Abstract
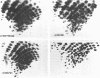
In July 1991, an influenza A virus, designated A/Maryland/12/91 (A/MD), was isolated from the bronchial secretions of a 27-year-old animal caretaker. He had been admitted to the hospital with bilateral pneumonia and died of acute respiratory distress syndrome 13 days later. Antigenic analyses with postinfection ferret antisera and monoclonal antibodies to recent H1 swine hemagglutinins indicated that the hemagglutinin of this virus was antigenically related to, but distinguishable from, those of other influenza A (H1N1) viruses currently circulating in swine. Oligonucleotide mapping of total viral RNAs revealed differences between A/MD and other contemporary swine viruses. However, partial sequencing of each RNA segment of A/MD demonstrated that all segments were related to those of currently circulating swine viruses. Sequence analysis of the entire hemagglutinin, nucleoprotein, and matrix genes of A/MD revealed a high level of identity with other contemporary swine viruses. Our studies on A/MD emphasize that H1N1 viruses in pigs obviously continue to cross species barriers and infect humans.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 1986 report of the AVMA Panel on Euthanasia. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986 Feb 1;188(3):252–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmüller A., Kunerl M., Müller K., Hinshaw V. S., Fitch W. M., Scholtissek C. Genetic relatedness of the nucleoprotein (NP) of recent swine, turkey, and human influenza A virus (H1N1) isolates. Virus Res. 1992 Jan;22(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90091-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer C. B., Roth M. G. A single amino acid change in the cytoplasmic domain alters the polarized delivery of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):413–421. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler-White A. J., Naeve C. W., Murphy B. R. Characterization of a gene coding for M proteins which is involved in host range restriction of an avian influenza A virus in monkeys. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):697–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.697-700.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrucci M. R., Donatelli I., Sidoli L., Barigazzi G., Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Genetic reassortment between avian and human influenza A viruses in Italian pigs. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):503–506. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. M., Hinshaw V. S., Kawaoka Y., Easterday B. C., Webster R. G. Influenza viral infection of swine in the United States 1988-1989. Arch Virol. 1991;116(1-4):261–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01319247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley A. J., Van Campen H., Philpott M. S., Easterday B. C., Hinshaw V. S. Pathological lesions in the lungs of ducks infected with influenza A viruses. Vet Pathol. 1989 Jan;26(1):1–5. doi: 10.1177/030098588902600101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. J., Bai Z. S., Kendal A. P. Laboratory-based surveillance of influenza A(H1N1) and A(H3N2) viruses in 1980-81: antigenic and genomic analyses. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(1):143–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. J., Black R. A., Kendal A. P. Pathways of evolution of influenza A (H1N1) viruses from 1977 to 1986 as determined by oligonucleotide mapping and sequencing studies. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):299–313. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacso C. C., Couch R. B., Six H. R., Young J. F., Quarles J. M., Kasel J. A. Sporadic occurrence of zoonotic swine influenza virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):833–835. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.833-835.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Will C., Buckard K., Kuroda K., Ortmann D., Munk K., Scholtissek C., Schnittler H., Drenckhahn D., Klenk H. D. Structure and assembly of hemagglutinin mutants of fowl plague virus with impaired surface transport. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1495–1505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1495-1505.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y. Z., Markushin S. G., Klimov A. I., Lotte V. D., Ginzburg V. P. Studies on a temperature-sensitive mutant of fowl plague virus having a mutation in gene 7 coding for the M protein. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):291–304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman O. T., Bean W. J., Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Evolution of the nucleoprotein gene of influenza A virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1487-1497.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptmann R., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Bachmayer H., Almond J. W. Nucleotide sequence of the haemagglutinin gene of influenza virus A/England/321/77. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):215–220. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw V. S., Bean W. J., Jr, Webster R. G., Easterday B. C. The prevalence of influenza viruses in swine and the antigenic and genetic relatedness of influenza viruses from man and swine. Virology. 1978 Jan;84(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 integral membrane protein is a homotetramer stabilized by formation of disulfide bonds. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):32–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90115-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimov A. I., Sokolov N. I., Orlova N. G., Ginzburg V. P. Correlation of amino acid residues in the M1 and M2 proteins of influenza virus with high yielding properties. Virus Res. 1991 Mar;19(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90098-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Lai C. J., Choppin P. W. Sequences of mRNAs derived from genome RNA segment 7 of influenza virus: colinear and interrupted mRNAs code for overlapping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luoh S. M., McGregor M. W., Hinshaw V. S. Hemagglutinin mutations related to antigenic variation in H1 swine influenza viruses. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1066–1073. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1066-1073.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Nuclear transport of influenza virus ribonucleoproteins: the viral matrix protein (M1) promotes export and inhibits import. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90576-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerome K., Sakamoto S., Yano N., Yamamoto T., Kobayashi S., Webster R. G., Oya A. Antigenic characteristics and genome composition of a naturally occurring recombinant influenza virus isolated from a pig in Japan. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2611–2620. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble S., McGregor M. S., Wentworth D. E., Hinshaw V. S. Antigenic and genetic conservation of the haemagglutinin in H1N1 swine influenza viruses. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):1197–1200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobusawa E., Aoyama T., Kato H., Suzuki Y., Tateno Y., Nakajima K. Comparison of complete amino acid sequences and receptor-binding properties among 13 serotypes of hemagglutinins of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Ritchey M. B., Schulman J. L., Kilbourne E. D. Genetic composition of a high-yielding influenza A virus recombinant: a vaccine strain against "Swine" influenza. Science. 1976 Oct 15;194(4262):334–335. doi: 10.1126/science.968486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P. A., Kendal A. P., Zakowski P. C., Cox N. J., Trautman M. S., Cherry J. D., Auerbach D. M., McCusker J., Belliveau R. R., Kappus K. D. Lack of significant person-to-person spread of swine influenza-like virus following fatal infection in an immunocompromised child. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Feb;119(2):152–158. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto L. H., Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90452-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. S., Bootman J. S., Newman R., Oxford J. S., Daniels R. S., Webster R. G., Schild G. C. Structural changes in the haemagglutinin which accompany egg adaptation of an influenza A(H1N1) virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers G. N., Daniels R. S., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C., Wang X. F., Higa H. H., Paulson J. C. Host-mediated selection of influenza virus receptor variants. Sialic acid-alpha 2,6Gal-specific clones of A/duck/Ukraine/1/63 revert to sialic acid-alpha 2,3Gal-specific wild type in ovo. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7362–7367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rota P. A., Rocha E. P., Harmon M. W., Hinshaw V. S., Sheerar M. G., Kawaoka Y., Cox N. J., Smith T. F. Laboratory characterization of a swine influenza virus isolated from a fatal case of human influenza. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1413–1416. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1413-1416.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Bürger H., Kistner O., Shortridge K. F. The nucleoprotein as a possible major factor in determining host specificity of influenza H3N2 viruses. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheerar M. G., Easterday B. C., Hinshaw V. S. Antigenic conservation of H1N1 swine influenza viruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. A., Lamb R. A. Alterations to influenza virus hemagglutinin cytoplasmic tail modulate virus infectivity. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):790–803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.790-803.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Burgert E. O., Jr, Dowdle W. R., Noble G. R., Campbell R. J., Van Scoy R. E. Isolation of swine influenza virus from autopsy lung tissue of man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 25;294(13):708–710. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603252941308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. H., Buckler-White A. J., London W. T., Tierney E. L., Murphy B. R. The avian influenza virus nucleoprotein gene and a specific constellation of avian and human virus polymerase genes each specify attenuation of avian-human influenza A/Pintail/79 reassortant viruses for monkeys. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2857–2863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2857-2863.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Russell P. K. Swine influenza A at Fort Dix, New Jersey (January-February 1976). IV. Summary and speculation. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136 (Suppl):S376–S380. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement_3.s376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Bean W. J., Gorman O. T., Chambers T. M., Kawaoka Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):152–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.152-179.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Cox N. J. Structural basis of immune recognition of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:737–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Rocha E. P., Regenery H. L., Kendal A. P., Cox N. J. Genetic and antigenic analyses of influenza A (H1N1) viruses, 1986-1991. Virus Res. 1993 Apr;28(1):37–55. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2762-2772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]