Abstract
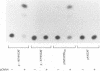
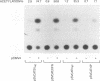
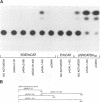
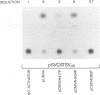
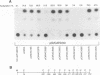
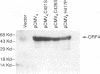
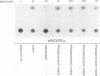
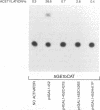
Varicella-zoster virus is the etiological agent of chickenpox and zoster in humans and belongs to the Alphaherpesvirinae subfamily within the family Herpesviridae. Much of the current understanding of gene regulation in alphaherpesviruses has been derived from studies of the prototype herpes simplex virus (HSV). In HSV, two virus-encoded, trans-regulatory proteins, ICP4 and ICP27, are essential for the replicative cycle of the virus. ICP4 is important in modulating HSV genes of all three kinetic classes, whereas the trans-regulatory effects of ICP27 are primarily associated with the expression of late genes. Recent evidence indicates that the trans-regulatory effects of ICP27 involve posttranscriptional processing of target gene transcripts (R. M. Sandri-Golding and G. E. Mendoza, Genes Dev. 6:848-863, 1992). The ICP27 homolog in varicella-zoster virus is a 452-amino-acid polypeptide encoded by the open reading frame 4 (ORF4) gene. Contrary to what is found with ICP27, we show that the ORF4 polypeptide is a transcriptional activator of diverse target promoters and has a critical requirement for the presence of upstream elements within these promoters to mediate its transcriptional effects. Evidence is also presented to implicate a critical role for the cysteine-rich, C-terminal region of the ORF4 polypeptide in its trans-regulatory functions. Specifically, by oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis, we demonstrate that of 10 cysteine residues in the ORF4 polypeptide, only C-421 and C-426 are essential for transactivator function and suggest that these cysteine residues may participate in critical protein-protein interactions rather than protein-nucleic acid interactions to mediate ORF4 inducibility.
Full text
PDF


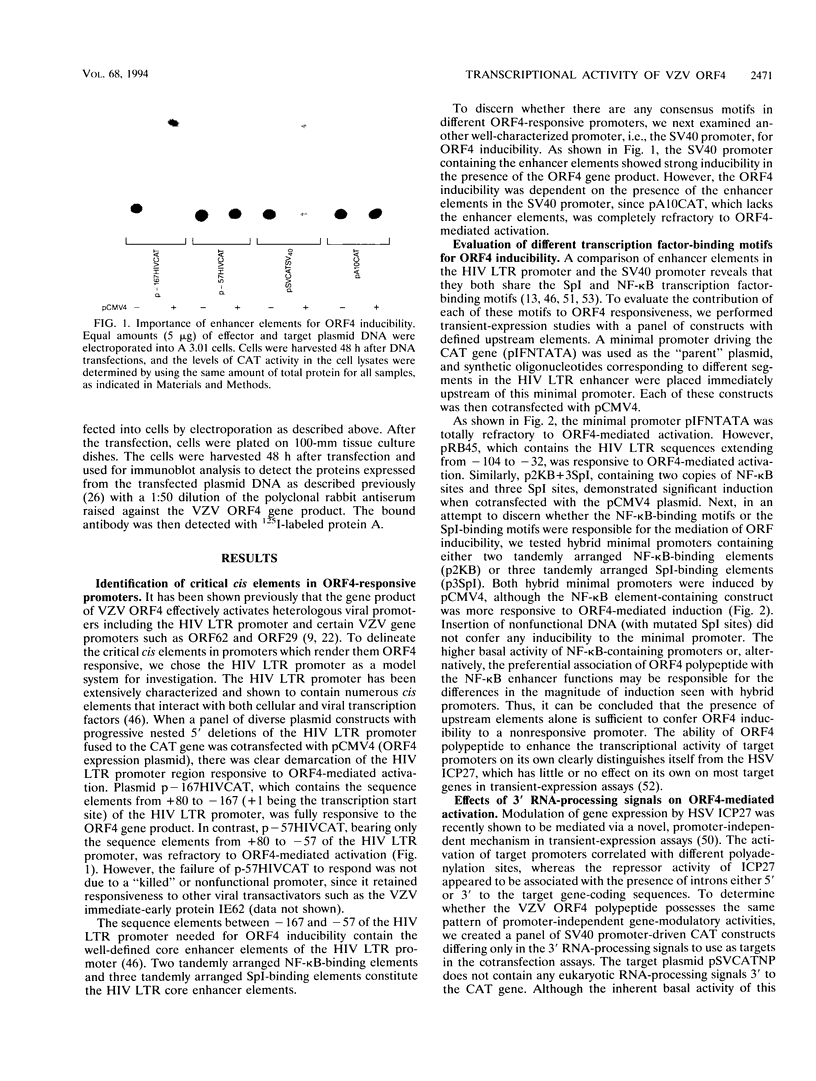
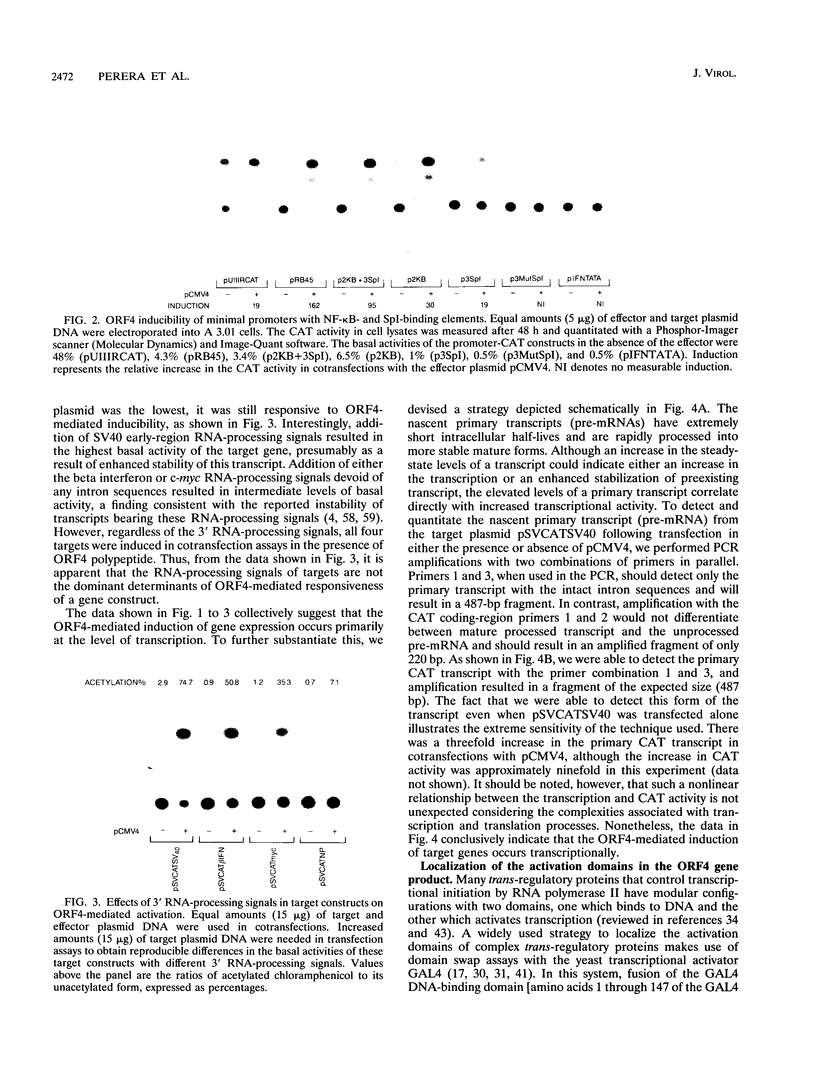
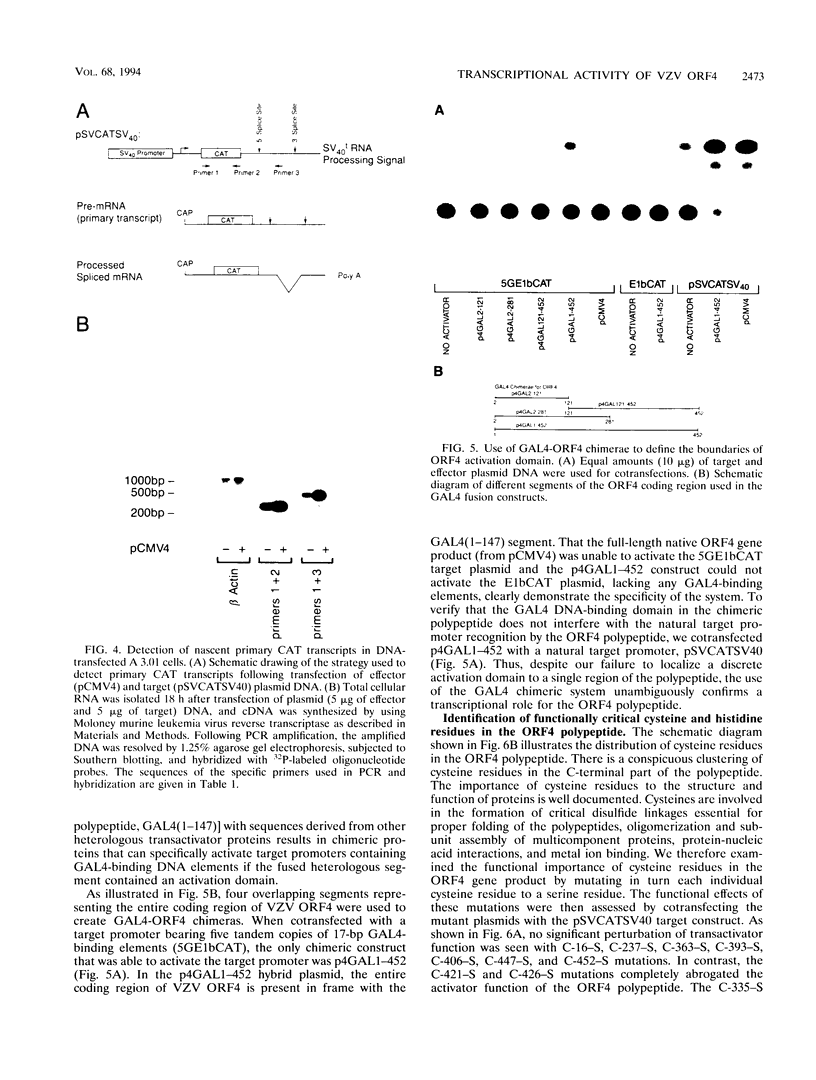
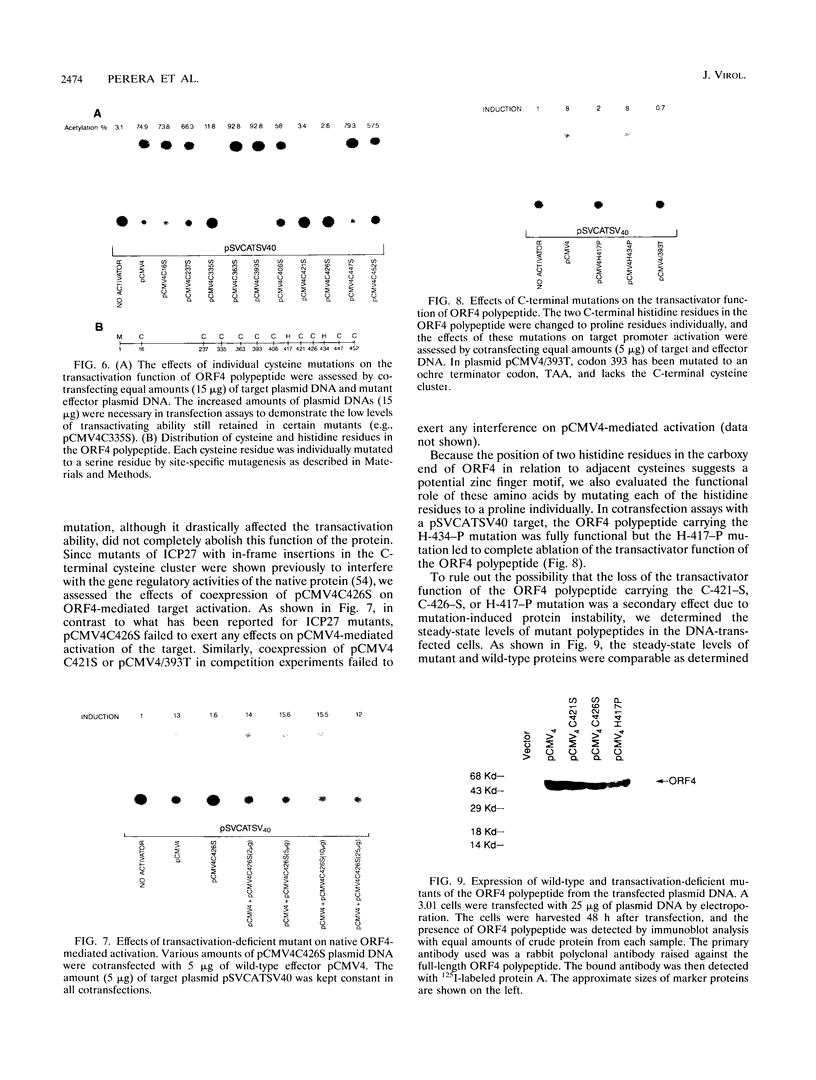



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Braun D. K., Pereira L., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha proteins 0, 4, and 27 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.108-118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Campadelli-Fiume G., Foa-Tomasi L., Cassai E. Evidence that herpes simplex virus DNA is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase B. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):996–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.996-1001.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activities of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP4 genes specifying nonsense peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4491–4511. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defechereux P., Melen L., Baudoux L., Merville-Louis M. P., Rentier B., Piette J. Characterization of the regulatory functions of varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 4 gene product. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4379–4385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4379-4385.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VI. Synthesis and modification of viral polypeptides in enucleated cells. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):720–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.720-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T., Benn S., Rabson A., Theodore T., Hoggan M. D., Martin M., Lightfoote M., Sell K. Characterization of a continuous T-cell line susceptible to the cytopathic effects of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackers P., Defechereux P., Baudoux L., Lambert C., Massaer M., Merville-Louis M. P., Rentier B., Piette J. Characterization of regulatory functions of the varicella-zoster virus gene 63-encoded protein. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3899–3903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3899-3903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley K. A., Pitha P. M. Characterization of a mouse interferon gene locus II. Differential expression of alpha-interferon genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):825–839. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Senechek D., Rice S. A., Smith J. L. Stages in the nuclear association of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional activator protein ICP4. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):276–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.276-284.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. R. Tinkering with enzymes: what are we learning? Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1252–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.3296192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M. F., Ptashne M., Green M. R. GAL4 derivatives function alone and synergistically with mammalian activators in vitro. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):659–664. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame 61 protein transactivates VZV gene promoters and enhances the infectivity of VZV DNA. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4290–4295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4290-4295.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 10 protein, the herpes simplex virus VP16 homolog, transactivates herpesvirus immediate-early gene promoters. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2739–2746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2739-2746.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Bednarik D. P., Raj N. B., Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Hayward G. S., Pitha P. M. Activation of human immunodeficiency virus by herpesvirus infection: identification of a region within the long terminal repeat that responds to a trans-acting factor encoded by herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7408–7412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M., Hayward G. S. Herpes simplex virus infection selectively stimulates accumulation of beta interferon reporter gene mRNA by a posttranscriptional mechanism. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3811–3822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3811-3822.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of exogenous human beta interferon gene in simian cells defective in interferon synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. Regulation of varicella-zoster virus gene expression in human T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5298-5304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Ruyechan W. T., Hayward G. S., Straus S. E., Hay J. A major transactivator of varicella-zoster virus, the immediate-early protein IE62, contains a potent N-terminal activation domain. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4474–4483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4474-4483.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Sadeghi-Zadeh M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate early protein, IE62, can positively regulate its cognate promoter. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90197-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Zinc fingers. Sci Am. 1993 Feb;268(2):56-9, 62-5. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0293-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Mendoza G. E. A herpesvirus regulatory protein appears to act post-transcriptionally by affecting mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):848–863. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Sekulovich R. E., Hardwicke M. A., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Mutations in the activation region of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27 can be trans dominant. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3656–3666. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3656-3666.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. H., Zhao Y., O'Callaghan D. J. The equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) UL3 gene, an ICP27 homolog, is necessary for full activation of gene expression directed by an EHV-1 late promoter. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):1105–1109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.1105-1109.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Tanaka M., Herr W. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):624–630. doi: 10.1038/341624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telford E. A., Watson M. S., McBride K., Davison A. J. The DNA sequence of equine herpesvirus-1. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):304–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90706-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. Postinduction repression of the beta-interferon gene is mediated through two positive regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7799–7803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. Postinduction turnoff of beta-interferon gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1329–1337. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]