Abstract
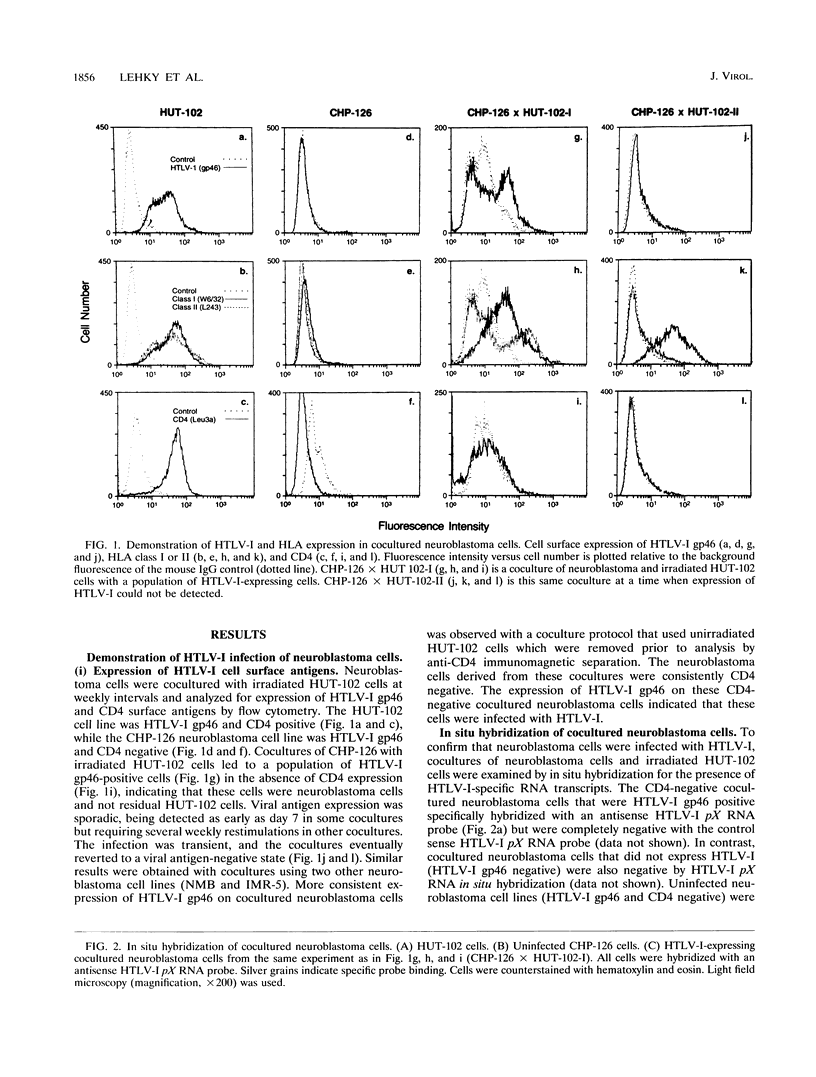
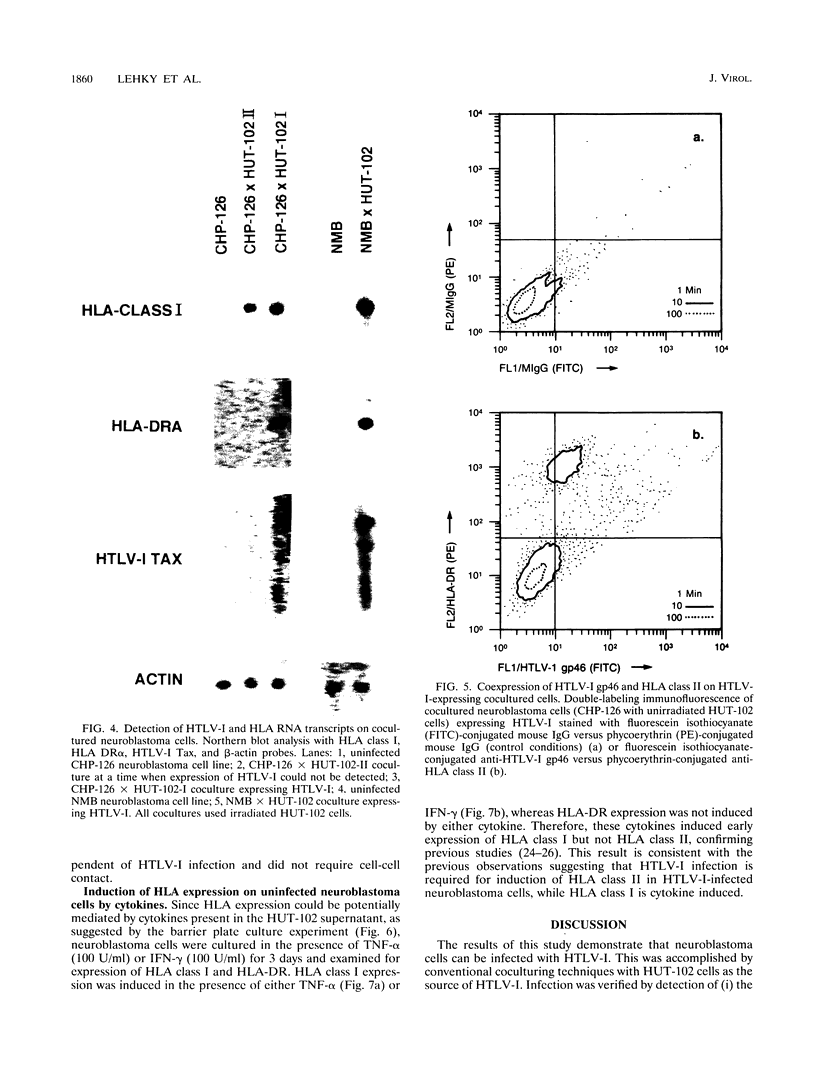
Human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is associated with a neurologic disease, HTLV-I-associated myelopathy-tropical spastic paraparesis, in which both pathological and immunological changes are observed within the central nervous system. The pathogenesis of infection in HTLV-I-associated myopathy-tropical spastic paraparesis is not well understood with respect to the cell tropism of HTLV-I and its relationship to the destruction of neural elements. In this study, neuroblastoma cells were infected with HTLV-I by coculturing with HUT-102 cells to demonstrate that cells of neuronal origin are susceptible to this retroviral infection. HTLV-I infection of the neuroblastoma cells was confirmed by verifying the presence of HTLV-I gp46 surface antigens by flow cytometry and by verifying the presence of HTLV-I pX RNA by Northern (RNA) blotting and in situ hybridization techniques. To determine whether HTLV-I infection could potentially lead to changes in cell surface recognition by the immune system, the infected neuroblastoma cells were analyzed for altered HLA expression. The HTLV-I-infected, cocultured neuroblastoma cells were shown, through cell surface antigen expression and RNA transcripts, to express HLA classes I and II. In contrast, cocultured neuroblastoma cells that did not become infected with HTLV-I expressed only HLA class I. HLA class I expression was enhanced by the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and gamma interferon and in the presence of HUT-102 supernatant. In this system, expression of HLA class I and II molecules appeared to be regulated by different mechanisms. HLA class I expression was probably induced by cytokines present in the HUT-102 supernatant and was not dependent on HTLV-I infection. HLA class II expression required HTLV-I infection of the cells. The observation of HTLV-I infection leading to HLA induction in these neuroblastoma cells provides a possible mechanism for immunologic recognition of infected neuronal cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderton B. H., Breinburg D., Downes M. J., Green P. J., Tomlinson B. E., Ulrich J., Wood J. N., Kahn J. Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):84–86. doi: 10.1038/298084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagavati S., Ehrlich G., Kula R. W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Udani V., Poiesz B. J. Detection of human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I DNA and antigen in spinal fluid and blood of patients with chronic progressive myelopathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 5;318(18):1141–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805053181801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhigjee A. I., Wiley C. A., Wachsman W., Amenomori T., Pirie D., Bill P. L., Windsor I. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: clinicopathologic correlation with localization of provirus to spinal cord. Neurology. 1991 Dec;41(12):1990–1992. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.12.1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottler-Fox M., Fox C. H. Examining cells for infectious agents: a novel approach. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1239–1240. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1239-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan E. P., Pierce M. L., Dhib-Jalbut S. Interleukin-1 beta decreases HLA class II expression on a glioblastoma multiforme cell line. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jul;33(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90030-B. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. H., Tenner-Rácz K., Rácz P., Firpo A., Pizzo P. A., Fauci A. S. Lymphoid germinal centers are reservoirs of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1051–1057. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Barin F., Vernant J. C., Gout O., Maurs L., Calender A., de Thé G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 24;2(8452):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Gout O. Chronic myelopathy associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I). Ann Intern Med. 1992 Dec 1;117(11):933–946. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-11-933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma S., Naruo K., Tsukamoto K., Sugamura K., Hinuma Y. Production of cytotoxic factor(s) in human T cell lines transformed by a human retrovirus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1052–1058. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91722-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Uemura Y., Fujishita M., Kitagawa T., Yamashita M., Imamura J., Ohtsuki Y., Taguchi H., Miyoshi I. Isolation of HTLV-I from cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with myelopathy. Lancet. 1986 Aug 16;2(8503):397–398. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Dhib-Jalbut S., Mikovits J. A., Robbins D. S., Wolf A. L., Bergey G. K., Lohrey N. C., Weislow O. S., Ruscetti F. W. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection of monocytes and microglial cells in primary human cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11784–11788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y. Pathology of chronic myelopathy associated with HTLV-I infection (HAM/TSP). J Neurol Sci. 1990 Apr;96(1):103–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90060-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., McFarlin D. E., Robinson S., Voskuhl R., Martin R., Brewah A., Newell A. J., Koenig S. HTLV-I-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HTLV-I-associated neurological disease. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):651–657. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Raine C. S., Mingioli E. S., McFarlin D. E. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):540–543. doi: 10.1038/331540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Shida H., McFarlin D. E., Fauci A. S., Koenig S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurological disease. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):245–248. doi: 10.1038/348245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Zaninovic V., Mora C., Rodgers-Johnson P., Sheremata W. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek C., McFarlin D. E. Immunological findings in neurological diseases associated with antibodies to HTLV-I: activated lymphocytes in tropical spastic paraparesis. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S196–S200. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kira J., Itoyama Y., Koyanagi Y., Tateishi J., Kishikawa M., Akizuki S., Kobayashi I., Toki N., Sueishi K., Sato H. Presence of HTLV-I proviral DNA in central nervous system of patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jan;31(1):39–45. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Sidwell B., DeMars R., Orr H. T. Isolation of HLA locus-specific DNA probes from the 3'-untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5175–5178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koralnik I. J., Lemp J. F., Jr, Gallo R. C., Franchini G. In vitro infection of human macrophages by human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Nov;8(11):1845–1849. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A. Biological significance of HLA-A,B,C expression in neuroblastoma and related cell lines. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;271:409–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Fisher C. A., Whelan J. P. Striking paucity of HLA-A, B, C and beta 2-microglobulin on human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2471–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., George D. L. Interferon-mediated induction of class I MHC products in human neuronal cell lines: analysis of HLA and beta 2-m RNA, and HLA-A and HLA-B proteins and polymorphic specificities. J Interferon Res. 1986 Jun;6(3):257–265. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A. MHC regulation in neural cells. Distribution of peripheral and internal beta 2-microglobulin and class I molecules in human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):512–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberski P. P., Rodgers-Johnson P., Char G., Piccardo P., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. HTLV-I-like viral particles in spinal cord cells in Jamaican tropical spastic paraparesis. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S185–S187. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Kalyanaraman V. S., Popovic M., Sarin P., Gallo R. C. Infection and transformation of fresh human umbilical cord blood cells by multiple sources of human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV). Int J Cancer. 1983 Apr 15;31(4):413–420. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauerhoff T., Pujol-Borrell R., Mirakian R., Bottazzo G. F. Differential expression and regulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) products in neural and glial cells of the human fetal brain. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jul;18(4):271–289. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90049-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi I., Kubonishi I., Yoshimoto S., Akagi T., Ohtsuki Y., Shiraishi Y., Nagata K., Hinuma Y. Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukaemic T cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):770–771. doi: 10.1038/294770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Traugott U., Scheinberg L. C., Raine C. S. Tropical spastic paraparesis: a model of virus-induced, cytotoxic T-cell-mediated demyelination? Ann Neurol. 1989 Oct;26(4):523–530. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Iwasaki Y., Izumo S., Kobayashi I., Yoshioka A. Search for human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral sequences by polymerase chain reaction in the central nervous system tissue of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Arch Virol. 1992;124(1-2):31–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01314623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul N. L., Lenardo M. J., Novak K. D., Sarr T., Tang W. L., Ruddle N. H. Lymphotoxin activation by human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cell lines: role for NF-kappa B. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5412–5419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5412-5419.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers-Johnson P., Morgan O. S., Mora C., Sarin P., Ceroni M., Piccardo P., Garruto R. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. The role of HTLV-I in tropical spastic paraparesis in Jamaica. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S121–S126. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M., Suzumura A., Kondo N., Marunouchi T. Induction of cytokines in glial cells by trans activator of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 16;313(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81181-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semmes O. J., Jeang K. T. Mutational analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax: regions necessary for function determined with 47 mutant proteins. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7183–7192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7183-7192.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., Lampson L. A. Immune modulation within the brain: recruitment of inflammatory cells and increased major histocompatibility antigen expression following intracerebral injection of interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90121-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Harlan R. E., Pfaff D. W., Schachter B. S. Combination of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization in the same tissue section of rat pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jan;34(1):39–43. doi: 10.1177/34.1.3510246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terunuma H., Iwasaki Y., Tsukamoto T., Konno H., Yamamoto T., Ohara Y. Neurotoxic activity in HTLV-I carrier lymphocyte culture. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Sep;92(2-3):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(89)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe K., Saida T., Kim S. U. Human and simian glial cells infected by human T-lymphotropic virus type I in culture. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1989 Nov;48(6):610–619. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198911000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu E., Dickson D. W., Jacobson S., Raine C. S. Neuroaxonal dystrophy in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: neuropathologic and neuroimmunologic correlations. Acta Neuropathol. 1993;86(3):224–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00304136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Watabe K., Saida T., Kim S. U. Increased susceptibility of human fetal astrocytes to human T-lymphotropic virus type I in culture. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 Mar;50(2):97–107. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199103000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Rossi A., Aldovini A., Franchini G., Mann D., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Clonal selection of T lymphocytes infected by cell-free human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I: parameters of virus integration and expression. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]