Abstract
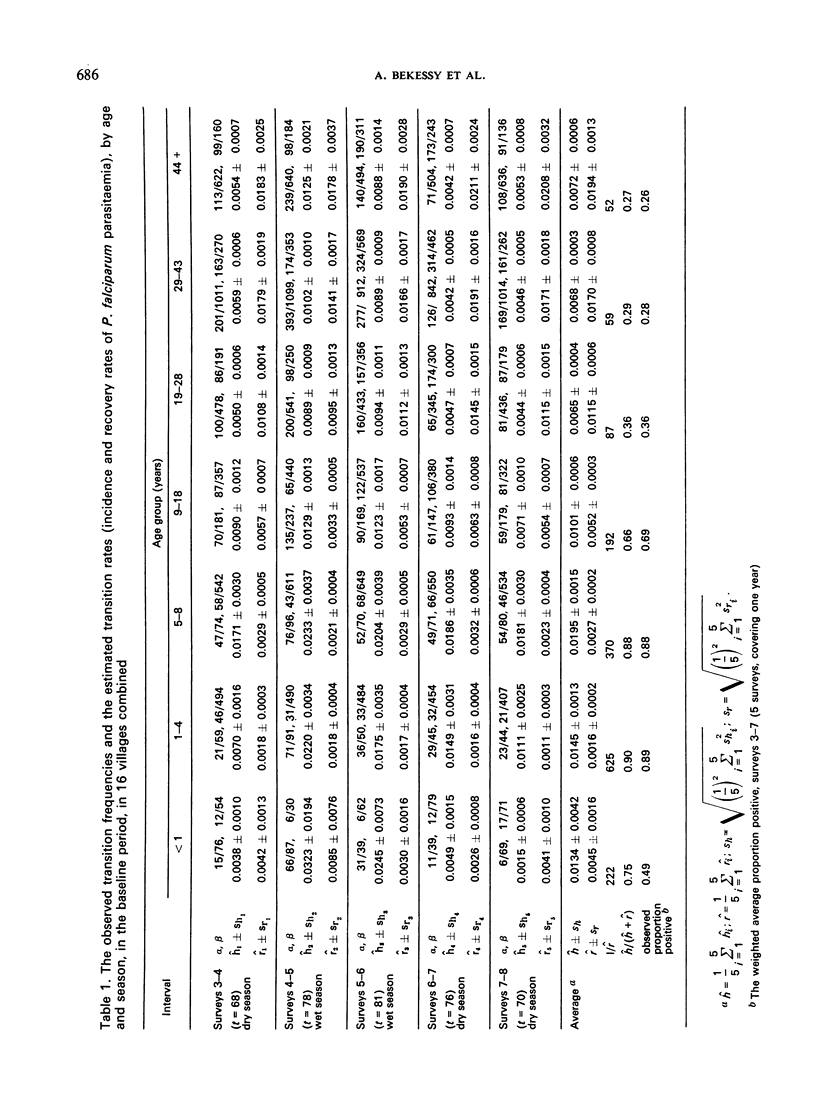
A method is described of estimating the malaria incidence rate ĥ and the recovery rate r from longitudinal data. The method is based on the assumption that the phenomenon of patent parasitaemia can be represented by a reversible two-state catalytic model; it is applicable to all problems that can be represented by such a model.
The method was applied to data on falciparum malaria from the West African savanna and the findings suggested that immunity increases the rate of recovery from patent parasitaemia by a factor of up to 10, and also reduces the number of episodes of patent parasitaemia resulting from one inoculation. Under the effect of propoxur, ĥ varies with the estimated man-biting rate of the vector while r̂ increases, possibly owing to reduced super-infection.
Full text
PDF