Abstract
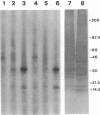
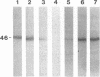
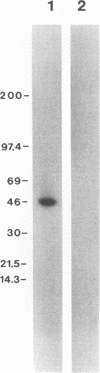
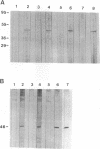
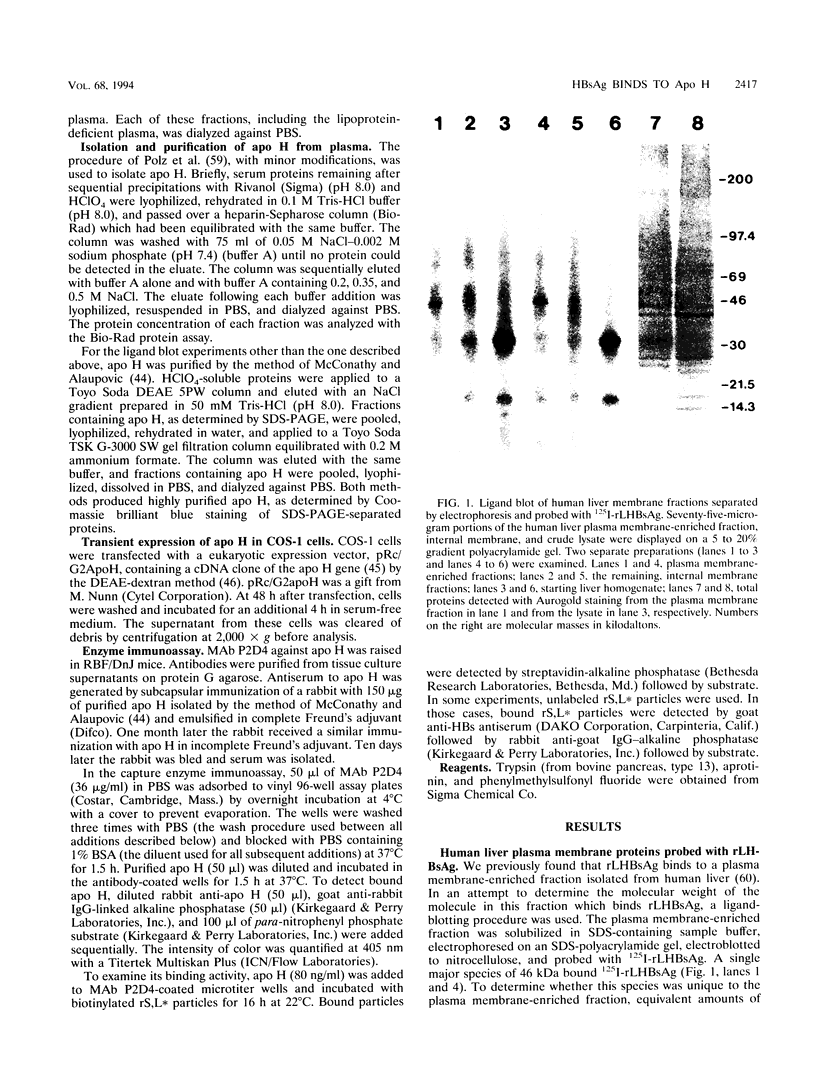
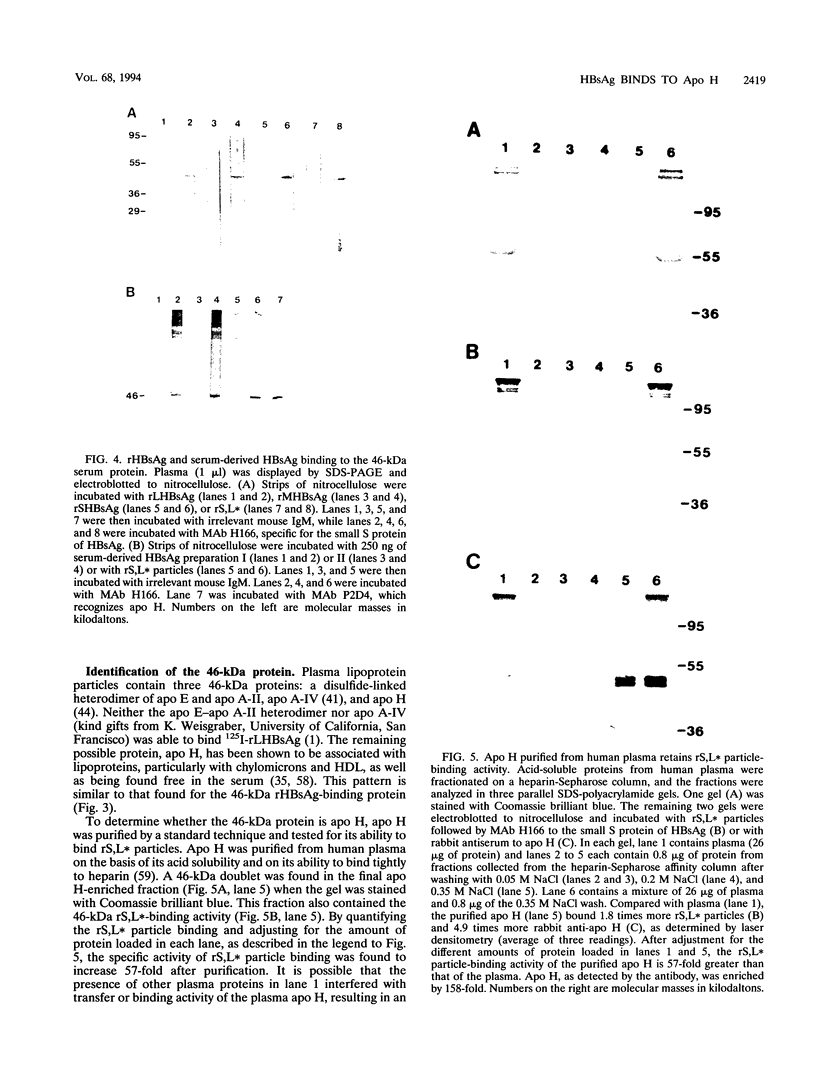
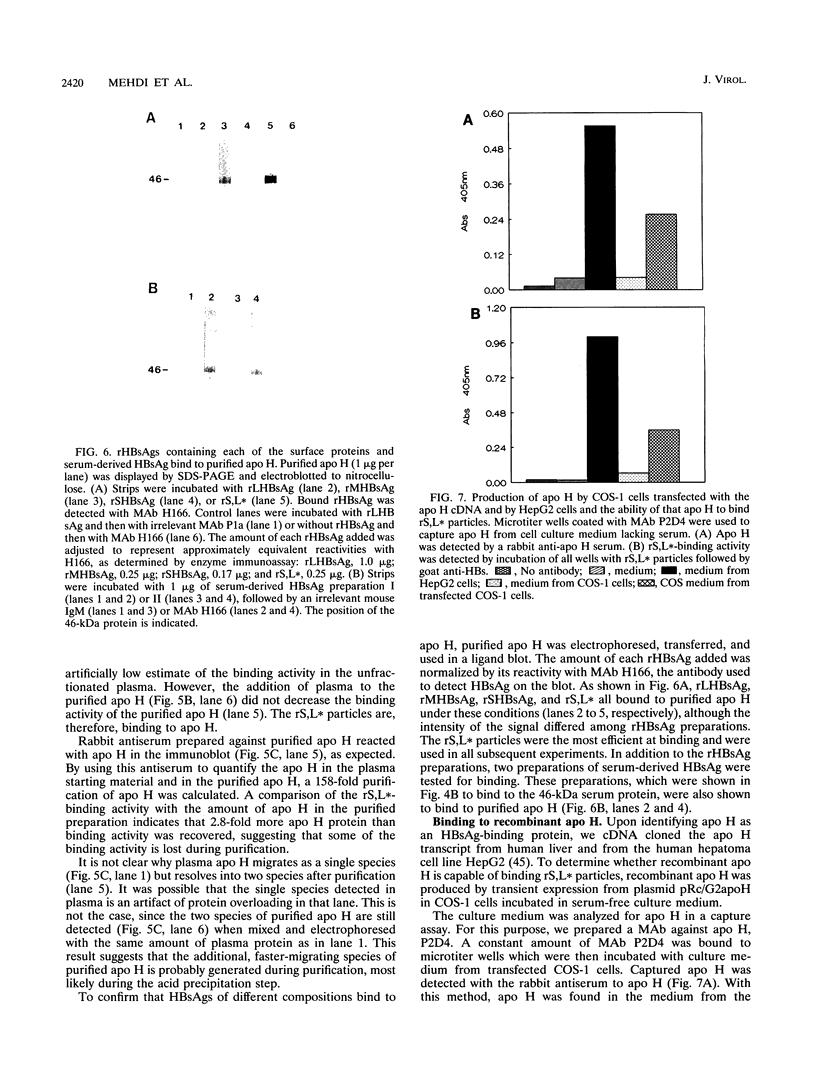
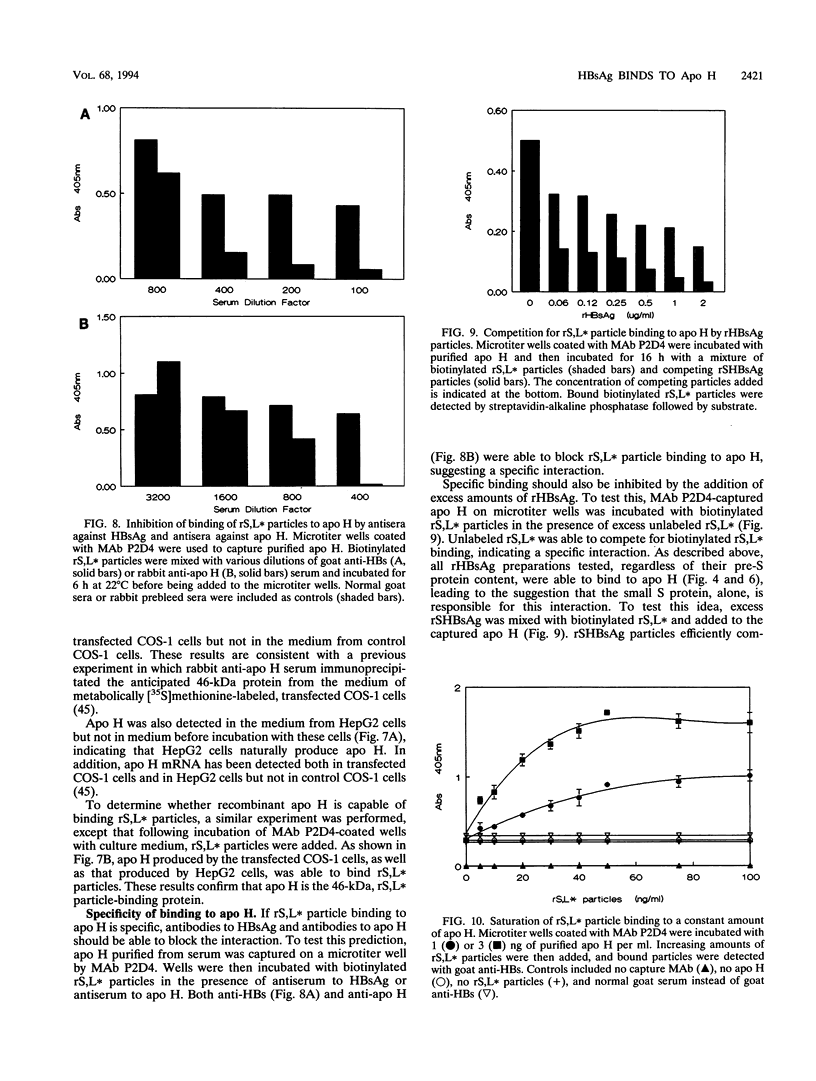
We have previously demonstrated that a plasma membrane-enriched fraction isolated from human liver is capable of binding recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen (rHBsAg) (P. Pontisso, M. A. Petit, M. Bankowski, and M. E. Peeples, J. Virol. 63:1981-1988, 1989). In this study we have separated the plasma membrane proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and used a ligand-blotting technique to identify a 46-kDa rHBsAg-binding protein. This protein could be removed from the membranes with a weakly acidic buffer, implying that it is peripherally bound. Examination of human serum revealed that the 46-kDa binding protein is a serum protein. Isolation of plasma lipoproteins revealed that the binding protein is in part associated with chylomicrons and high-density lipoproteins, both of which are targeted to the hepatocyte during the normal course of lipid metabolism. The binding protein was identified as apolipoprotein H (apo H), also known as beta 2-glycoprotein I, on the basis of copurification of the rHBsAg-binding activity with the apo H protein and the ability of cDNA-expressed apo H to bind rHBsAg. Serum-derived HBsAg also binds to apo H, indicating that binding is not unique to rHBsAg. Binding is saturable, requires only the small S protein of rHBsAg, and is inhibited by excess rHBsAg, antibodies to HBsAg, and antibodies to apo H. The binding activity of apo H is destroyed upon reduction, indicating that 1 or more of its 22 disulfide bonds are required for interaction with rHBsAg. The possibility that an interaction between hepatitis B virus particles and lipoprotein particles may facilitate entry of the virus into hepatocytes is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Touster O. Isolation of rat liver plasma membrane fragments in isotonic sucrose. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:90–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bchini R., Capel F., Dauguet C., Dubanchet S., Petit M. A. In vitro infection of human hepatoma (HepG2) cells with hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3025–3032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3025-3032.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Ihrke G., Herz J., Stanley K. K. The LDL-receptor-related protein, LRP, is an apolipoprotein E-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):162–164. doi: 10.1038/341162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen E., Halkier T., Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Kristensen T. Complete primary structure of bovine beta 2-glycoprotein I: localization of the disulfide bridges. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 14;31(14):3611–3617. doi: 10.1021/bi00129a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendes R., Burger A., Voges D., Demange P., Huber R. Calcium influx through annexin V ion channels into large unilamellar vesicles measured with fura-2. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81507-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Methods for studying the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:69–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budkowska A., Quan C., Groh F., Bedossa P., Dubreuil P., Bouvet J. P., Pillot J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) binding factor in human serum: candidate for a soluble form of hepatocyte HBV receptor. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4316–4322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4316-4322.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J. The annexin family of calcium-binding proteins. Review article. Cell Calcium. 1989 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash S., Rao K. V., Panda S. K. Receptor for pre-S1(21-47) component of hepatitis B virus on the liver cell: role in virus cell interaction. J Med Virol. 1992 Jun;37(2):116–121. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörig R. E., Marcil A., Chopra A., Richardson C. D. The human CD46 molecule is a receptor for measles virus (Edmonston strain). Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A., Paroli M., Testa U., Benvenuto R., Peschle C., Balsano F., Barnaba V. Transferrin receptor mediates uptake and presentation of hepatitis B envelope antigen by T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1195–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gries A., Nimpf J., Wurm H., Kostner G. M., Kenner T. Characterization of isoelectric subspecies of asialo-beta 2-glycoprotein I. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):531–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2600531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripon P., Diot C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Reproducible high level infection of cultured adult human hepatocytes by hepatitis B virus: effect of polyethylene glycol on adsorption and penetration. Virology. 1993 Feb;192(2):534–540. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripon P., Diot C., Thézé N., Fourel I., Loreal O., Brechot C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Hepatitis B virus infection of adult human hepatocytes cultured in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4136–4143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4136-4143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Wall D. A., Ma A. Isolation of rat hepatocyte plasma membranes. I. Presence of the three major domains. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):217–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Takai E., Ohnuma H., Kitajima K., Tsuda F., Machida A., Mishiro S., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A synthetic peptide vaccine involving the product of the pre-S(2) region of hepatitis B virus DNA: protective efficacy in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9174–9178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambouris A. M., Roach P. D., Calvert G. D., Nestel P. J. Retroendocytosis of high density lipoproteins by the human hepatoma cell line, HepG2. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jul-Aug;10(4):582–590. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.4.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Enjyoji K. Amino acid sequence and location of the disulfide bonds in bovine beta 2 glycoprotein I: the presence of five Sushi domains. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 17;30(50):11687–11694. doi: 10.1021/bi00114a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. L., Kruski A. W. Density gradient ultracentrifugation of serum lipoproteins in a swinging bucket rotor. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:170–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klickstein L. B., Wong W. W., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Wilson J. G., Fearon D. T. Human C3b/C4b receptor (CR1). Demonstration of long homologous repeating domains that are composed of the short consensus repeats characteristics of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1095–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniskern P. J., Hagopian A., Burke P., Dunn N., Emini E. A., Miller W. J., Yamazaki S., Ellis R. W. A candidate vaccine for hepatitis B containing the complete viral surface protein. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):82–87. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai K., Kaplan M., Peeples M. E. The Vero cell receptor for the hepatitis B virus small S protein is a sialoglycoprotein. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai K., Peeples M. E. Physiology and function of the vero cell receptor for the hepatitis B virus small S protein. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):332–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90488-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Steck T. L. Cholesterol-rich intracellular membranes: a precursor to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15592–15597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. S., Brewer H. B., Jr, Osborne J. C., Jr beta 2-Glycoprotein I. Molecular properties of an unusual apolipoprotein, apolipoprotein H. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4765–4770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders W. P., Glansbeek H. L., de Bruin W. C., Yap S. H. Binding of the major and large HBsAg to human hepatocytes and liver plasma membranes: putative external and internal receptors for infection and secretion of hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1990 Jul;12(1):141–147. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Miyamoto H., Baba K., Oda K., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptide (P31) with the receptor for polymerized human as well as chimpanzee albumins. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):268–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1984 Dec 1;25(12):1277–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L. Development of antiviral therapy for chronic infection with hepatitis B virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:167–183. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleer W. J., Buynak E. B., Maigetter R. Z., Wampler D. E., Miller W. J., Hilleman M. R. Human hepatitis B vaccine from recombinant yeast. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):178–180. doi: 10.1038/307178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Isolation and characterization of other apolipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:297–310. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Nunn M., Steel D. M., Whitehead A. S., Perez M., Walker L., Peeples M. E. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the human gene encoding apolipoprotein H (beta 2-glycoprotein I). Gene. 1991 Dec 15;108(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90449-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi H., Ono E., Gupta K. C. Initiation of translation at CUG, GUG, and ACG codons in mammalian cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naniche D., Varior-Krishnan G., Cervoni F., Wild T. F., Rossi B., Rabourdin-Combe C., Gerlier D. Human membrane cofactor protein (CD46) acts as a cellular receptor for measles virus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6025–6032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6025-6032.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Seto B., Strick N. Antibodies to synthetic peptides from the preS1 region of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) envelope (env) protein are virus-neutralizing and protective. Vaccine. 1989 Jun;7(3):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Li Y. Y. Cells transfected with human interleukin 6 cDNA acquire binding sites for the hepatitis B virus envelope protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1561–1569. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Sproul P., Ralph H. E., Valinsky J. Detection of receptors for hepatitis B virus on cells of extrahepatic origin. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):448–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90014-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Strick N., Sproul P. Search for hepatitis B virus cell receptors reveals binding sites for interleukin 6 on the virus envelope protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):461–469. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E. Differential detergent treatment allows immunofluorescent localization of the Newcastle disease virus matrix protein within the nucleus of infected cells. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E., Komai K., Radek R., Bankowski M. J. A cultured cell receptor for the small S protein of hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Capel F., Dubanchet S., Mabit H. PreS1-specific binding proteins as potential receptors for hepatitis B virus in human hepatocytes. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90309-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Kostner G. M. The binding of beta 2-glycoprotein-I to human serum lipoproteins: distribution among density fractions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Wurm H., Kostner G. M. Studies on the composition of the protein part of triglyceride rich lipoproteins of human serum: isolation of polymorphic forms of beta 2-glycoprotein-I. Artery. 1981;9(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Petit M. A., Bankowski M. J., Peeples M. E. Human liver plasma membranes contain receptors for the hepatitis B virus pre-S1 region and, via polymerized human serum albumin, for the pre-S2 region. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1981–1988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1981-1988.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Ruvoletto M. G., Gerlich W. H., Heermann K. H., Bardini R., Alberti A. Identification of an attachment site for human liver plasma membranes on hepatitis B virus particles. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):522–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90564-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Ruvoletto M. G., Tiribelli C., Gerlich W. H., Ruol A., Alberti A. The preS1 domain of hepatitis B virus and IgA cross-react in their binding to the hepatocyte surface. J Gen Virol. 1992 Aug;73(Pt 8):2041–2045. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-8-2041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Puppione D. L. Sequential flotation ultracentrifugation. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:155–170. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkasserer A., Estaller C., Weiss E. H., Sim R. B., Day A. J. Complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of human beta 2-glycoprotein I. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):387–391. doi: 10.1042/bj2770387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]