Abstract
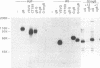
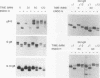
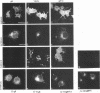
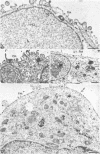
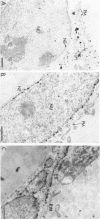
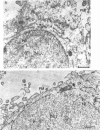
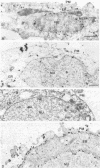
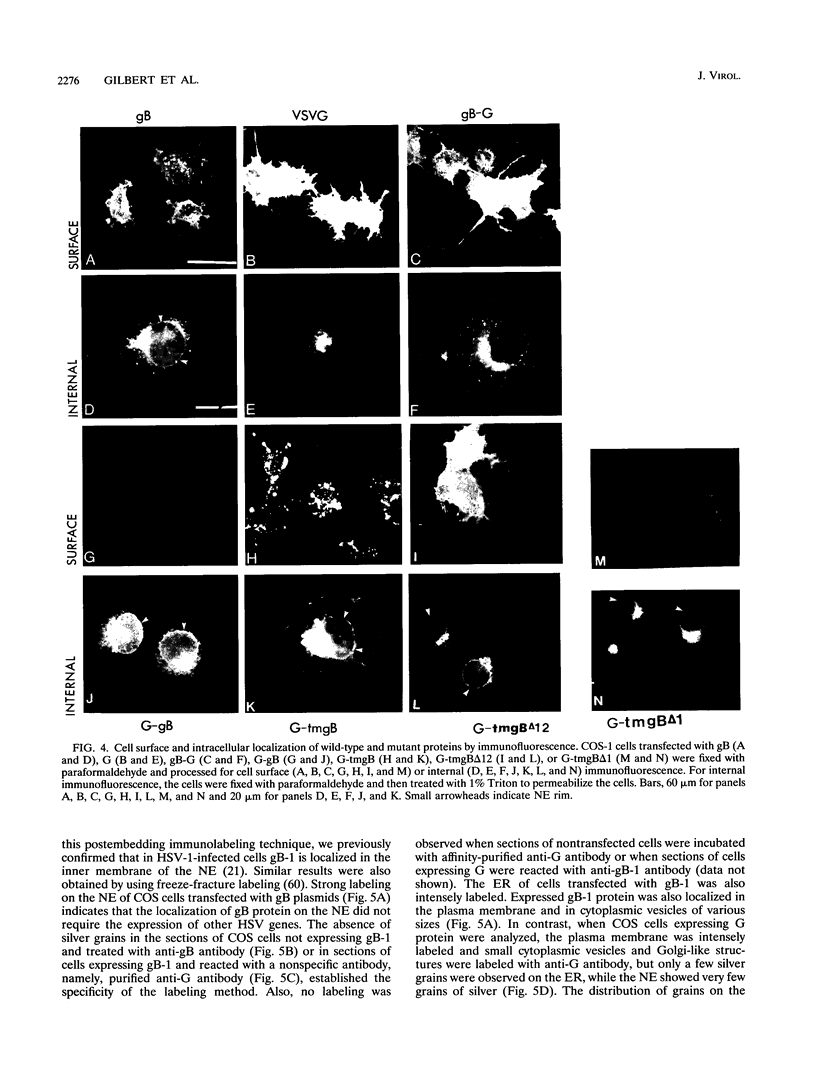
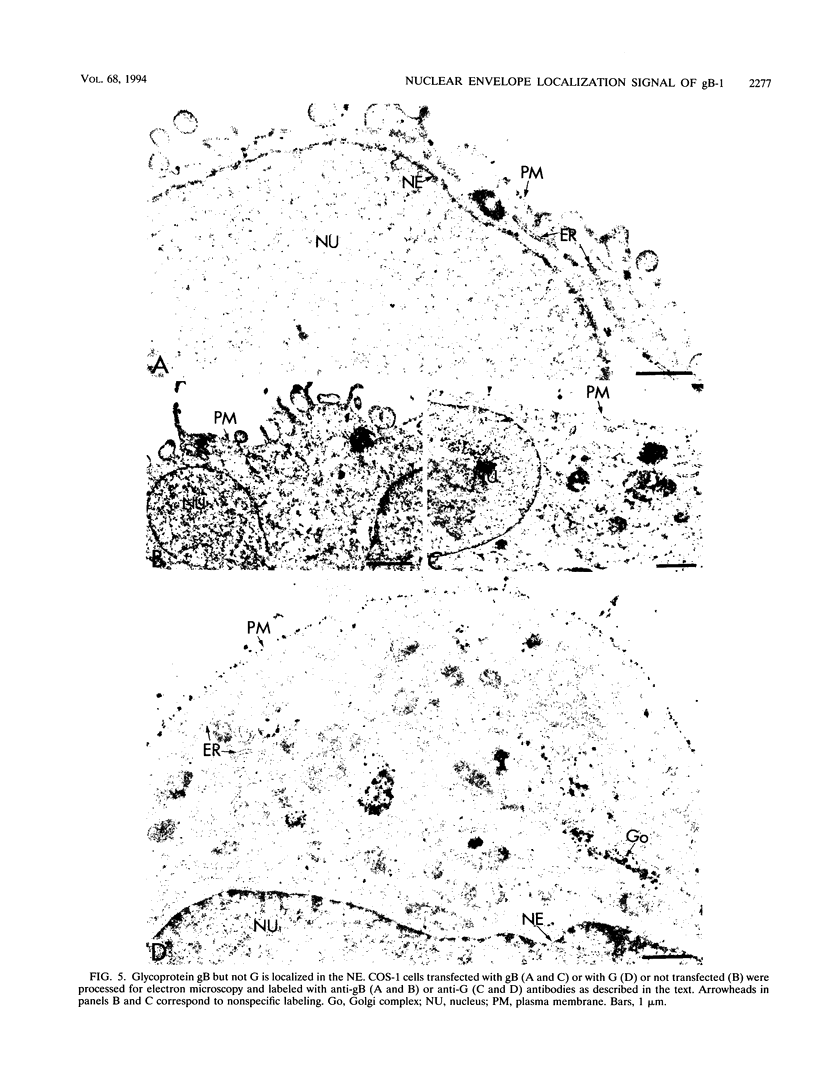
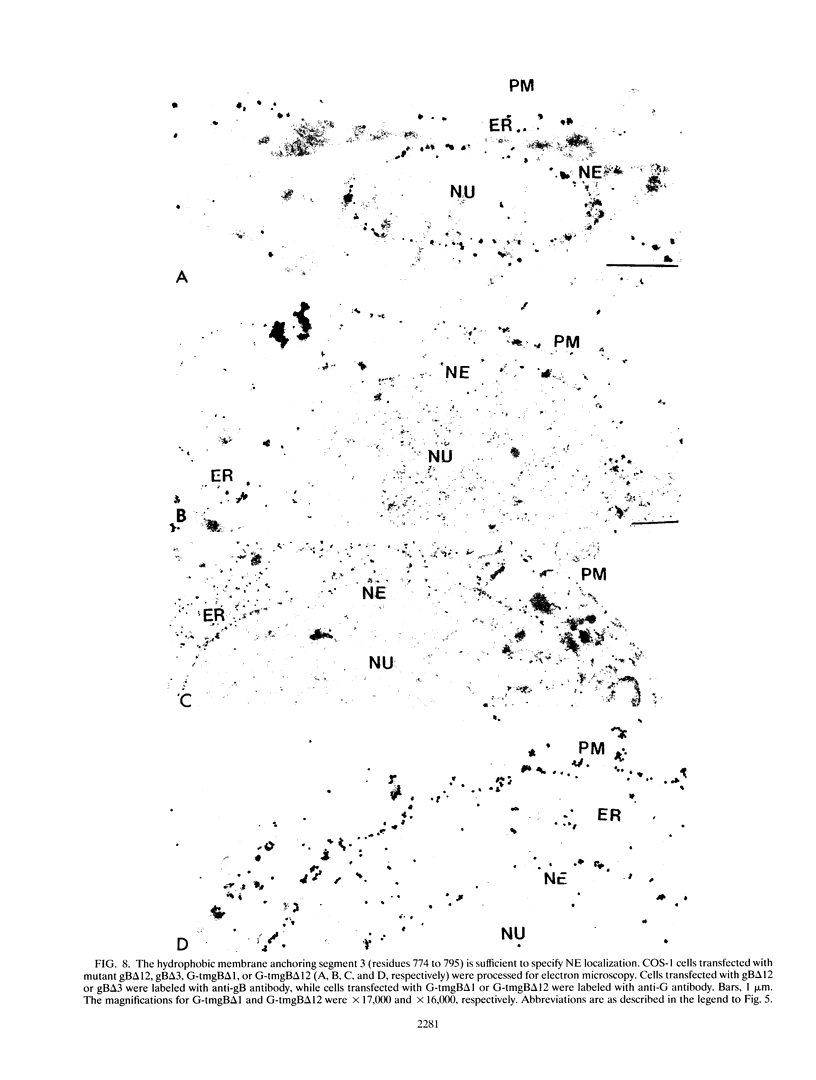
We have used the glycoprotein gB of herpes simplex virus type 1 (gB-1), which buds from the inner nuclear membrane, as a model protein to study localization of membrane proteins in the nuclear envelope. To determine whether specific domains of gB-1 glycoprotein are involved in localization in the nuclear envelope, we have used deletion mutants of gB-1 protein as well as chimeric proteins constructed by replacing the domains of the cell surface glycoprotein G of vesicular stomatitis virus with the corresponding domains of gB. Mutant and chimeric proteins expressed in COS cells were localized by immunoelectron microscopy. A chimeric protein (gB-G) containing the ectodomain of gB and the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of G did not localize in the nuclear envelope. When the ectodomain of G was fused to the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of gB, however, the resulting chimeric protein (G-gB) was localized in the nuclear envelope. Substitution of the transmembrane domain of G with the 69 hydrophobic amino acids containing the membrane anchoring domain of gB allowed the hybrid protein (G-tmgB) to be localized in the nuclear envelope, suggesting that residues 721 to 795 of gB can promote retention of proteins in the nuclear envelope. Deletion mutations in the hydrophobic region further showed that a transmembrane segment of 21 hydrophobic amino acids, residues 774 to 795 of gB, was sufficient for localization in the nuclear envelope. Since wild-type gB and the mutant and chimeric proteins that were localized in the nuclear envelope were also retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, the membrane spanning segment of gB could also influence retention in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki D., Lee N., Yamaguchi N., Dubois C., Fukuda M. N. Golgi retention of a trans-Golgi membrane protein, galactosyltransferase, requires cysteine and histidine residues within the membrane-anchoring domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4319–4323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of the intracellular transport of the membrane glycoprotein (G) of vesicular stomatitis virus in infected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. The nuclear envelope and nuclear transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):514–520. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J., Pettitt J. M., Schachter H., Sarkar M., Gleeson P. A. The transmembrane and flanking sequences of beta 1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I specify medial-Golgi localization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24433–24440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher M., Raviprakash K., Ghosh H. P. Acid pH-induced fusion of cells by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gB an gD. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5862–5868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence specifying the glycoprotein gene, gB, of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danscher G., Nörgaard J. O. Light microscopic visualization of colloidal gold on resin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Dec;31(12):1394–1398. doi: 10.1177/31.12.6631001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessev G. N. Nuclear envelope structure. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;4(3):430–435. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90008-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. The nuclear membrane. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):942–947. doi: 10.1126/science.1439805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Lamb R. A., Rose J. K., Helenius A. Folding and assembly of viral membrane proteins. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):545–562. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D., Hunter E. Transport of membrane proteins to the cell surface. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;170:107–139. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76389-2_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H. Using recombinant DNA techniques to study protein targeting in the eucaryotic cell. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:403–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Burke B. Functional organization of the nuclear envelope. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:335–374. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Choudhury N., Butcher M., Ghosh H. P. Expression from cloned DNA of biologically active glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1 in mammalian cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):689–699. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and maturation of glycoproteins of enveloped animal viruses. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 Jan-Feb;2(1):26–39. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R., Ghosh H. P. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gB in the nuclear envelope of infected cells. Virus Res. 1993 Jun;28(3):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90023-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Parton R. G., Lucocq J., van Deurs B., Brown D., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. The immunofluorescent era of membrane traffic. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;3(7):214–219. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90114-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. R., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Identification of a consensus motif for retention of transmembrane proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3153–3162. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J. Vectors used for expression in mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:487–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85041-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga J., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J. Studies on herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Capone J., Irving R. A., Rhee S. H., Bilan P., Toneguzzo F., Hofmann T., Ghosh H. P. Viral membrane glycoproteins: comparison of the amino terminal amino acid sequences of the precursor and mature glycoproteins of three serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Drone C., Sat E., Ghosh H. P. Mutational analysis of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G for membrane fusion domains. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4070–4077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4070-4077.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzio J. P., Banting G. Eukaryotic membrane traffic: retrieval and retention mechanisms to achieve organelle residence. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Oct;18(10):395–398. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ROSE H. M., HOLDEN M., JONES E. P. Electron microscopic observations on the development of herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:643–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E. Golgi retention signals: do membranes hold the key? Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90001-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Graham F. L., Hanke T., Johnson D. C. Protection of mice against lethal challenge with herpes simplex virus by vaccination with an adenovirus vector expressing HSV glycoprotein B. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):244–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90064-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S. Sequences within and adjacent to the transmembrane segment of alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase specify Golgi retention. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3577–3588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S., Morgan C., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. II. Sequence of development. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):517–536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.517-536.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Lucocq J. M., Mackay D., Warren G. The membrane spanning domain of beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase specifies trans Golgi localization. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3567–3575. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Slusarewicz P., Hoe M. H., Warren G. Kin recognition. A model for the retention of Golgi enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 6;330(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80906-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachl C., Burke R. L., Stuve L. L., Sanchez-Pescador L., Van Nest G., Masiarz F., Dina D. Expression of cell-associated and secreted forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gB in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):315–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.315-325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Munro S. Sorting of membrane proteins in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):603–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90479-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Kousoulas K. G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Anatomy of the herpes simplex virus 1 strain F glycoprotein B gene: primary sequence and predicted protein structure of the wild type and of monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.243-253.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F. Protein localization and virus assembly at intracellular membranes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;170:67–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76389-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasile L., Ghosh K., Raviprakash K., Ghosh H. P. Effects of deletions in the carboxy-terminal hydrophobic region of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gB on intracellular transport and membrane anchoring. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4856-4866.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviprakash K., Rasile L., Ghosh K., Ghosh H. P. Shortened cytoplasmic domain affects intracellular transport but not nuclear localization of a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1777–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Carlemalm E., Villiger W., Garavito M. Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 May;29(5):663–671. doi: 10.1177/29.5.6166664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. Domains of virus glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:1–44. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60315-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M., Graham F. L., Prevec L. Expression of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus by infectious adenovirus vectors. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):417–427. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Blobel G. The first membrane spanning region of the lamin B receptor is sufficient for sorting to the inner nuclear membrane. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):631–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer M., Courtney R. J. Differential rates of processing and transport of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):520–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.520-525.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soullam B., Worman H. J. The amino-terminal domain of the lamin B receptor is a nuclear envelope targeting signal. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift A. M., Machamer C. E. A Golgi retention signal in a membrane-spanning domain of coronavirus E1 protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):19–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Cirone M., Pavan A., Zompetta C., Barile G., Frati L., Faggioni A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus envelope glycoproteins on the inner nuclear membrane of virus-producing cells. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):828–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.828-832.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Di Lazzaro C., Pavan A., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Herpes simplex virus envelopment and maturation studied by fracture label. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):554–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.554-561.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Lotti L. V., Pavan A., Migliaccio G., Bonatti S. Free diffusion to and from the inner nuclear membrane of newly synthesized plasma membrane glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):733–737. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak R. W., Blobel G. The single transmembrane segment of gp210 is sufficient for sorting to the pore membrane domain of the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1441–1449. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]