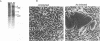
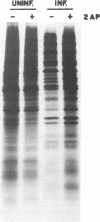
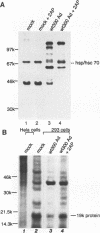
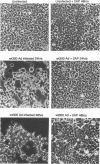
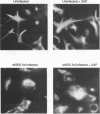
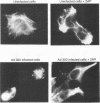
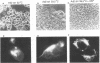
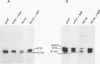Abstract
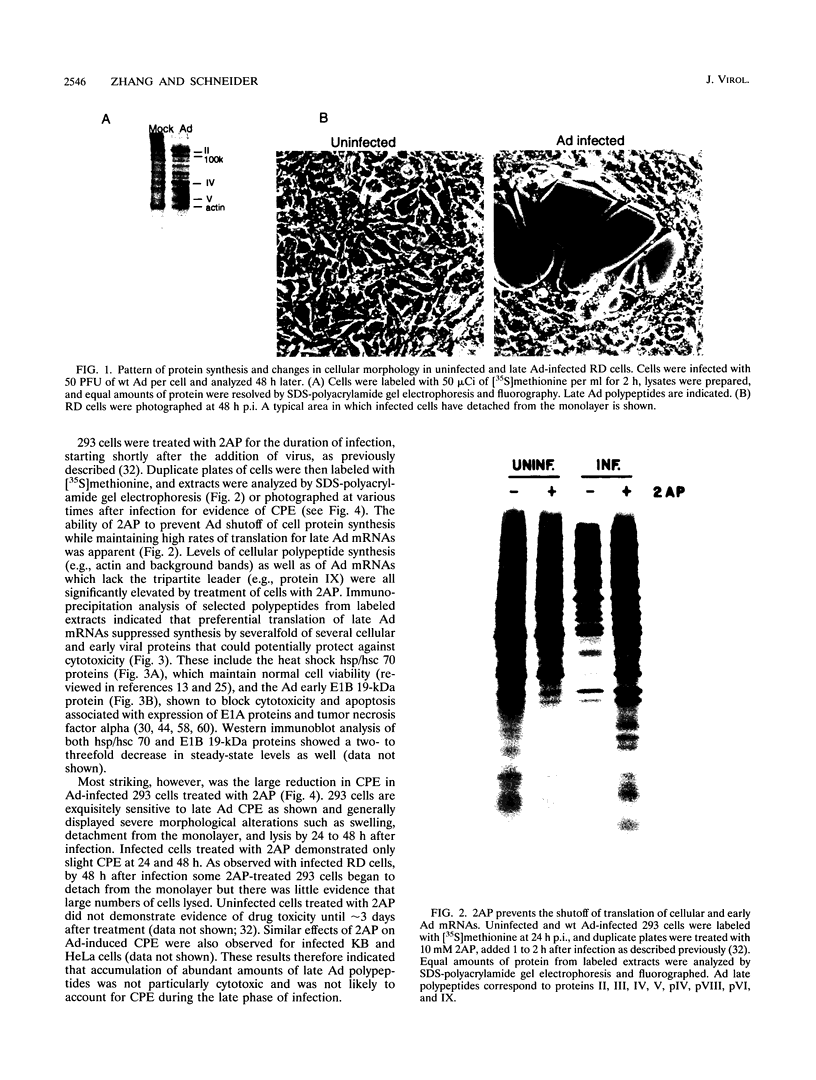
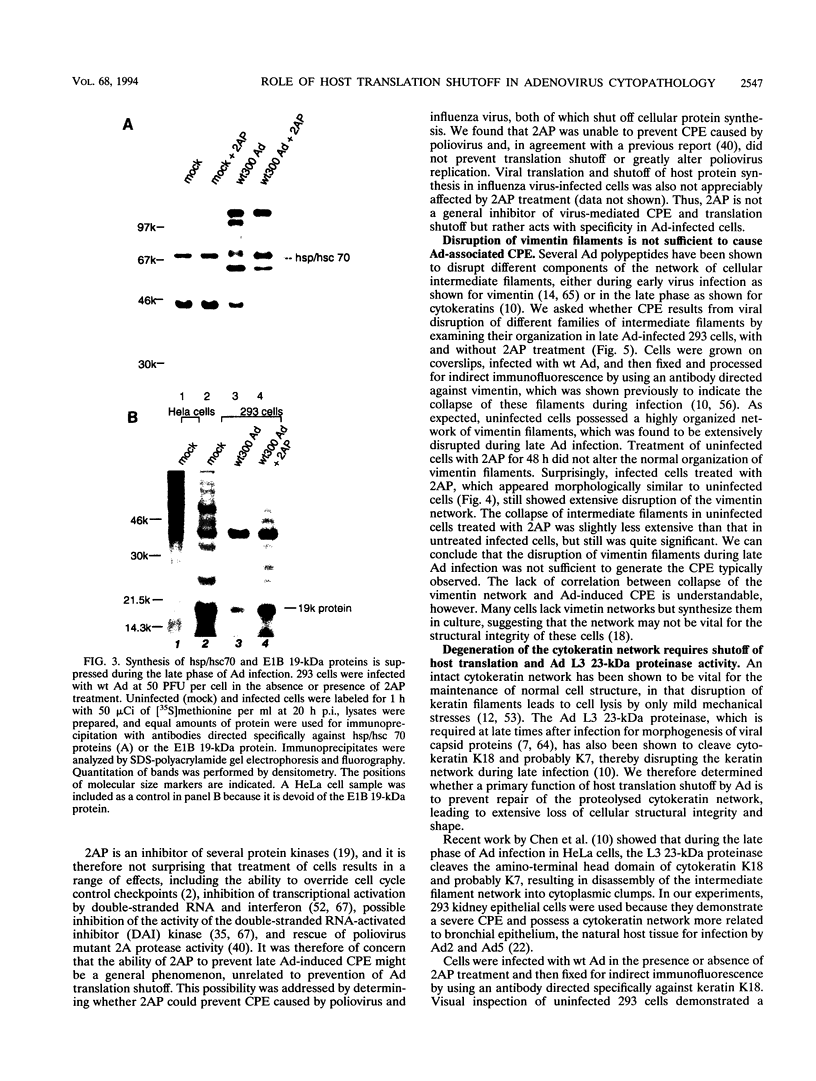
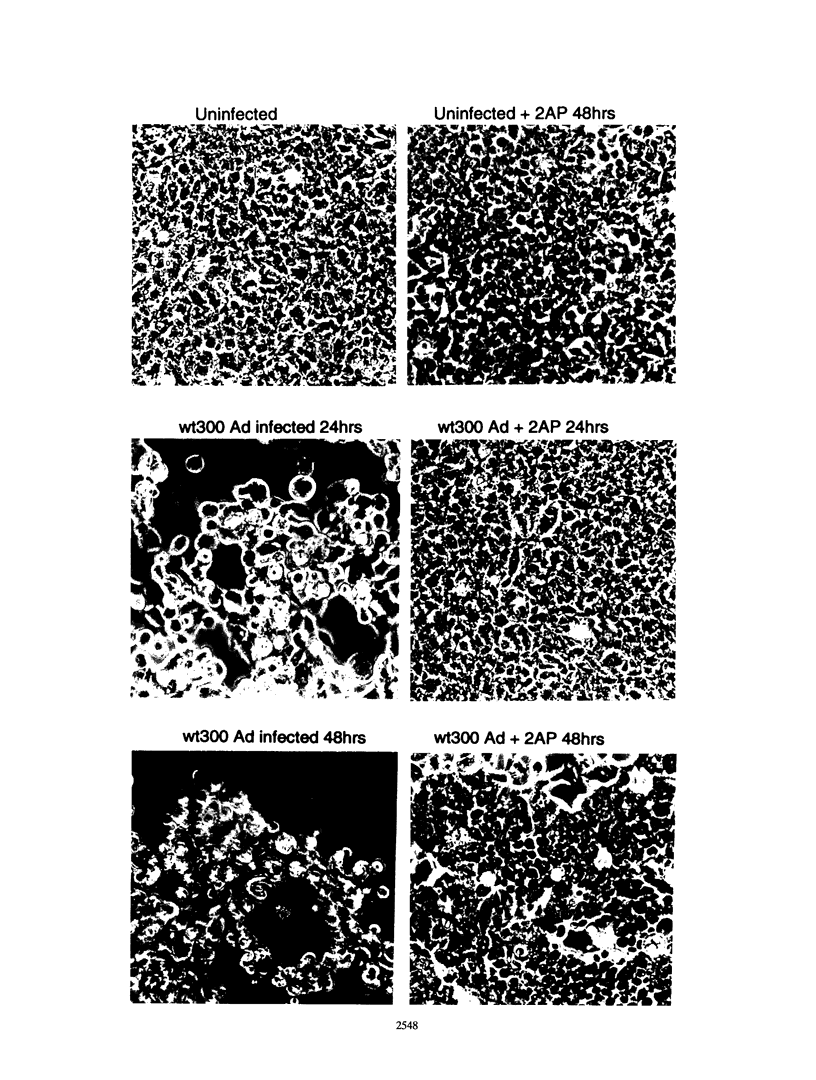
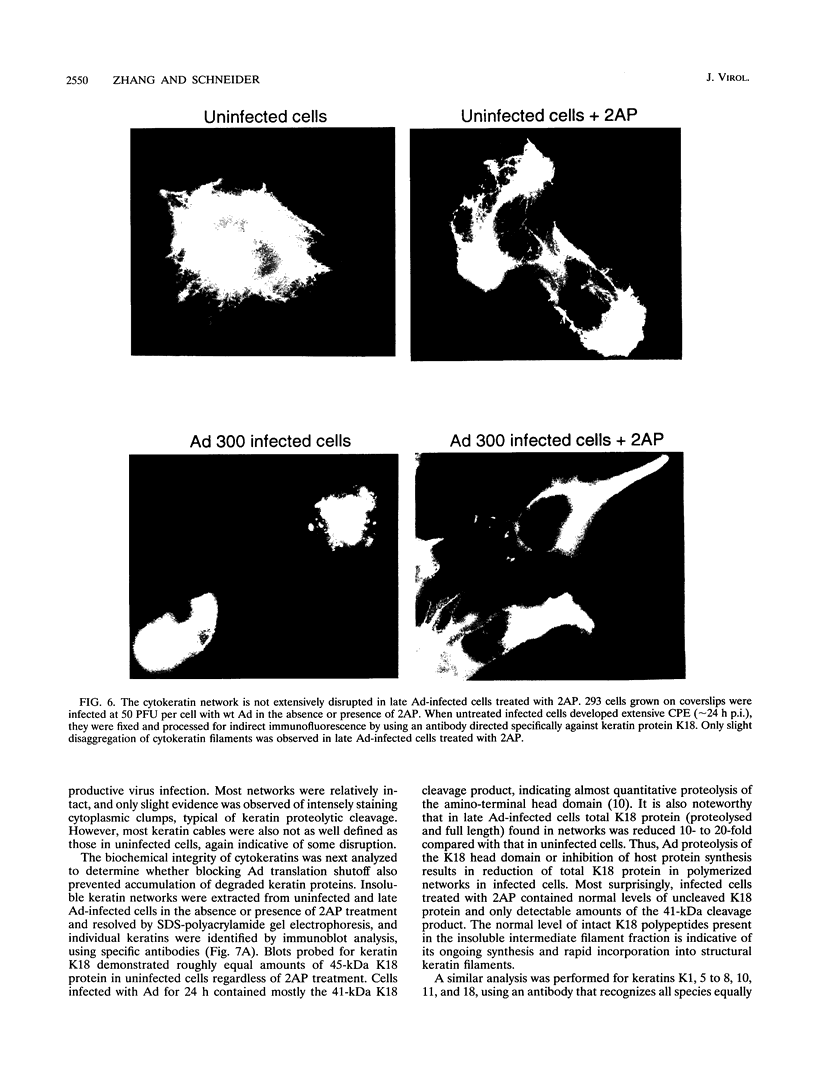
Infection of animal cells by a number of viruses generally results in an array of metabolic defects, including inhibition of host DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis, and morphological alterations known as cytopathic effects. For adenovirus infection there is a profound loss of cell structural integrity and a marked inhibition of host protein synthesis, the latter generally assumed necessary to enhance virus production. We examined the purpose of viral inhibition of cell translation and found that it was related in part to cytopathic wasting of infected cells. We show that viral shutoff of host translation promotes destruction of the intermediate filament network, particularly cytokeratins which are proteolysed at keratins K7 and K18 by the adenovirus late-acting L3 23-kDa proteinase. We found that if adenovirus is prevented from inhibiting cell translation, the intermediate filament network remains relatively intact, keratin proteins are still synthesized, and cells possess an almost normal morphological appearance and lyse poorly, reducing the release of nascent virus particles by several hundredfold. Remarkably, in tissue culture cells the accumulation of late viral structural proteins is only marginally reduced if host translation shutoff does not occur. Thus, a surprising major function for adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis is to enhance impairment of cellular structural integrity, facilitating cell lysis and release of progeny adenovirus particles.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers K., Fuchs E. Expression of mutant keratin cDNAs in epithelial cells reveals possible mechanisms for initiation and assembly of intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreassen P. R., Margolis R. L. 2-Aminopurine overrides multiple cell cycle checkpoints in BHK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2272–2276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aneskievich B. J., Taichman L. B. Epithelium-specific response of cultured keratinocytes to infection with adenovirus type 2. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Oct;91(4):309–314. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S. Adenovirus type 5 early region 1b gene product is required for efficient shutoff of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baribault H., Blouin R., Bourgon L., Marceau N. Epidermal growth factor-induced selective phosphorylation of cultured rat hepatocyte 55-kD cytokeratin before filament reorganization and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1665–1676. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin M. T., Boulanger P. Processing of vimentin occurs during the early stages of adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2559–2566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2559-2566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti A. R., Weber J. Protease of adenovirus type 2: partial characterization. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., Pieper F. R. Intermediate filaments: known structure, unknown function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 12;1007(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Small J. V., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J., De Mey J., Celis A. Intermediate filaments in monkey kidney TC7 cells: focal centers and interrelationship with other cytoskeletal systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. H., Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. The adenovirus L3 23-kilodalton proteinase cleaves the amino-terminal head domain from cytokeratin 18 and disrupts the cytokeratin network of HeLa cells. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3507–3514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3507-3514.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Wagner E., Zatloukal K., Phillips S., Curiel D. T., Birnstiel M. L. High-efficiency receptor-mediated delivery of small and large (48 kilobase gene constructs using the endosome-disruption activity of defective or chemically inactivated adenovirus particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6094–6098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Hutton M. E., Vassar R., Fuchs E. A function for keratins and a common thread among different types of epidermolysis bullosa simplex diseases. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1661–1674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gross C. A. Is hsp70 the cellular thermometer? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Lackinger E., Zatloukal K., Franke W. W. Turnover of cytokeratin polypeptides in mouse hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Nov;173(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Racaniello V., Villamarin A., Palladino F., Schneider R. J. The adenovirus tripartite leader may eliminate the requirement for cap-binding protein complex during translation initiation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2059–2066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2059-2066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eloit M., Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Toma B., Perricaudet M. Construction of a defective adenovirus vector expressing the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gp50 and its use as a live vaccine. J Gen Virol. 1990 Oct;71(Pt 10):2425–2431. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-10-2425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J. E., Opal P., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filament dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;4(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90065-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Brandt C. D., Wassermann F. E., Hall C. E., Spigland I., Kogon A., Elveback L. R. The virus watch program: a continuing surveillance of viral infections in metropolitan New York families. VI. Observations of adenovirus infections: virus excretion patterns, antibody response, efficiency of surveillance, patterns of infections, and relation to illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jan;89(1):25–50. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Mittnacht S., Grund C., Jorcano J. L. Integration of different keratins into the same filament system after microinjection of mRNA for epidermal keratins into kidney epithelial cells. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Prince G. A. Role of early genes in pathogenesis of adenovirus pneumonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Lundholm-Beauchamp U., Horswood R. L., Pernis B., Wold W. S., Chanock R. M., Prince G. A. Role of early region 3 (E3) in pathogenesis of adenovirus disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3823–3827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Aquino L., Duerksen-Hughes P. J., Day D., Horton T. M., Yei S. P., Wold W. S. The E1B 19,000-molecular-weight protein of group C adenoviruses prevents tumor necrosis factor cytolysis of human cells but not of mouse cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3083–3094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3083-3094.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis involves inactivation of cap-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90161-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis is prevented by the drug 2-aminopurine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7115–7119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P. Translational control mediated by eucaryotic initiation factor-2 is restricted to specific mRNAs in transfected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Goodman S. L., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Disruption of the keratin filament network during epithelial cell division. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. K., Vikstrom K., Goldman R. D. Keratin incorporation into intermediate filament networks is a rapid process. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):843–855. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacini D. L., Dubovi E. J., Clyde W. A., Jr A new animal model for human respiratory tract disease due to adenovirus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):92–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Moore M., Logan J., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B-55K transforming polypeptide modulates transport or cytoplasmic stabilization of viral and host cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Porter D. D., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Ginsberg H. S. Pathogenesis of adenovirus type 5 pneumonia in cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):101–111. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.101-111.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Debbas M., Sabbatini P., Hockenbery D., Korsmeyer S., White E. The adenovirus E1A proteins induce apoptosis, which is inhibited by the E1B 19-kDa and Bcl-2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROHL W. A., SCHLESINGER R. W. QUANTITATIVE STUDIES OF NATURAL AND EXPERIMENTAL ADENOVIRUS INFECTIONS OF HUMAN CELLS. II. PRIMARY CULTURES AND THE POSSIBLE ROLE OF ASYNCHRONOUS VIRAL MULTIPLICATION IN THE MAINTENANCE OF INFECTION. Virology. 1965 Jun;26:208–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Goldman R. D. Recent insights into the assembly, dynamics, and function of intermediate filament networks. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1991;19(2):67–79. doi: 10.1002/cm.970190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach R. E. Cap recap: the involvement of eIF-4F in regulating gene expression. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90461-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. A., Scheper G. C., Kleijn M., De Boer M., Voorma H. O. Dependence of the adenovirus tripartite leader on the p220 subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F during in vitro translation. Effect of p220 cleavage by foot-and-mouth-disease-virus L-protease on in vitro translation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Coulombe P. A., Degenstein L., Albers K., Fuchs E. Mutant keratin expression in transgenic mice causes marked abnormalities resembling a human genetic skin disease. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):365–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90645-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Blose S. H., Stillman B. W. Nuclear envelope localization of an adenovirus tumor antigen maintains the integrity of cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2865–2875. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):120–130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R., Sabbatini P., Denton A. Adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein overcomes the cytotoxicity of E1A proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2968–2978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2968-2978.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Specific disruption of intermediate filaments and the nuclear lamina by the 19-kDa product of the adenovirus E1B oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9886–9890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Grodzicker T., Stillman B. W. Mutations in the gene encoding the adenovirus early region 1B 19,000-molecular-weight tumor antigen cause the degradation of chromosomal DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):410–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.410-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Sabbatini P., Debbas M., Wold W. S., Kusher D. I., Gooding L. R. The 19-kilodalton adenovirus E1B transforming protein inhibits programmed cell death and prevents cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2570–2580. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Spector D., Welch W. Differential distribution of the adenovirus E1A proteins and colocalization of E1A with the 70-kilodalton cellular heat shock protein in infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4153–4166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4153-4166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano T., Tokui T., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Shibata M., Kikuchi K., Tsuiki S., Yamauchi T., Inagaki M. Phosphorylation of keratin intermediate filaments by protein kinase C, by calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):281–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh-Kai L., Akusjärvi G., Aleström P., Pettersson U., Tremblay M., Weber J. Genetic identification of an endoproteinase encoded by the adenovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Z. H., Wang X., Qian X. Y. Nuclear matrix-intermediate filament system and its alteration in adenovirus infected HeLa cell. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1988 Feb;12(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(88)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Dolph P. J., Schneider R. J. Secondary structure analysis of adenovirus tripartite leader. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10679–10684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]