Abstract
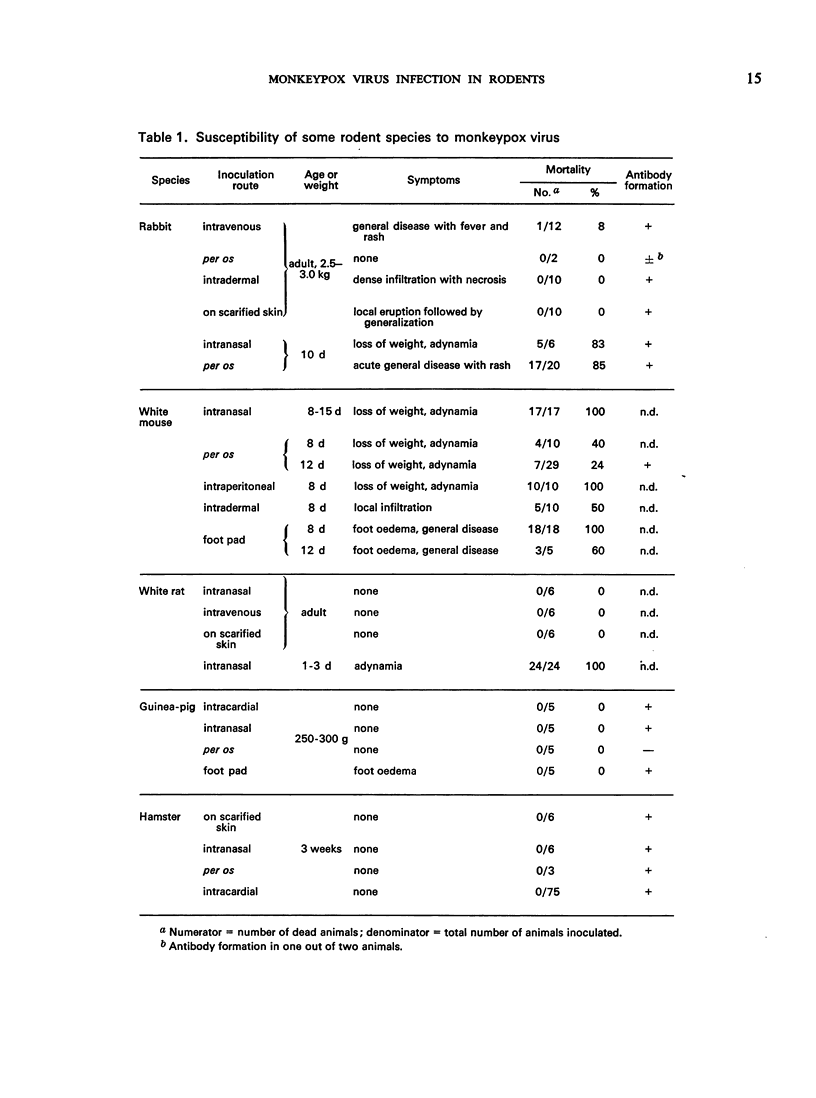
The authors studied the susceptibility of five species of rodent to monkeypox virus inoculated by various routes and the course of the infection. Reactions varied from complete resistance to lethal generalized infection with rash. Rabbits and white mice appeared to be the most susceptible species and young animals were more susceptible than adults. Monkeypox virus was found to infect young animals by natural routes, i.e., per os and intranasally. Transmission by contact occurred among 10-day-old rabbits. Since antibodies to monkeypox virus may persist for over a year in the sera of convalescent animals, serological examination of animals is recommended for studying the ecology of this virus.
Full text
PDF


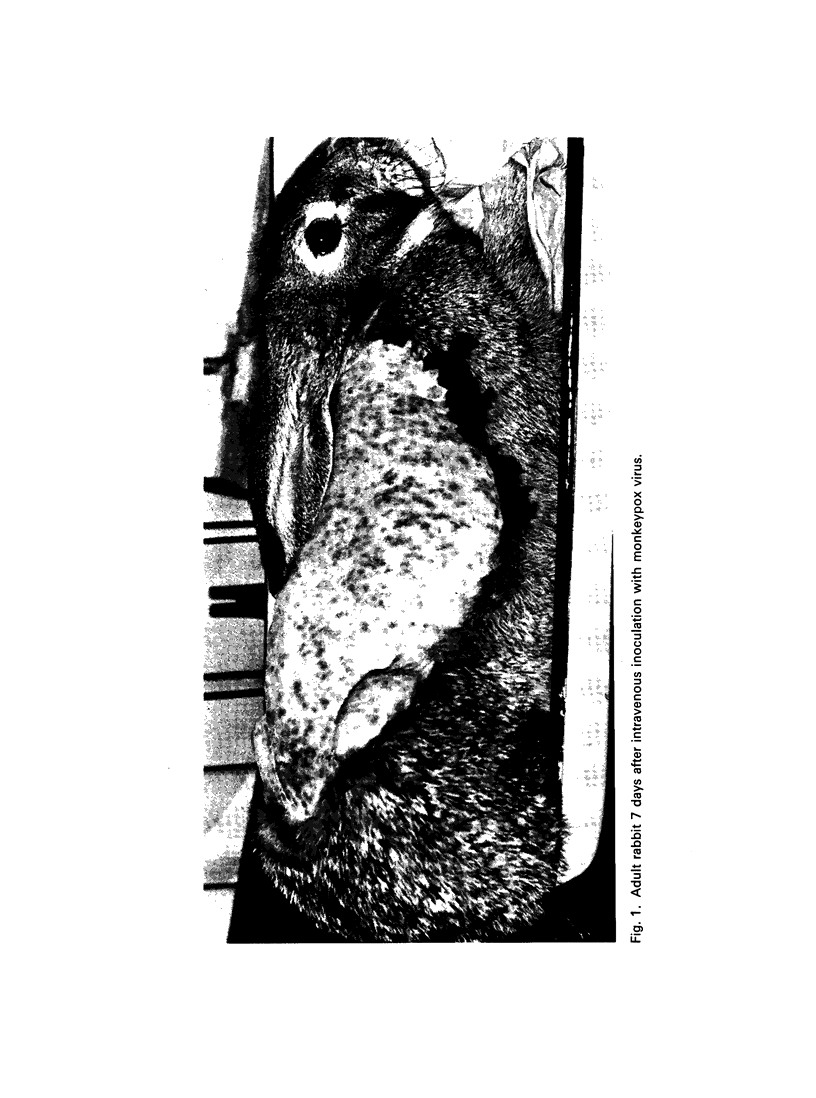
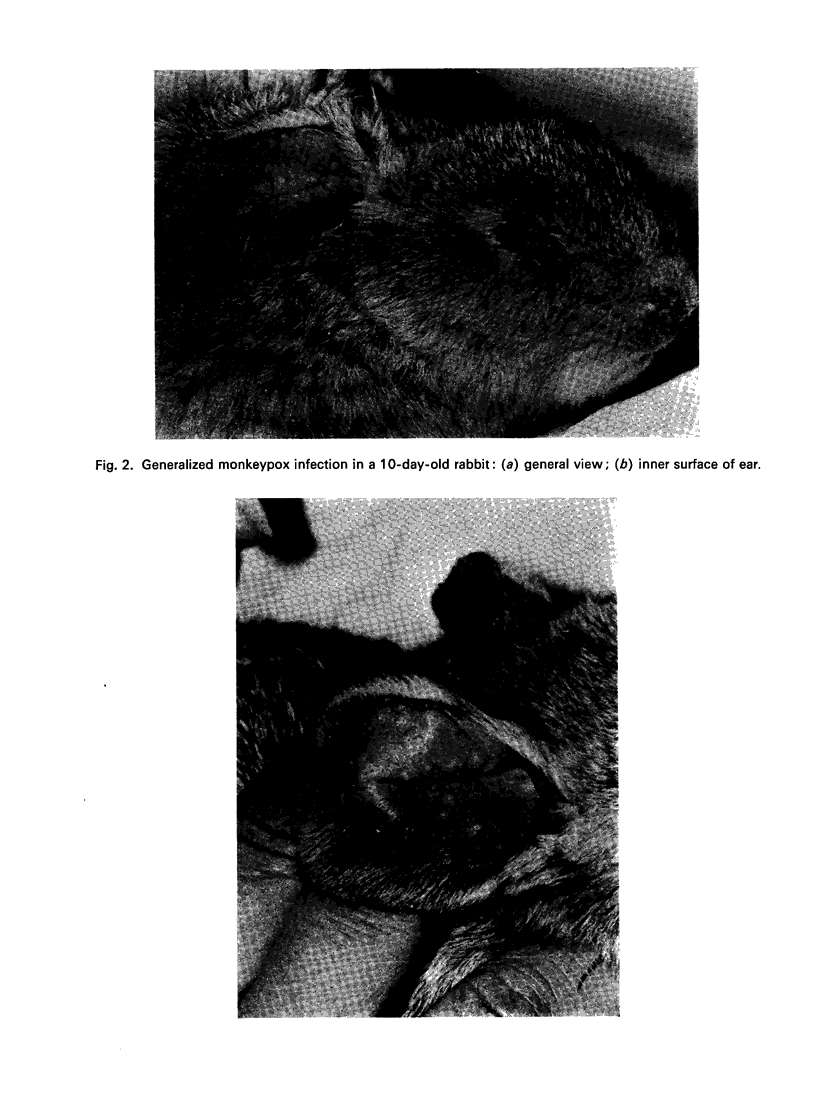


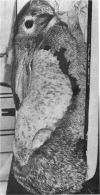
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Foster S. O., Brink E. W., Hutchins D. L., Pifer J. M., Lourie B., Moser C. R., Cummings E. C., Kuteyi O. E., Eke R. E., Titus J. B. Human monkeypox. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(5):569–576. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gispen R., Verlinde J. D., Zwart P. Histopathological and virological studies on monkeypox. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;21(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01241445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marennikova S. S., Gurvich E. B., Shelukhina E. M. Comparison of the properties of five pox virus strains isolated from monkeys. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;33(3):201–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01254676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]