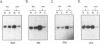Abstract
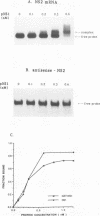
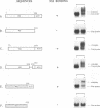
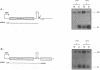
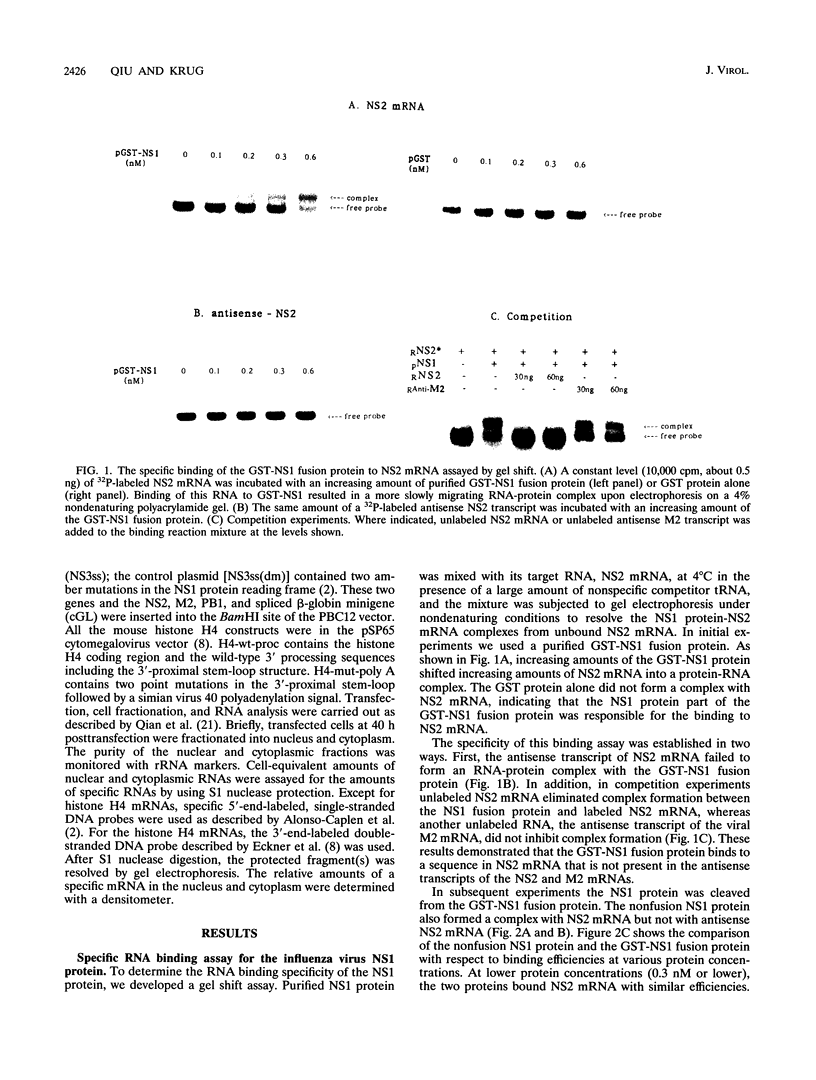
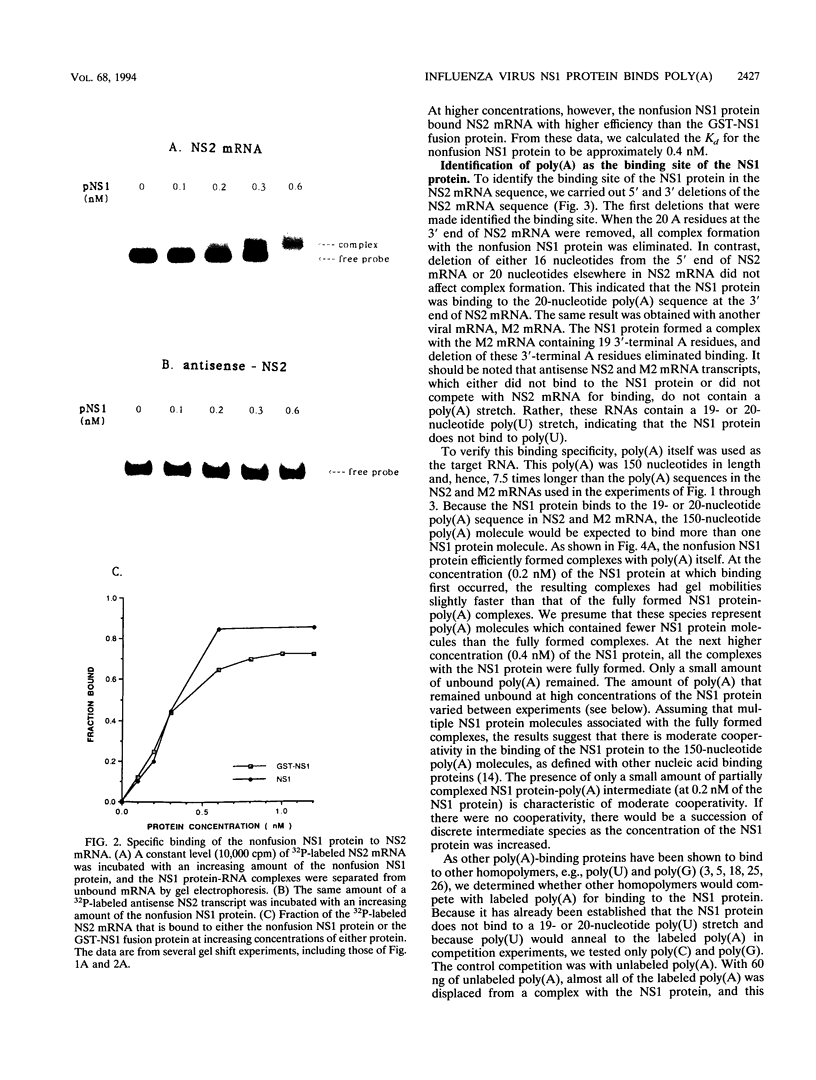
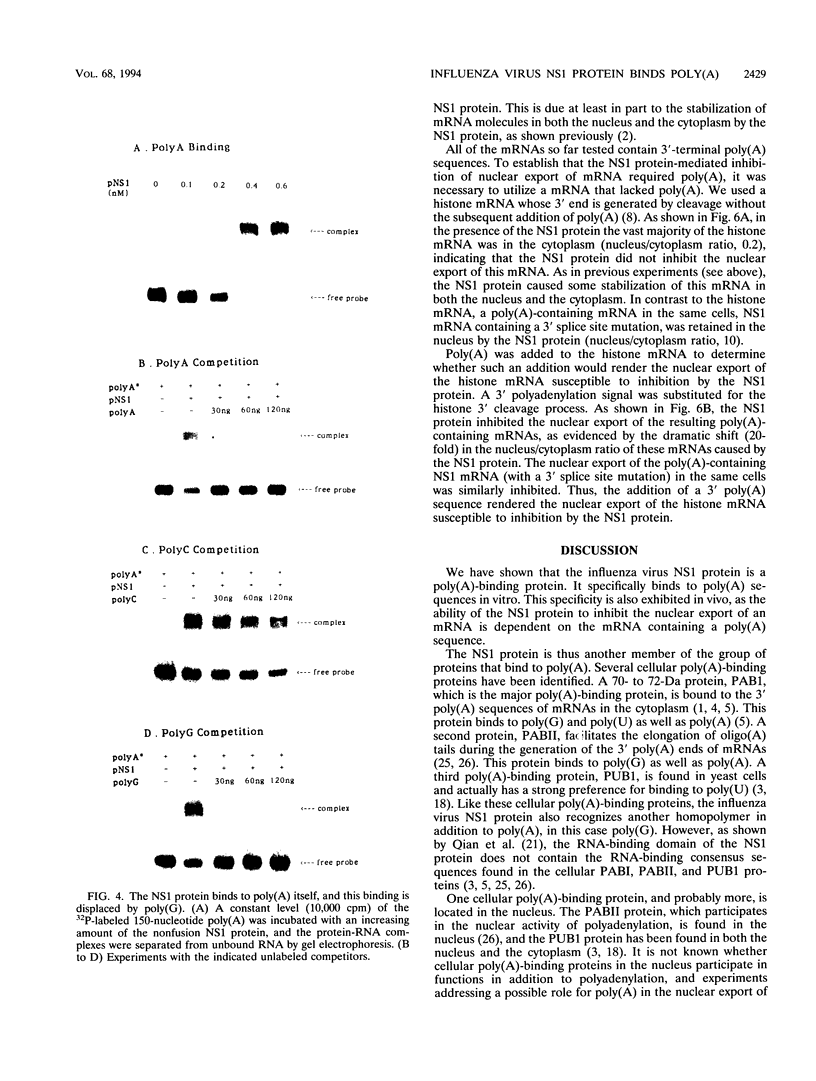
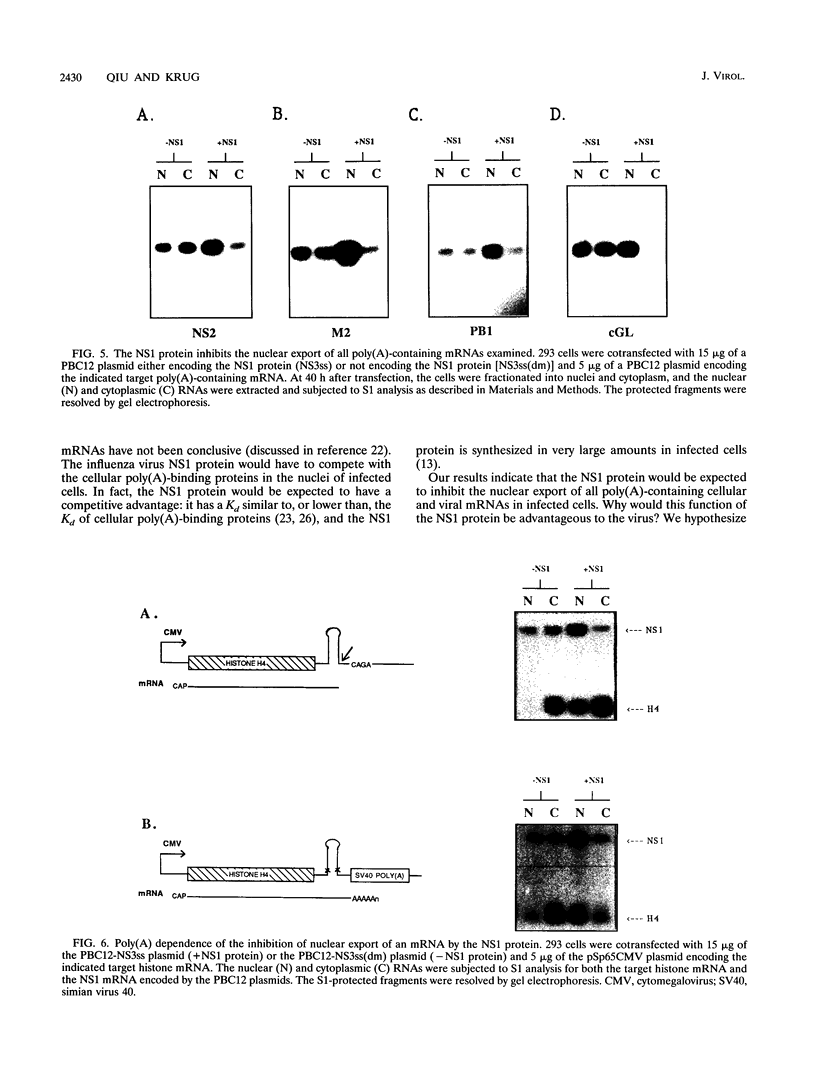
The influenza virus NS1 protein inhibits the nuclear export of a spliced viral mRNA, NS2 mRNA (F. V. Alonso-Caplen, M. E. Nemeroff, Y. Qiu, and R. M. Krug, Genes Dev. 6:255-267, 1992). To identify the sequence in NS2 mRNA that is recognized by the NS1 protein, we developed a gel shift assay for the formation of specific RNA-protein complexes. With this assay, it was established that the NS1 protein binds to the poly(A) sequence at the 3' end of NS2 mRNA and of other mRNAs. In addition, the NS1 protein was shown to bind to poly(A) itself. This specificity was also observed in vivo. The NS1 protein inhibited the nuclear export of every poly(A)-containing mRNA that was tested. In contrast, the NS1 protein failed to inhibit the nuclear export of an mRNA whose 3' end was generated by cleavage without subsequent addition of poly(A). Addition of poly(A) to this mRNA enabled the NS1 protein to inhibit mRNA export. The implications of these results for the role of the NS1 protein during virus infection are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Nemeroff M. E., Qiu Y., Krug R. M. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: the influenza virus NS1 protein regulates the transport of spliced NS2 mRNA and its precursor NS1 mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):255–267. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. T., Paddy M. R., Swanson M. S. PUB1 is a major nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylated RNA-binding protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6102–6113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. The protein responsible for the repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):717–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Matunis E. L., Dreyfuss G. The multiple RNA-binding domains of the mRNA poly(A)-binding protein have different RNA-binding activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3419–3424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Ellmeier W., Birnstiel M. L. Mature mRNA 3' end formation stimulates RNA export from the nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3513–3522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaphy S., Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 regulator of virion expression (Rev) protein binds to an RNA stem-loop structure located within the Rev response element region. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):685–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Krug R. M. Metabolism and expression of RNA polymerase II transcripts in influenza virus-infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2198–2206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Mayeda A., Kozak D., Binns G. Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, and Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90627-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M., Overman L. B., Datta S. Salt-dependent changes in the DNA binding co-operativity of Escherichia coli single strand binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Tiley L. S., McCarn D. F., Rusche J. R., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. HIV-1 structural gene expression requires binding of the Rev trans-activator to its RNA target sequence. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90670-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matunis M. J., Matunis E. L., Dreyfuss G. PUB1: a major yeast poly(A)+ RNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6114–6123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Bouloy M., Ulmanen I., Krug R. M. A unique cap(m7GpppXm)-dependent influenza virion endonuclease cleaves capped RNAs to generate the primers that initiate viral RNA transcription. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):847–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Penhoet E. E. The structure and synthesis of influenza virus phosphoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5368–5376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X. Y., Alonso-Caplen F., Krug R. M. Two functional domains of the influenza virus NS1 protein are required for regulation of nuclear export of mRNA. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2433–2441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2433-2441.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U., Kunerl M., Scholtissek C. Influenza A virus late mRNAs are specifically retained in the nucleus in the presence of a methyltransferase or a protein kinase inhibitor. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):227–233. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E. A novel poly(A)-binding protein acts as a specificity factor in the second phase of messenger RNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):759–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90119-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Lustig A., Jenö P., Maurer P. Mammalian poly(A)-binding protein II. Physical properties and binding to polynucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2937–2945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]