Abstract
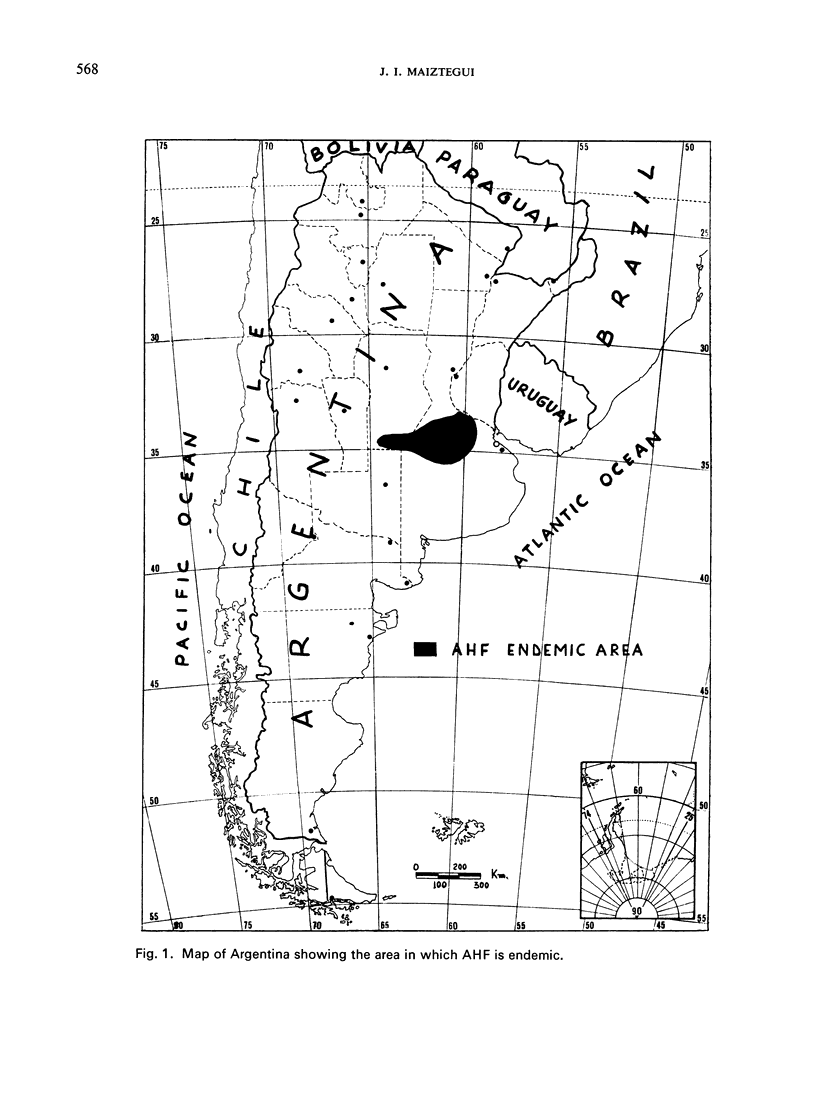
The epidemiology of Argentine haemorrhagic fever (AHF) is closely related to cricetine rodents acting as natural hosts of Junin virus. The endemo-epidemic area, which has increased 5 times since the disease was first recognized 15-20 years ago, is located in a densely populated region of Argentina. It has been shown that the virus of LCM is active in humans and rodents of the AHF endemic area; this demonstrates the simultaneous presence of two arenaviruses pathogenic for man in a given geographic location.
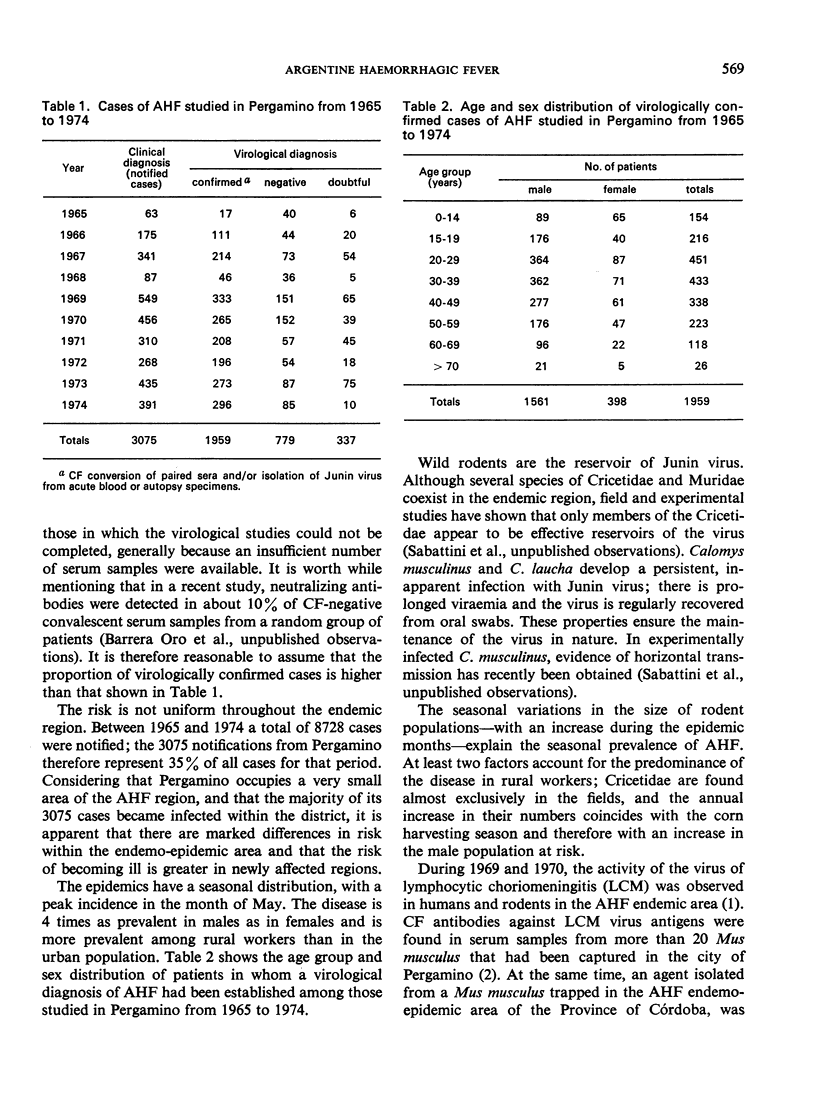
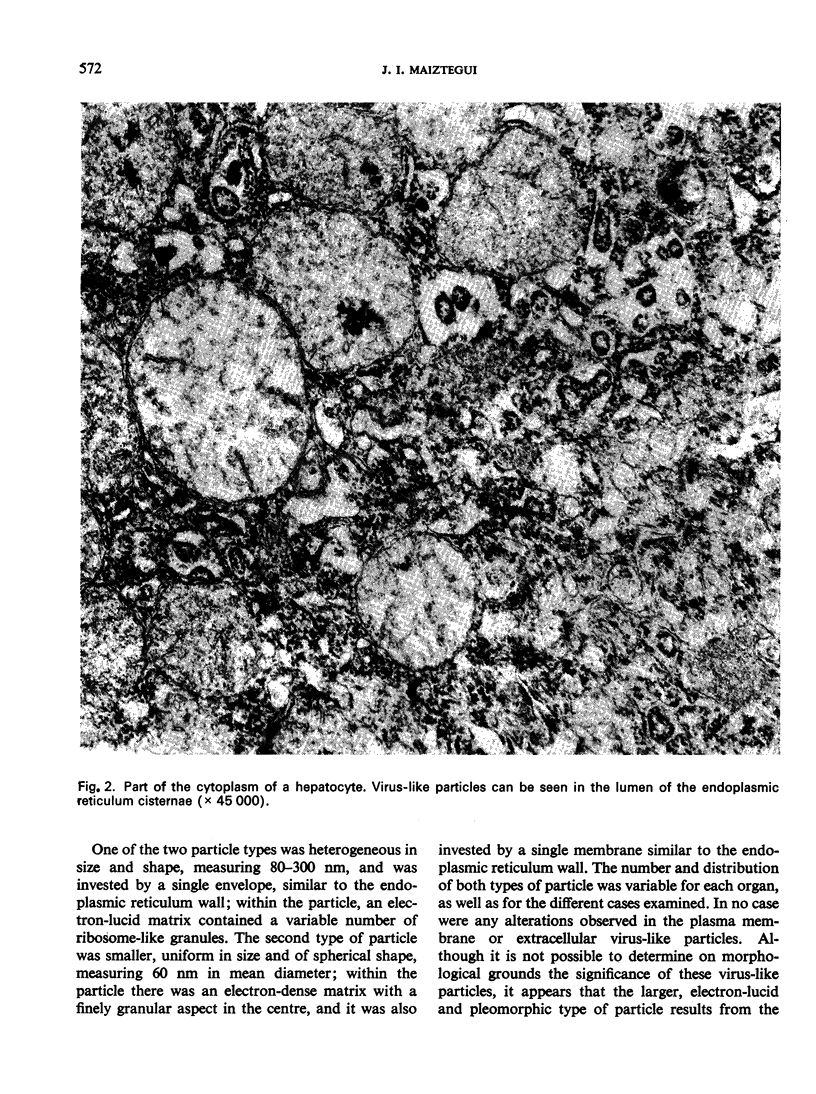
The disease is characterized by haematological, renal, neurological and cardiovascular changes. Electron microscopy and immunohistochemical studies have shown cytopathic changes, characteristic intracellular virus-like particles, and antigenic determinants of Junin virus in different organs from 9 cases of AHF. No deposits of immunoglobulins or C3 were found in the kidneys; in addition, an absence of fibrinogen and C3 in the hepatocytes and of immunoglobulins in the spleen was observed. These findings suggest a direct viral pathogenic action in the human disease.
Ultrastructural and immunofluorescence studies in tissues of guinea-pigs inoculated with two strains of Junin virus revealed the presence of the same types of virus-like particles and antigenic determinants of Junin virus as were encountered in the human subjects with AHF.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVAREZ AMBROSETTI E., CINTORA F. A., LOCICERO R., MAGNONI C., MILANI H., VACCAREZZA R. Fiebre hemorrágica epidémica: observaciones clínicas. Dia Med. 1959 Mar 5;31(10):232–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agrest A., Sanchez Avalos J. C., Arce M., Slepoy A. Fiebre hemorrágica argentina y coagulopatía por consumo. Medicina (B Aires) 1969 May-Jun;29(3):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxaca M. C., de Guerrero L. B., Parodi A. S., Rugiero H. R., González Cappa S. Viremia en enfermos de fiebre hemorragica Argentina. Rev Asoc Med Argent. 1965 May;79(5):230–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsner B., Schwarz E., Mando O. G., Maiztegui J., Vilches A. Pathology of 12 fatal cases of Argentine hemorrhagic fever. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1973 Mar;22(2):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiztegui J. I., Sabattini M. S., Barrera Oro J. G. Actividad del virus de la coriomeningitis linfocitica (LCM) en el área endémica de fiebre hemorrágica Argentina (FHA). 1. Estudios serológicos en roedores capturados en la ciudad de Pergamino. Medicina (B Aires) 1972 Mar-Apr;32(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A. Immunofluorescence study of the carrier state and mechanism of vertical transmission in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in mice. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):395–402. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pablo Garay R. Patogenia de la encefalitis por virus Junín: estudios en ratón lactante. Medicina (B Aires) 1971 Sep-Oct;31(5):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUGGIERO H., RUGIERO H. R., CINTORA F. A., MAGNONI C., MAGLIO F., GONZALEZCAMBACERES C., ASTARLOA L., SQUASSI G. FIEBRE HEMORR'AGICA ARGENTINA. 3. APARATO CARDIOVASCULAR. Rev Asoc Med Argent. 1964 Jul;78:360–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabattini M. S., Barrera Oro J. G., Maiztegui J. I., de Ferradas B. R. Actividad del virus de la coriomeningitis linfocítica en el sea endémica de fiebre hemorrágica Argentina (FHA). II. Aislaminto a partir de un Mus musculus campestre capturado en el sudeste de Cordoba. Medicina (B Aires) 1974 Jul-Aug;34(4):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E. R., Mando O. G., Maiztegui J. I., Vilches A. M., Otero E. R., Berrutti Z. C. alteraciones de la coagulación en la fiebre hemorrágica argentina. Medicina (B Aires) 1972 May-Jun;32(3):247–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




