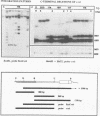
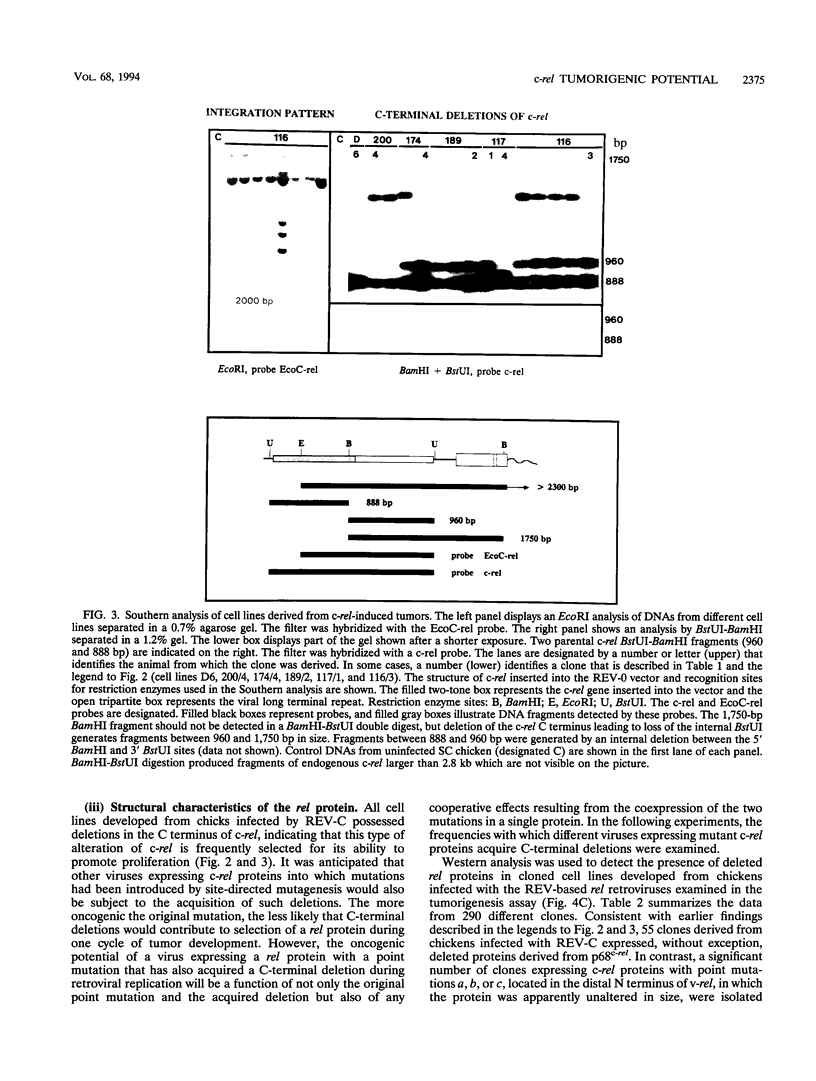
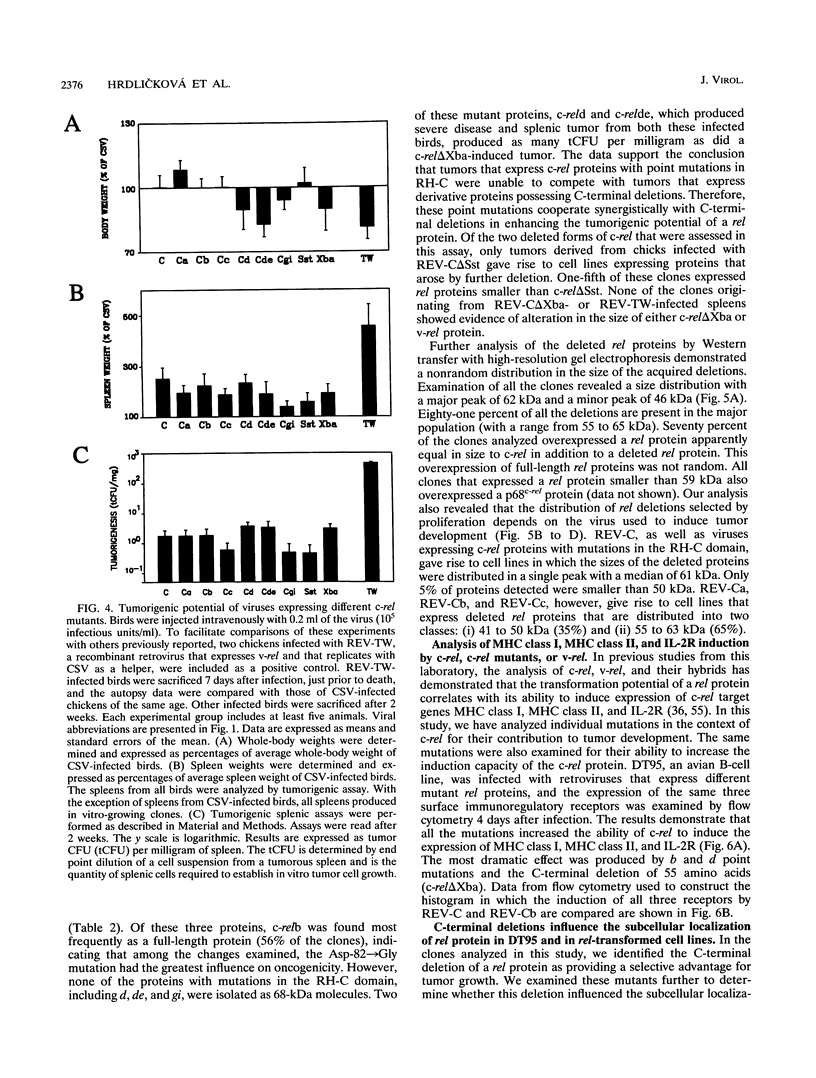
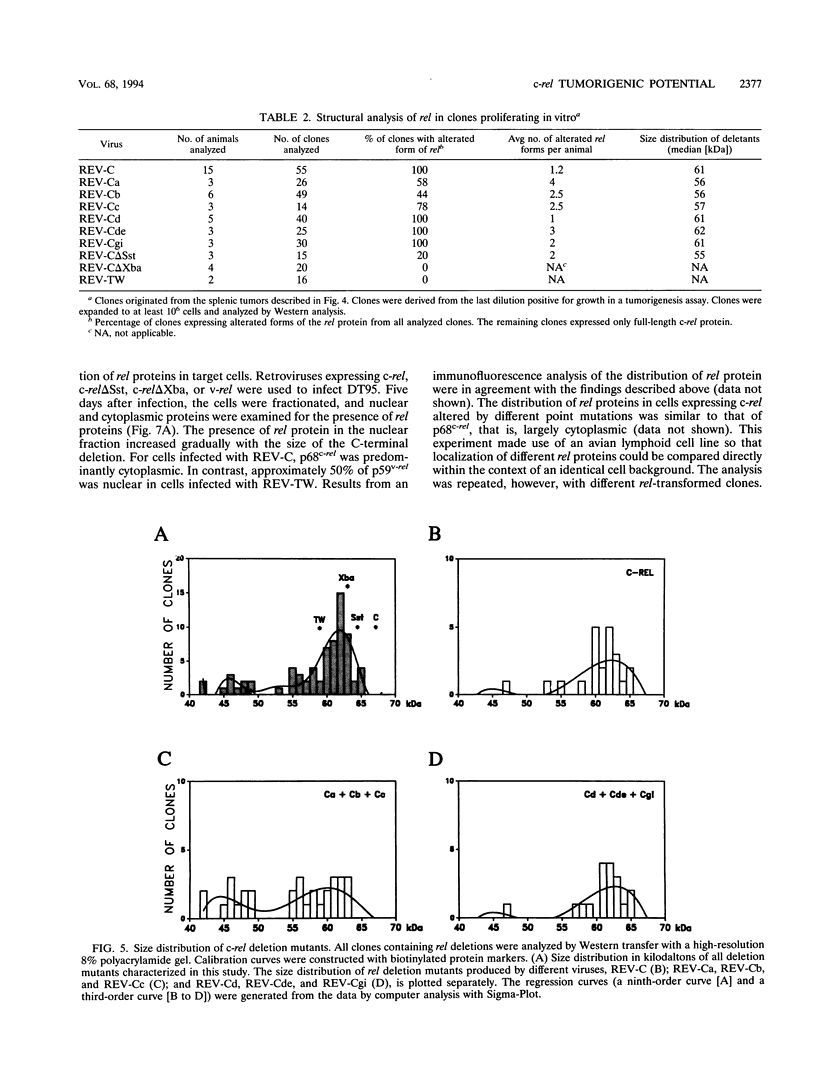
Abstract
The c-rel proto-oncogene belongs to the NF-kappa B/rel and I kappa B gene families, which regulate several inducible processes, including self-defense/repair and embryogenesis. Transduction of the c-rel transcription factor by the avian retrovirus resulted in the formation of a highly oncogenic virus, reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T (REV-T), that encodes the oncogene v-rel. To examine the oncogenic potential of c-rel, we inserted it into a REV-T-based retroviral vector, rescued virus [REV-C(CSV)], and infected 1-day-old chicks. All birds developed tumors, and all cell lines established from REV-C-induced tumors expressed c-rel proteins that lacked C-terminal sequences. These proteins, responsible for both in vivo and in vitro cell proliferation, were apparently selected for their oncogenic potential. In order to examine the cooperation of C-terminal deletions with other oncogenic alterations in vivo, point mutations present in the N-terminal and middle regions of v-rel were analyzed by a similar protocol. The data obtained support four conclusions. (i) c-rel proteins bearing any of three single-amino-acid mutations present in the N-terminal portion of v-rel were sufficiently oncogenic to induce tumor development in the absence of additional mutations. (ii) Combining a mutation from the N-terminal region of v-rel with a deletion of the C-terminal sequences of c-rel increases the oncogenicity of the protein in an additive manner. (iii) Mutations present in the middle of v-rel cooperated synergistically with C-terminal deletions to produce highly transforming viruses. (iv) Deletion of c-rel produced a variety of transforming rel proteins with sizes that extended from 42 to 65 kDa. The most frequently isolated rel deletion was 62 kDa in size. To examine the basis for the selection of different rel mutants, their ability to induce immunoregulatory surface receptors was analyzed. The data revealed a correlation between the induction capacity of these mutants and their corresponding contribution to in vivo tumorigenic potential. Moreover, an analysis of the subcellular localization of different rel proteins revealed an inverse correlation between the size of the protein and the proportion in the nucleus of lymphoid cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba T. W., Giroir B. P., Humphries E. H. Cell lines derived from avian lymphomas exhibit two distinct phenotypes. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. F., Ewert D. L., Olson W. C., Humphries E. H. Reticuloendotheliosis virus REV-T(REV-A)-induced neoplasia: development of tumors within the T-lymphoid and myeloid lineages. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6054–6062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6054-6062.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. F., Humphries E. H. A nonimmunosuppressive helper virus allows high efficiency induction of B cell lymphomas by reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):89–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. V., Temin H. M. Mutational analysis of v-rel, the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. NF-kappa B and related proteins: Rel/dorsal homologies meet ankyrin-like repeats. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Apr;17(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90321-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehmelt G., Walker A., Kabrun N., Mellitzer G., Beug H., Zenke M., Enrietto P. J. Hormone-regulated v-rel estrogen receptor fusion protein: reversible induction of cell transformation and cellular gene expression. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4641–4652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose H. R., Jr The Rel family: models for transcriptional regulation and oncogenic transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 14;1114(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(92)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler P., Brown K., Timmer W., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Fauci A. S. Mutational analysis of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B and inhibition of NF-kappa B activity by trans-dominant p50 mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):288–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.288-293.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Chang D., Mosialos G., Gilmore T. D. p105, the NF-kappa B p50 precursor protein, is one of the cellular proteins complexed with the v-Rel oncoprotein in transformed chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3758–3767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3758-3767.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Simmons D. L., Gilmore T. D. Cloning and expression of a chicken c-rel cDNA: unlike p59v-rel, p68c-rel is a cytoplasmic protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan M. M., Chen C. L., Ager L. L., Cooper M. D. Identification of the avian homologues of mammalian CD4 and CD8 antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2133–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Cihak J., Lösch U., Cooper M. D. Differential expression of two T cell receptors, TcR1 and TcR2, on chicken lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):539–543. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Mak T. W., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T DNA and isolation of a novel variant of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T by molecular cloning. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):800–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.800-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Temin H. M. Substitution of 5' helper virus sequences into non-rel portion of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T suppresses transformation of chicken spleen cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cihak J., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Trainer H., Schranner I., Merkenschlager M., Lösch U. Characterization and functional properties of a novel monoclonal antibody which identifies a T cell receptor in chickens. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):533–537. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone M., Simonsen M., Skjødt K., Linnet K., Olsson L. Mouse monoclonal antibodies to class I and class II antigens of the chicken MHC. Evidence for at least two class I products of the B complex. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00364870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl J. A., McKinsey T. A., Hannink M. Differential pp40I kappa B-beta inhibition of DNA binding by rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1769–1778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerre S., Sista P., Sun S. C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. The c-rel protooncogene product represses NF-kappa B p65-mediated transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler R., Bergmann A., Hiromi Y., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a gene involved in dorsoventral pattern formation of Drosophila, is related to the I kappa B gene family of vertebrates. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):613–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. Different localization of the product of the v-rel oncogene in chicken fibroblasts and spleen cells correlates with transformation by REV-T. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Gerondakis S. Structure of a mammalian c-rel protein deduced from the nucleotide sequence of murine cDNA clones. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
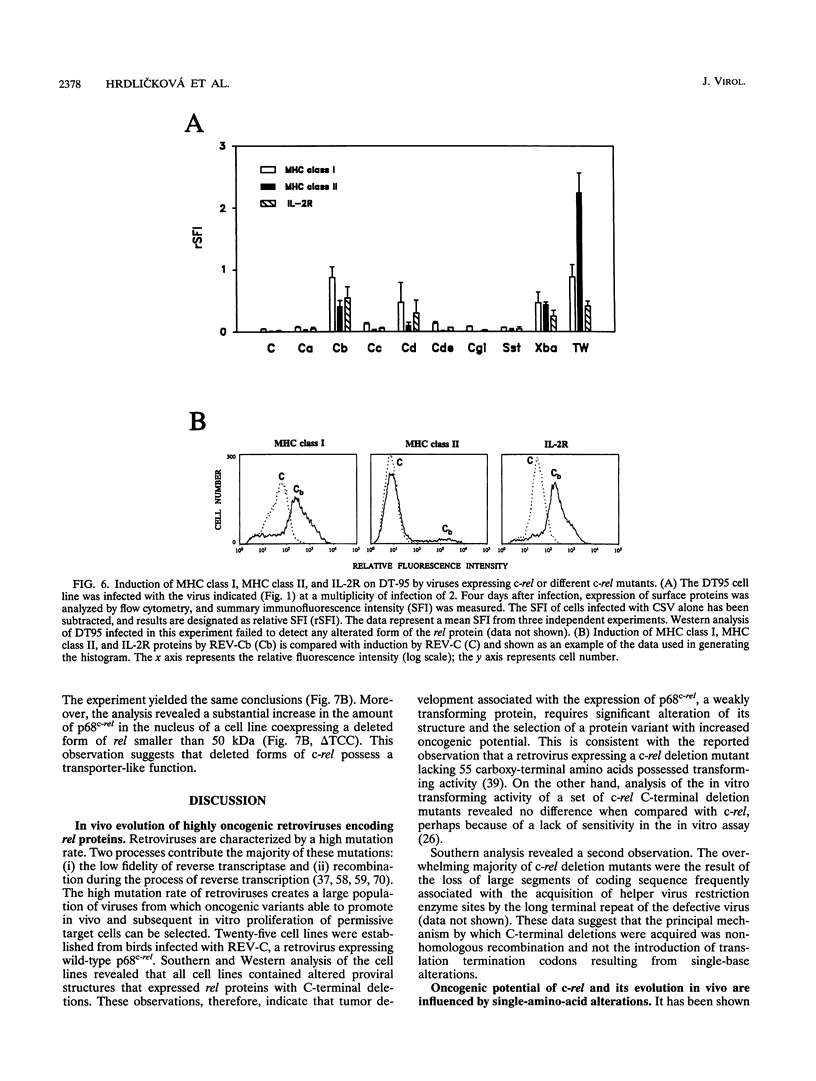
- Hrdlicková R., Nehyba J., Humphries E. H. v-rel induces expression of three avian immunoregulatory surface receptors more efficiently than c-rel. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):308–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.308-319.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S. Characterization of the Drosophila cactus locus and analysis of interactions between cactus and dorsal proteins. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90596-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochel T., Mushinski J. F., Rice N. R. The v-rel and c-rel proteins exist in high molecular weight complexes in avian and murine cells. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):615–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochel T., Rice N. R. v-rel- and c-rel-protein complexes bind to the NF-kappa B site in vitro. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. The RxxRxRxxC motif conserved in all Rel/kappa B proteins is essential for the DNA-binding activity and redox regulation of the v-Rel oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3094–3106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Tempelis C. H. Characterization of a receptor on activated chicken T cells. Dev Comp Immunol. 1991 Fall;15(4):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(91)90025-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Israël N., Ten R., Blank V., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Inhibition of transcription factors belonging to the rel/NF-kappa B family by a transdominant negative mutant. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1827–1832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu D., Thompson J. D., Gorski G. K., Rice N. R., Mayer M. G., Yunis J. J. Alterations at the rel locus in human lymphoma. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell P. C., Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. Transcriptional activity of rel family proteins. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Boehmelt G., Enrietto P. J. Mutations in the rel-homology domain alter the biochemical properties of v-rel and render it transformation defective in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1137–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Gilmore T. D. v-Rel and c-Rel are differentially affected by mutations at a consensus protein kinase recognition sequence. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Hamer P., Capobianco A. J., Laursen R. A., Gilmore T. D. A protein kinase-A recognition sequence is structurally linked to transformation by p59v-rel and cytoplasmic retention of p68c-rel. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5867–5877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møller L. B., Kaufman J., Verland S., Salomonsen J., Avila D., Lambris J. D., Skjødt K. Variations in the cytoplasmic region account for the heterogeneity of the chicken MHC class I (B-F) molecules. Immunogenetics. 1991;34(2):110–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00211423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
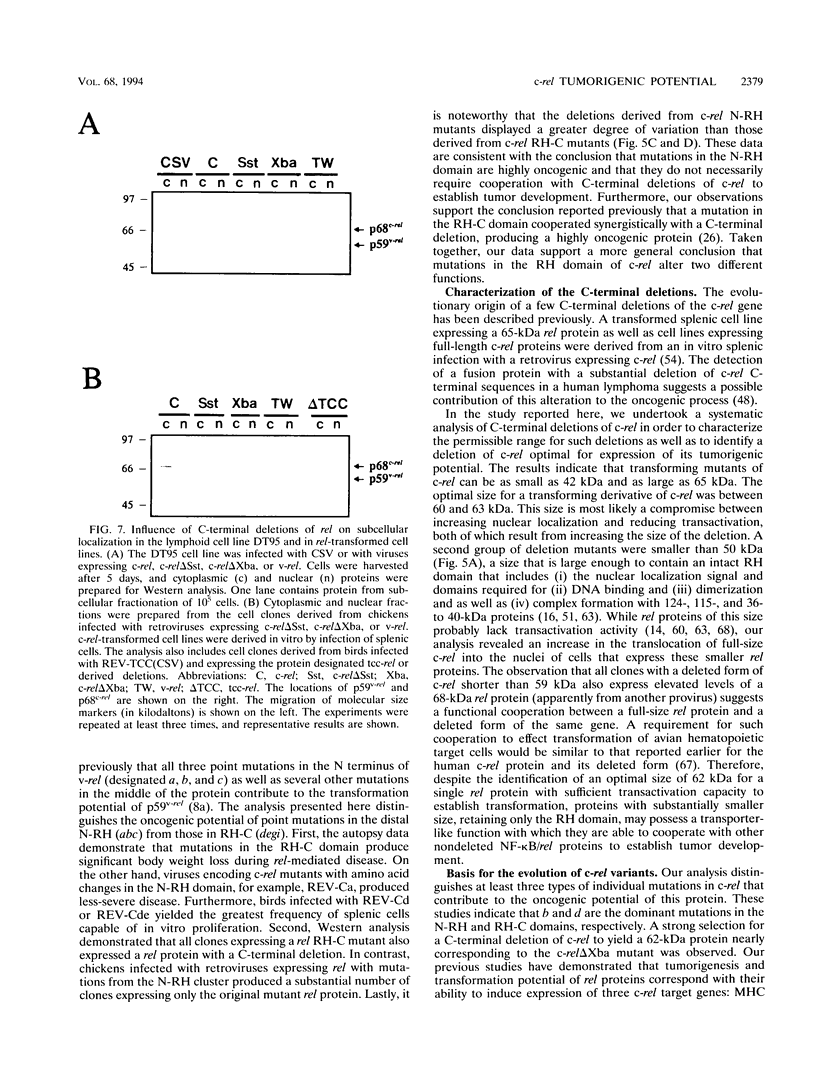
- Nehyba J., Hrdlicková R., Humphries E. H. Evolution of the oncogenic potential of v-rel: rel-induced expression of immunoregulatory receptors correlates with tumor development and in vitro transformation. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2039–2050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2039-2050.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri A., Chang C. C., Lombardi L., Salina M., Corradini P., Maiolo A. T., Chaganti R. S., Dalla-Favera R. B cell lymphoma-associated chromosomal translocation involves candidate oncogene lyt-10, homologous to NF-kappa B p50. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Takimoto G., McKeithan T. W. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 is related to genes implicated in cell lineage determination and cell cycle control. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):991–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90347-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: deletions and deletions with insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6024–6028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: substitutions, frameshifts, and hypermutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Gilmore T. D. vRel is an inactive member of the Rel family of transcriptional activating proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3122–3130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3122-3130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Gilmore T. D. Transformation by the vRel oncoprotein requires sequences carboxy-terminal to the Rel homology domain. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2245–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Hiebsch R. R., Bose H. R., Jr, Gilden R. V. Nucleotide sequence of v-rel: the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6229–6233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Quantitative immunocytochemical assay for infectious avian retroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2481–2485. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Huang G. P., Sica A., Ghosh P., Young H. A., Longo D. L., Rice N. R. Kappa B site-dependent activation of the interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene promoter by human c-Rel. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4067–4075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Snoeyenbos G. H. Experimental salmonellosis in the chicken. 2. Fate of a temperature-sensitive filamentous mutant. Avian Dis. 1974 Apr-Jun;18(2):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. H., Stein B., Ganchi P. A., Hoffman J. A., Kaufman P. A., Ballard D. W., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene: insights into the mechanism of transcriptional activation, repression, and transformation. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5018–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5018-5029.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Temin H. M. Rate and mechanism of nonhomologous recombination during a single cycle of retroviral replication. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):234–238. doi: 10.1126/science.8421784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]