Abstract
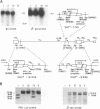
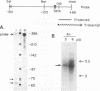
As do many other alphaherpesviruses, pseudorabies virus (PRV) transcribes a limited portion of its viral genome in latently infected neurons during latency. The sequence of the PRV latency-associated transcript (LAT) is bounded on its 5' end by a putative promoter region which contains sequence elements similar to those characterized for the herpes simplex virus (HSV) LAT promoter. Using the bacterial beta-galactosidase gene as a reporter, we have assayed PRV LAT promoter activity in the genomic environment in recombinant HSVs. The PRV LAT promoter-beta-galactosidase reporter gene was recombined into the terminal and internal long repeat regions (RL regions), replacing the normal HSV LAT promoter, the cap site, and the first 60 bases of the primary transcript. When recombined into the RL region, appreciable reporter gene expression was observed following infection of two cell lines of neuronal origin; little or no activity was seen with these recombinants following infection of rabbit skin or mouse embryo fibroblasts. No significant expression was seen when the promoter was recombined into the gC locus in the long unique region in any of the cell types utilized. Such results suggest that the PRV latency promoter contains neuronal cell-specific elements and that the HSV RL region provides an appropriate genomic environment for the manifestation of that specificity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batchelor A. H., O'Hare P. Regulation and cell-type-specific activity of a promoter located upstream of the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3269–3279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3269-3279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom D. C., Devi-Rao G. B., Hill J. M., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K. Molecular analysis of herpes simplex virus type 1 during epinephrine-induced reactivation of latently infected rabbits in vivo. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1283–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1283-1292.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. Cloning of the latency gene and the early protein 0 gene of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5260–5271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5260-5271.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. Detection of pseudorabies virus transcripts in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected swine. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2908–2913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2908-2913.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi-Rao G. B., Bloom D. C., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA replication and gene expression during explant-induced reactivation of latently infected murine sensory ganglia. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1271–1282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1271-1282.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devi-Rao G. B., Goodart S. A., Hecht L. M., Rochford R., Rice M. K., Wagner E. K. Relationship between polyadenylated and nonpolyadenylated herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2179–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2179-2190.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Sederati F., Devi-Rao G., Flanagan W. M., Farrell M. J., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Feldman L. T. Identification of the latency-associated transcript promoter by expression of rabbit beta-globin mRNA in mouse sensory nerve ganglia latently infected with a recombinant herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3844–3851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3844-3851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Wagner E. K. A bi-functional reporter plasmid for the simultaneous transient expression assay of two herpes simplex virus promoters. Virus Genes. 1987 Nov;1(1):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00125686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodart S. A., Guzowski J. F., Rice M. K., Wagner E. K. Effect of genomic location on expression of beta-galactosidase mRNA controlled by the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL38 promoter. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2973–2981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2973-2981.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzowski J. F., Wagner E. K. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 strict late UL38 promoter/leader reveals two regions critical in transcriptional regulation. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5098–5108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5098-5108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. M., Sedarati F., Javier R. T., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Herpes simplex virus latent phase transcription facilitates in vivo reactivation. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. J., Goodart S. A., Rice M. K., Guzowski J. F., Wagner E. K. Mutational analysis of sequences downstream of the TATA box of the herpes simplex virus type 1 major capsid protein (VP5/UL19) promoter. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5109–5116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5109-5116.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbalzano A. N., Shepard A. A., DeLuca N. A. Functional relevance of specific interactions between herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 and sequences from the promoter-regulatory domain of the viral thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2620–2631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2620-2631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Delhon G., Bratanich A., Kutish G., Rock D. Analysis of the transcriptional promoter which regulates the latency-related transcript of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1164-1170.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutish G., Mainprize T., Rock D. Characterization of the latency-related transcriptionally active region of the bovine herpesvirus 1 genome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5730–5737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5730-5737.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Bogard C. L., Kosz-Vnenchak M., Hicks K. A., Coen D. M., Knipe D. M., Schaffer P. A. A deletion mutant of the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 reactivates from the latent state with reduced frequency. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2893–2900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2893-2900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Nadeau K. C., Rundle S. A., Schaffer P. A. The promoter of the latency-associated transcripts of herpes simplex virus type 1 contains a functional cAMP-response element: role of the latency-associated transcripts and cAMP in reactivation of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):48–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., McGeoch D. J. The DNA sequences of the long repeat region and adjoining parts of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2831–2846. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priola S. A., Gustafson D. P., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. A major portion of the latent pseudorabies virus genome is transcribed in trigeminal ganglia of pigs. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4755–4760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4755-4760.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priola S. A., Stevens J. G. The 5' and 3' limits of transcription in the pseudorabies virus latency associated transcription unit. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):852–856. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90628-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawtell N. M., Thompson R. L. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcription unit promotes anatomical site-dependent establishment and reactivation from latency. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2157–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2157-2169.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Johnson D. C., Pizer L. I., Everett R. D. The ICP4 binding sites in the herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D (gD) promoter are not essential for efficient gD transcription during virus infection. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):623–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.623-631.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) latency-associated transcripts and transcripts affected by the deletion in avirulent mutant HFEM: evidence for a new class of HSV-1 genes. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3281–3287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3281-3287.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts in the trigeminal ganglia of mice during acute infection and reactivation of latent infection. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1479–1485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1479-1485.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Lirette R. P., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts are evidently not essential for latent infection. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):505–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Human herpesviruses: a consideration of the latent state. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):318–332. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.318-332.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J. C., Ghiasi H., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. Identification of a major regulatory sequence in the latency associated transcript (LAT) promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Virology. 1991 May;182(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90672-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J. C., Ghiasi H., Slanina S. M., Nesburn A. B., Wheatley S. C., Lillycrop K., Wood J., Latchman D. S., Patel K., Wechsler S. L. Activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript (LAT) promoter in neuron-derived cells: evidence for neuron specificity and for a large LAT transcript. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5019–5028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5019-5028.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J., Ghiasi H., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. In vitro promoter activity associated with the latency-associated transcript gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2163–2169. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]