Abstract
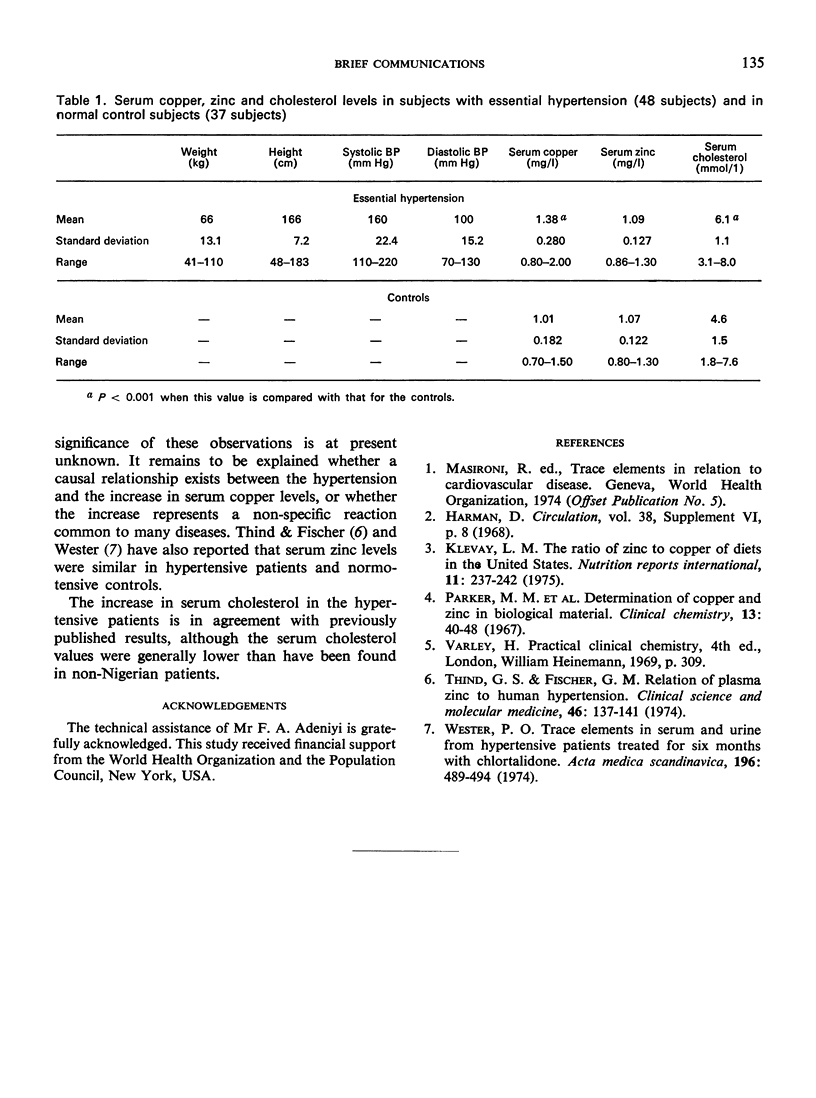
Serum copper and zinc levels were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy in 48 hypertensive Nigerians and in 37 normotensive controls. Serum copper and total cholesterol levels were significantly increased in the hypertensive patients, but their serum zinc levels did not differ from those of the controls.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Parker M. M., Humoller F. L., Mahler D. J. Determination of copper and zinc in biological material. Clin Chem. 1967 Jan;13(1):40–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thind G. S., Fischer G. M. Relationship of plasma zinc to human hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jan;46(1):137–141. doi: 10.1042/cs0460137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester P. O. Trace elements in serum and urine from hypertensive patients treated for six months with chlorthalidone. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Dec;196(6):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb01047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


