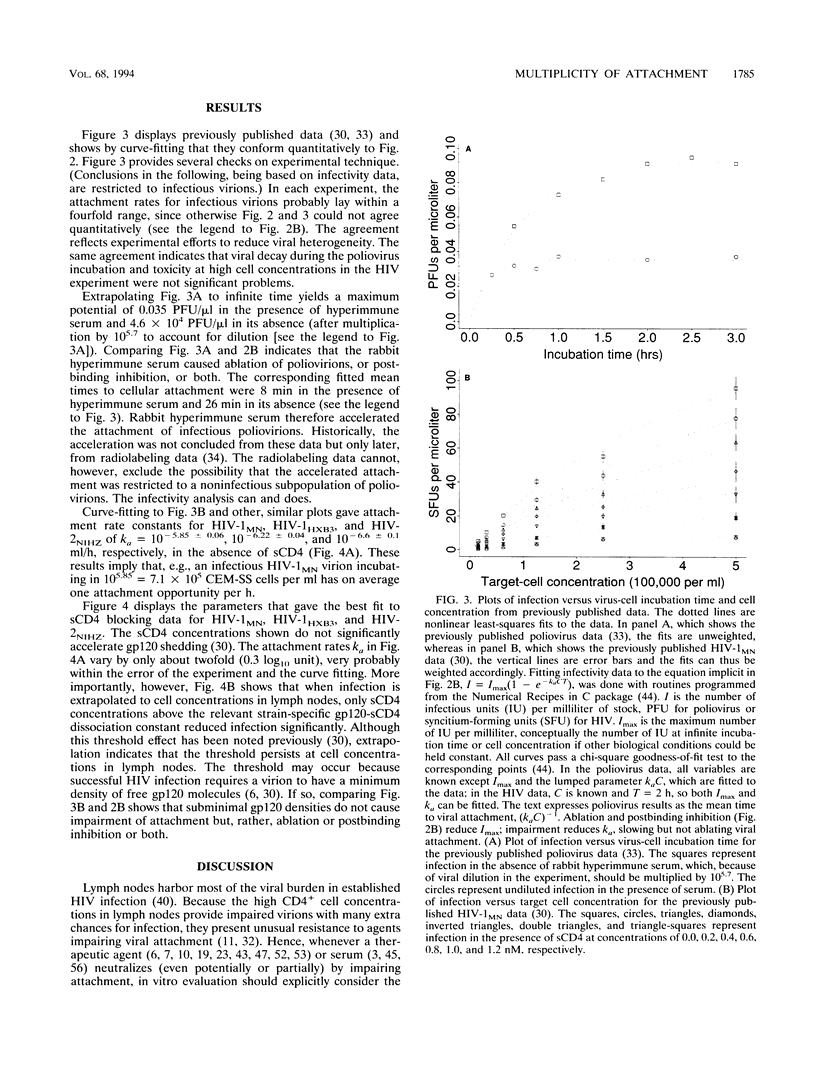
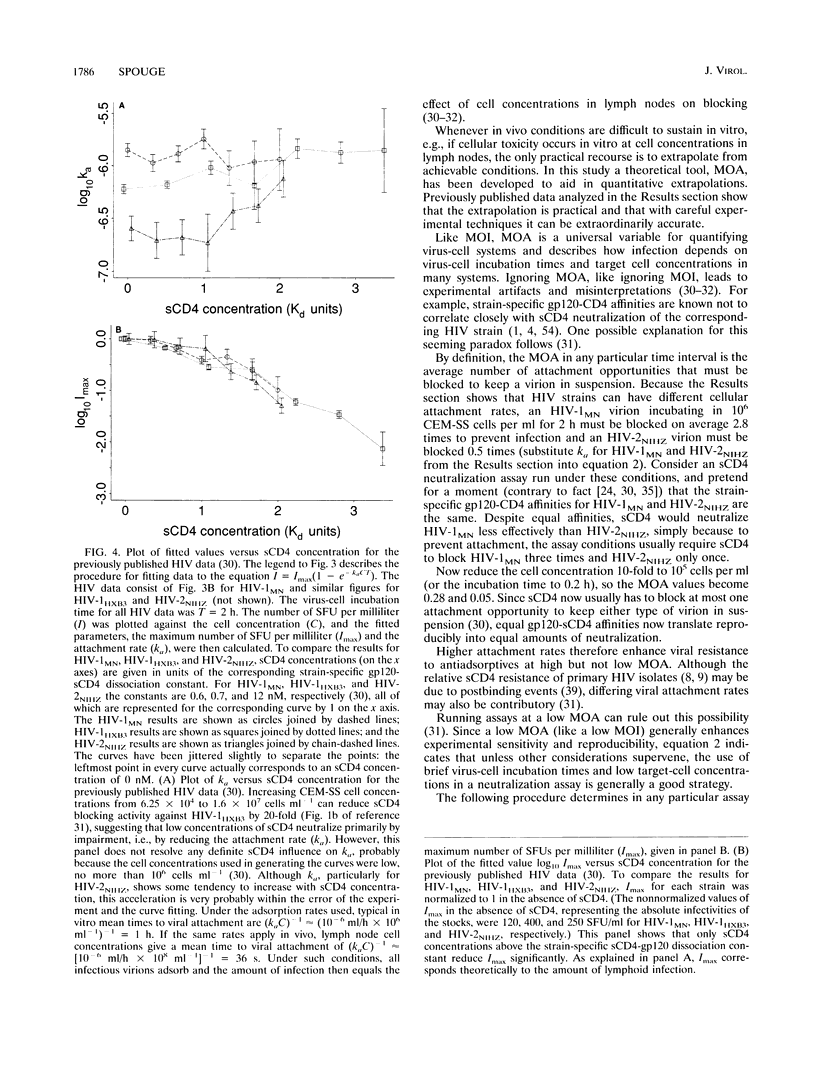
The multiplicity of attachment (MOA) of a virion in any particular time interval is the average number of cellular attachment opportunities that must be blocked to keep the virion in suspension. MOA is usually proportional to incubation time and cell concentration. Low MOA (like low multiplicity of infection) is required for reproducible assay of adsorptive blockers, and high MOA by itself can produce spurious synergies between adsorptive blockers, e.g., soluble CD4 (sCD4) and some antibodies. Poliovirus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) data show that viral neutralization conforms quantitatively to MOA and kinetic theory over large ranges of incubation times and target cell concentrations. Extrapolating sCD4 data beyond conditions achievable in vitro to those in vivo predicts that sCD4 concentrations above the strain-specific sCD4-gp120 dissociation constant are required to block lymphoid HIV significantly, in at least semiquantitative agreement with clinical results. The extrapolation is applicable to humoral neutralization data as well. MOA analysis also indicates that although completely stopping the attachment of individual virions to cells may still be an effective therapeutic strategy against established HIV infection, merely retarding attachment probably is not. The concept of MOA holds great promise for improving the therapeutic relevance of in vitro data and can be applied to any infectious agent, to many processes that impair or enhance infection steps, and to many assay end points, not just infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Smith D. H., Marsters S. A., Riddle L., Gregory T. J., Ho D. D., Capon D. J. Resistance of primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to soluble CD4 is independent of CD4-rgp120 binding affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Redfield R. R. HIV vaccine therapy. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1991;13 (Suppl 1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(91)90134-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brighty D. W., Rosenberg M., Chen I. S., Ivey-Hoyle M. Envelope proteins from clinical isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 that are refractory to neutralization by soluble CD4 possess high affinity for the CD4 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7802–7805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G. Penetration of viral genetic material into host cell. Adv Virus Res. 1982;27:141–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrn R. A., Sekigawa I., Chamow S. M., Johnson J. S., Gregory T. J., Capon D. J., Groopman J. E. Characterization of in vitro inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus by purified recombinant CD4. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4370–4375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4370-4375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury I. H., Koyanagi Y., Takamatsu K., Yoshida O., Kobayashi S., Yamamoto N. Evaluation of anti-human immunodeficiency virus effect of recombinant CD4-immunoglobulin in vitro: a good candidate for AIDS treatment. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1991;180(4):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00215247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Ho D. D. Relative resistance of primary HIV-1 isolates to neutralization by soluble CD4. Am J Med. 1991 Apr 10;90(4A):22S–26S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90407-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Li X. L., Moudgil T., Ho D. D. High concentrations of recombinant soluble CD4 are required to neutralize primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6574–6578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., McDougal J. S., Inacker R., Folena-Wasserman G., Arthos J., Rosenberg J., Maddon P. J., Axel R., Sweet R. W. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):82–84. doi: 10.1038/331082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Hillman K., Manischewitz J., Blumenthal R., Golding H. Kinetics of soluble CD4 binding to cells expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.132-138.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Willey R. L., Martin M. A., Blumenthal R. Kinetics of HIV-1 interactions with sCD4 and CD4+ cells: implications for inhibition of virus infection and initial steps of virus entry into cells. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90441-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormont D. Les primates comme modèles d'étude des lentivirus et du SIDA. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1990 Mar;38(3):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowbenko D., Nakamura G., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Riddle L., Harris R., Gregory T., Lasky L. Epitope mapping of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4703–4711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4703-4711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Kao S. Y., Lewis A. J., Crainic R., Wimmer E. Functional basis of poliovirus neutralization determined with monospecific neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.466-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Bertonis J. M., Meier W., Johnson V. A., Costopoulos D. S., Liu T., Tizard R., Walker B. D., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV infection is blocked in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):76–78. doi: 10.1038/331076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM A. F. Symposium on the biology of cells modified by viruses or antigens. III. Physiological conditions for studies of viral biosynthesis in mammalian cells. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Dec;23(4):224–231. doi: 10.1128/br.23.4.224-231.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Forte C. P., Marlor C. W., Meyer A. M., Hoover-Litty H., Wunderlich D., McClelland A. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated rhinovirus neutralization defined by two soluble forms of ICAM-1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6015–6023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6015-6023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY C., YOUNGNER J. S. STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE AND REPLICATION OF THE NUCLEIC ACID OF POLIOVIRUS. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:162–173. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Culp J. S., Chaikin M. A., Hellmig B. D., Matthews T. J., Sweet R. W., Rosenberg M. Envelope glycoproteins from biologically diverse isolates of immunodeficiency viruses have widely different affinities for CD4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Neutralization of poliovirus by cell receptors expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4697-4702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Peters D., Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus mutants resistant to neutralization with soluble cell receptors. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1596–1599. doi: 10.1126/science.2177226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler H., Goudsmit J., Nara P. Clonal dominance: cause for a limited and failing immune response to HIV-1 infection and vaccination. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(11):1158–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last-Barney K., Marlin S. D., McNally E. J., Cahill C., Jeanfavre D., Faanes R. B., Merluzzi V. J. Detection of major group rhinoviruses by soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1). J Virol Methods. 1991 Dec;35(3):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90067-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Merges M. J., Dembo M., Spouge J. L., Nara P. L. HIV requires multiple gp120 molecules for CD4-mediated infection. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):277–279. doi: 10.1038/346277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Merges M. J., Spouge J. L., Dembo M., Nara P. L. Blocking of human immunodeficiency virus infection depends on cell density and viral stock age. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3293–3300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3293-3300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Spouge J. L., Dembo M. Quantifying the infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4644–4648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL B. Studies on the interactions of poliomyelitis virus, antibody, and host cells in tissue culture system. Virology. 1958 Oct;6(2):424–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The interaction of neutralized poliovirus with HeLa cells. I. Adsorption. Virology. 1967 Feb;31(2):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Weiss R. A., Sattentau Q. J. Dissociation of gp120 from HIV-1 virions induced by soluble CD4. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2251501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R. Enhancement of soluble CD4-mediated HIV neutralization and gp 120 binding by CD4 autoantibodies and monoclonal antibodies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1273–1279. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P. Simple methods for monitoring HIV-1 and HIV-2 gp120 binding to soluble CD4 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: HIV-2 has a 25-fold lower affinity than HIV-1 for soluble CD4. AIDS. 1990 Apr;4(4):297–305. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199004000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Cannon M. J., Sewall A., Finlayson M., Okimoto M., Nemerow G. R. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus infection in vitro and in vivo by soluble CR2 (CD21) containing two short consensus repeats. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3559–3565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3559-3565.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff S. L., Kennedy M. S., Belperron A. A., Maddon P. J., McDougal J. S. Two mechanisms of soluble CD4 (sCD4)-mediated inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infectivity and their relation to primary HIV-1 isolates with reduced sensitivity to sCD4. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1461–1471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1461-1471.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L. THE EARLY INTERACTION OF ANIMAL VIRUSES AND CELLS. Prog Med Virol. 1963;5:43–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Butini L., Pizzo P. A., Schnittman S. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. Lymphoid organs function as major reservoirs for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9838–9842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Fauci A. S. New concepts in the immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 4;328(5):327–335. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302043280508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. R., Hideshima T., Cannon T., Mukherjee M., Mayer K. H., Byrn R. A. An IgG human monoclonal antibody that reacts with HIV-1/GP120, inhibits virus binding to cells, and neutralizes infection. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4325–4332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield R., Birx D., Ketter N., Polonis V., Johnson S., Davis C., Smith G., Oster C., Burke D. Vaccine therapy using rgp 160 in early HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Aug;8(8):1333–1333. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Merigan T. C., Gaut P., Hirsch M. S., Holodniy M., Flynn T., Liu S., Byington R. E., Henochowicz S., Gubish E. Recombinant soluble CD4 therapy in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. A phase I-II escalating dosage trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):247–253. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Byrn R. A., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Groopman J. E., Capon D. J. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1704–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.3500514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Weiner H. L. Interaction of viruses with cell surface receptors. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;80:27–61. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60366-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley S. A., Honnen W. J., Racho M. E., Chou T. C., Pinter A. Synergistic neutralization of HIV-1 by human monoclonal antibodies against the V3 loop and the CD4-binding site of gp120. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):461–467. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley S. A., Honnen W. J., Racho M. E., Hilgartner M., Pinter A. A human monoclonal antibody against the CD4-binding site of HIV1 gp120 exhibits potent, broadly neutralizing activity. Res Virol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(4):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(91)90010-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Redfield R. R. Soluble CD4: the first step. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):241–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Redfield R. R. Soluble CD4: the first step. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):241–242. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Lüke W., Karjalainen K. Soluble CD4 molecules neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/331084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Schneider J., Kiefer H., Karjalainen K. Highly efficient neutralization of HIV with recombinant CD4-immunoglobulin molecules. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):68–70. doi: 10.1038/339068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S., Tizard R., DeMarinis J., Pepinsky R. B., Zullo J., Schooley R., Fisher R. Resistance of primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to neutralization by soluble CD4 is not due to lower affinity with the viral envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1335–1339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. N., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Parker D., Roberts C., Duncan J., Weller I., Carne C., Tedder R. S., Pinching A. J. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in two cohorts of homosexual men: neutralising sera and association of anti-gag antibody with prognosis. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91964-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


