Abstract
Retroviral Gag proteins are targeted to the plasma membrane, where they play the central role in virion formation. Several studies have suggested that the membrane-binding signal is contained within the amino-terminal matrix sequence; however, the precise location has never been determined for the Gag protein of any retrovirus. In this report, we show that the first 31 residues of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag protein can function independently as a membrane-targeting domain when fused to heterologous proteins. A bipartite membrane-targeting motif was identified, consisting of the myristylated N-terminal 14 amino acids and a highly basic region that binds acidic phospholipids. Replacement of the N-terminal membrane-targeting domain of pp60v-src with that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag elicits efficient membrane binding and a transforming phenotype. Removal of myristate or the basic region results in decreased membrane binding of Gag-Src chimeras in vitro and impaired virion formation by Pr55gag in vivo. We propose that the N-terminal Gag sequence functions as a targeting signal to direct interaction with acidic phospholipids on the cytoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF



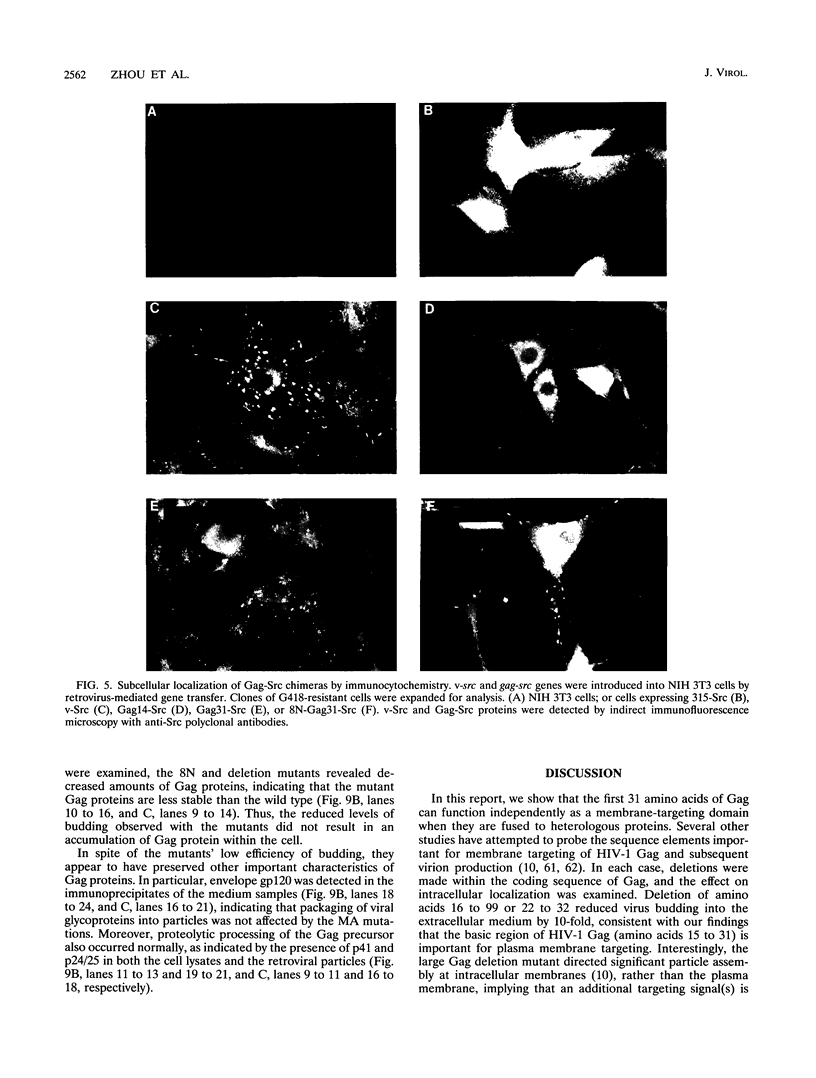
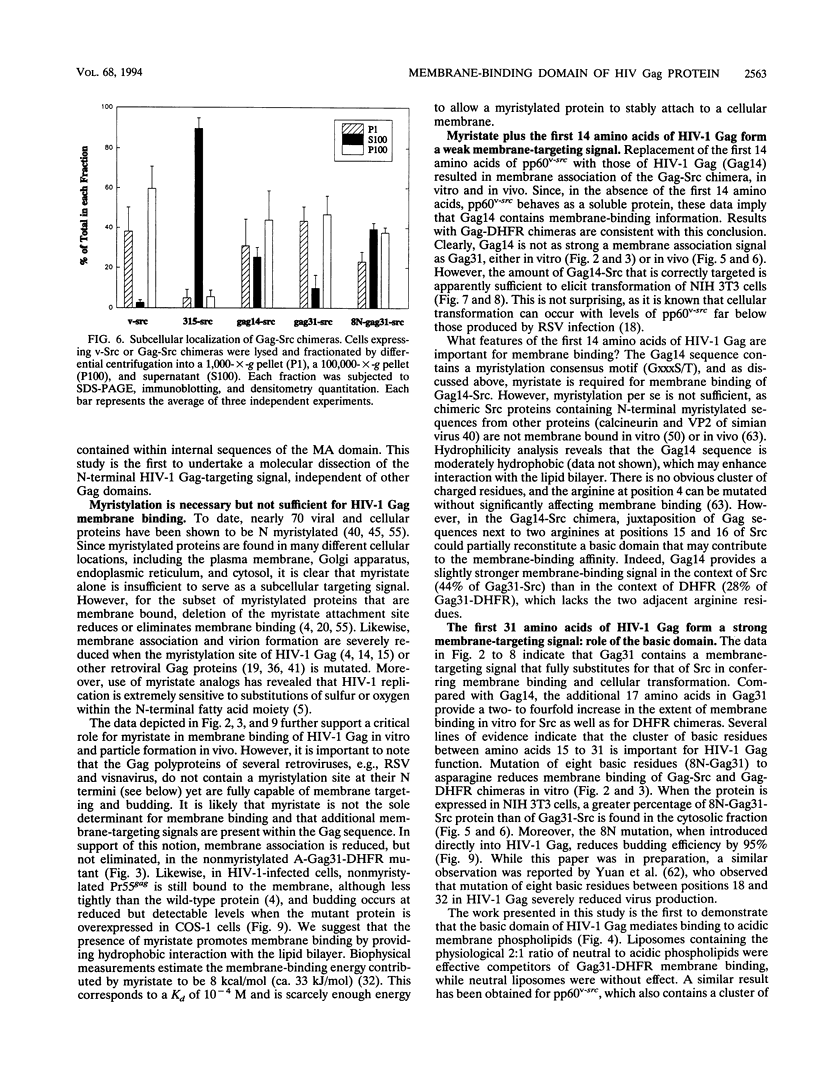

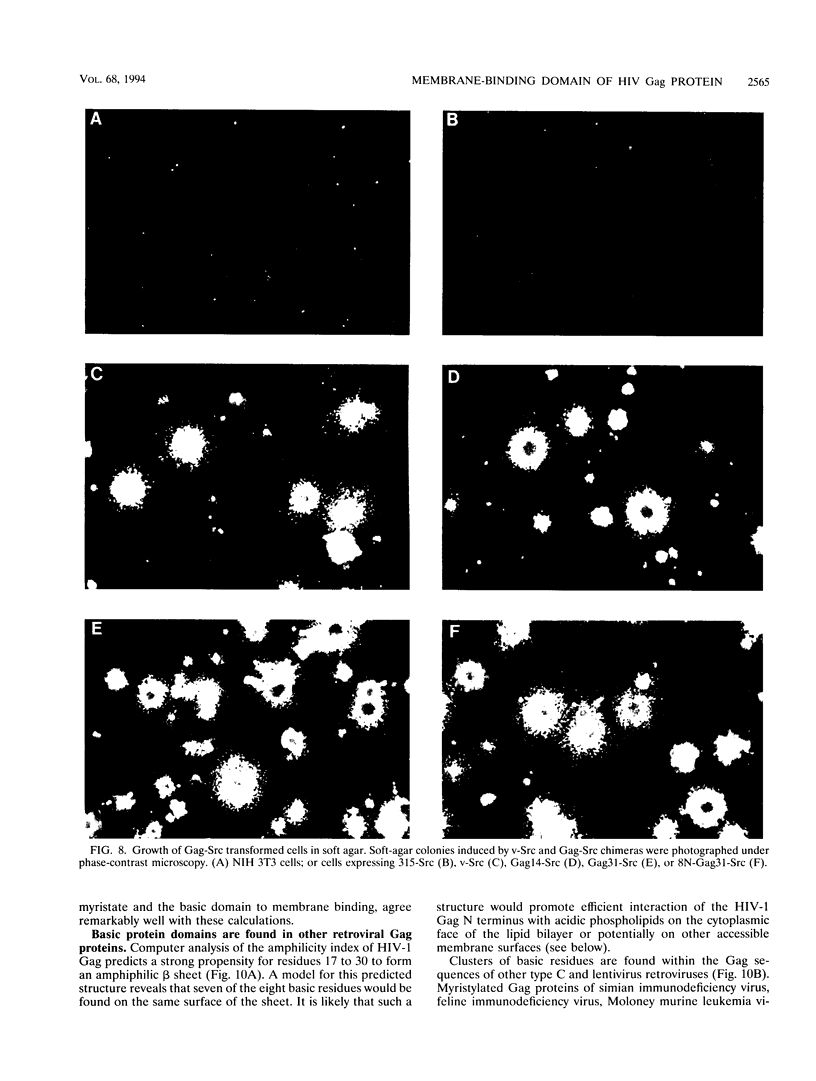

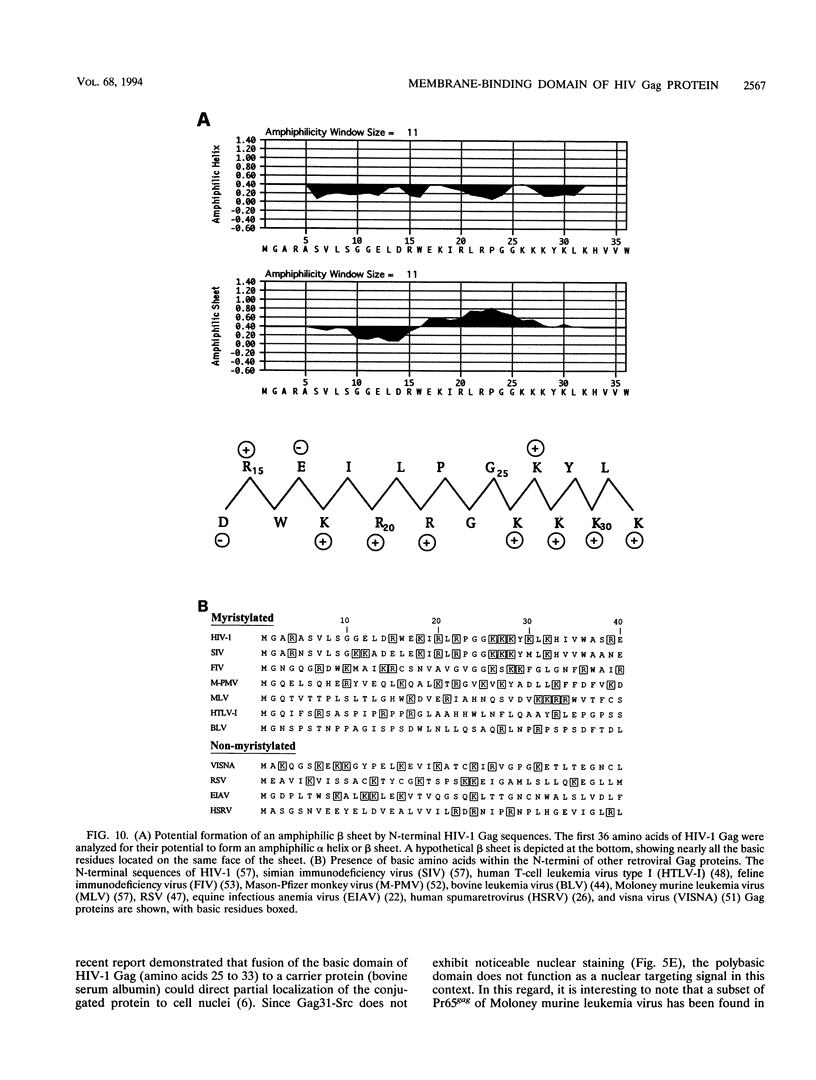


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenholz Y., Gibbes D., Litman B. J., Goll J., Thompson T. E., Carlson R. D. A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2806–2810. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. P., Nelle T. D., Wills J. W. Functional chimeras of the Rous sarcoma virus and human immunodeficiency virus gag proteins. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6487–6498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6487-6498.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. P., Rhee S., Craven R. C., Hunter E., Wills J. W. Amino acids encoded downstream of gag are not required by Rous sarcoma virus protease during gag-mediated assembly. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):272–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.272-280.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. L., Heuckeroth R. O., Kimata J. T., Ratner L., Gordon J. I. Replication of human immunodeficiency virus 1 and Moloney murine leukemia virus is inhibited by different heteroatom-containing analogs of myristic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8655–8659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M., Ratner L. Myristoylation-dependent replication and assembly of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):523–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S., Dempsey M. P., Sharova N., Adzhubel A., Spitz L., Lewis P., Goldfarb D., Emerman M., Stevenson M. A nuclear localization signal within HIV-1 matrix protein that governs infection of non-dividing cells. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):666–669. doi: 10.1038/365666a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deichaite I., Casson L. P., Ling H. P., Resh M. D. In vitro synthesis of pp60v-src: myristylation in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4295–4301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes D. J. Structure and function of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:495–527. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fäcke M., Janetzko A., Shoeman R. L., Kräusslich H. G. A large deletion in the matrix domain of the human immunodeficiency virus gag gene redirects virus particle assembly from the plasma membrane to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4972–4980. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4972-4980.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R. Assembly and morphology of HIV: potential effect of structure on viral function. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):617–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Jacobs E., de Foresta F., Thiriart C., Francotte M., Thines D., De Wilde M. Assembly and release of HIV-1 precursor Pr55gag virus-like particles from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90294-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Schatz G. The amino-terminal region of an imported mitochondrial precursor polypeptide can direct cytoplasmic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3149–3156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Majors J. E., Varmus H. E. Hormonal regulation of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene via a heterologous promoter defines a threshold dose for cellular transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen E. C., Kjeldgaard N. O., Pedersen F. S., Jørgensen P. A nucleotide substitution in the gag N terminus of the endogenous ecotropic DBA/2 virus prevents Pr65gag myristylation and virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3217-3223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The src protein contains multiple domains for specific attachment to membranes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1000–1009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Sherman L., Dahlberg J., Gazit A., Yaniv A., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis of equine infectious anemia virus proviral DNA. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mosior M., Chung L. A., Wu H., McLaughlin S. Binding of peptides with basic residues to membranes containing acidic phospholipids. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82037-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper A., MacKay B., Resh M. D. Rapid high resolution western blotting: from gel to image in a single day. Biotechniques. 1992 May;12(5):650–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna E. J., Hitt A. L. Cytoskeleton--plasma membrane interactions. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):955–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1439807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mervis R. J., Ahmad N., Lillehoj E. P., Raum M. G., Salazar F. H., Chan H. W., Venkatesan S. The gag gene products of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: alignment within the gag open reading frame, identification of posttranslational modifications, and evidence for alternative gag precursors. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3993–4002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3993-4002.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosior M., McLaughlin S. Peptides that mimic the pseudosubstrate region of protein kinase C bind to acidic lipids in membranes. Biophys J. 1991 Jul;60(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82038-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M. A., Meyer M. K., Decker G. L., Arlinghaus R. B. A subset of Pr65gag is nucleus associated in murine leukemia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1350–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1350-1356.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J., Morrow C. D. The nonmyristylated Pr160gag-pol polyprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 interacts with Pr55gag and is incorporated into viruslike particles. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6304–6313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6304-6313.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitzsch R. M., McLaughlin S. Binding of acylated peptides and fatty acids to phospholipid vesicles: pertinence to myristoylated proteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 5;32(39):10436–10443. doi: 10.1021/bi00090a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Horowitz B., Baker L., Shulman R. W., Ralph H., Valinsky J., Cundell A., Brotman B., Boehle W., Rey F. Failure of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immune globulin to protect chimpanzees against experimental challenge with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M., Peterson A., McLaughlin S. Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1 binds with high affinity to phospholipid vesicles containing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 29;31(51):12742–12747. doi: 10.1021/bi00166a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Erikson R. L. Highly specific antibody to Rous sarcoma virus src gene product recognizes a novel population of pp60v-src and pp60c-src molecules. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):409–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Interaction of tyrosine kinase oncoproteins with cellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 23;1155(3):307–322. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Membrane interactions of pp60v-src: a model for myristylated tyrosine protein kinases. Oncogene. 1990 Oct;5(10):1437–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Specific and saturable binding of pp60v-src to plasma membranes: evidence for a myristyl-src receptor. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. A single amino acid substitution within the matrix protein of a type D retrovirus converts its morphogenesis to that of a type C retrovirus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90289-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Yasunaga T., Tsuzuku-Kawamura J., Ohishi K., Ogawa Y., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of bovine leukemia virus: its evolutionary relationship to other retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):677–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Fatty acylation of proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:611–647. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman L., Resh M. D. Lysine residues form an integral component of a novel NH2-terminal membrane targeting motif for myristylated pp60v-src. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):415–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Alizon M., Staskus K., Klatzmann D., Cole S., Danos O., Retzel E., Tiollais P., Haase A., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of the visna lentivirus: relationship to the AIDS virus. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Barker C., Hunter E., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: an immunosuppressive D-type retrovirus. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbott R. L., Sparger E. E., Lovelace K. M., Fitch W. M., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A., Elder J. H. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of feline immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5743–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi H., Manenti S. Interaction of myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) with membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):9960–9963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Achacoso J. A. Creation and expression of myristylated forms of Rous sarcoma virus gag protein in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4331–4343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4331-4343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C. Form, function, and use of retroviral gag proteins. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):639–654. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199106000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Weldon R. A., Jr, Nelle T. D., Erdie C. R. Suppression of retroviral MA deletions by the amino-terminal membrane-binding domain of p60src. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3804–3812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3804-3812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Lee T. H., Essex M. The matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is required for incorporation of viral envelope protein into mature virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4966-4971.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan X., Yu X., Lee T. H., Essex M. Mutations in the N-terminal region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 matrix protein block intracellular transport of the Gag precursor. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6387–6394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6387-6394.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]