Abstract
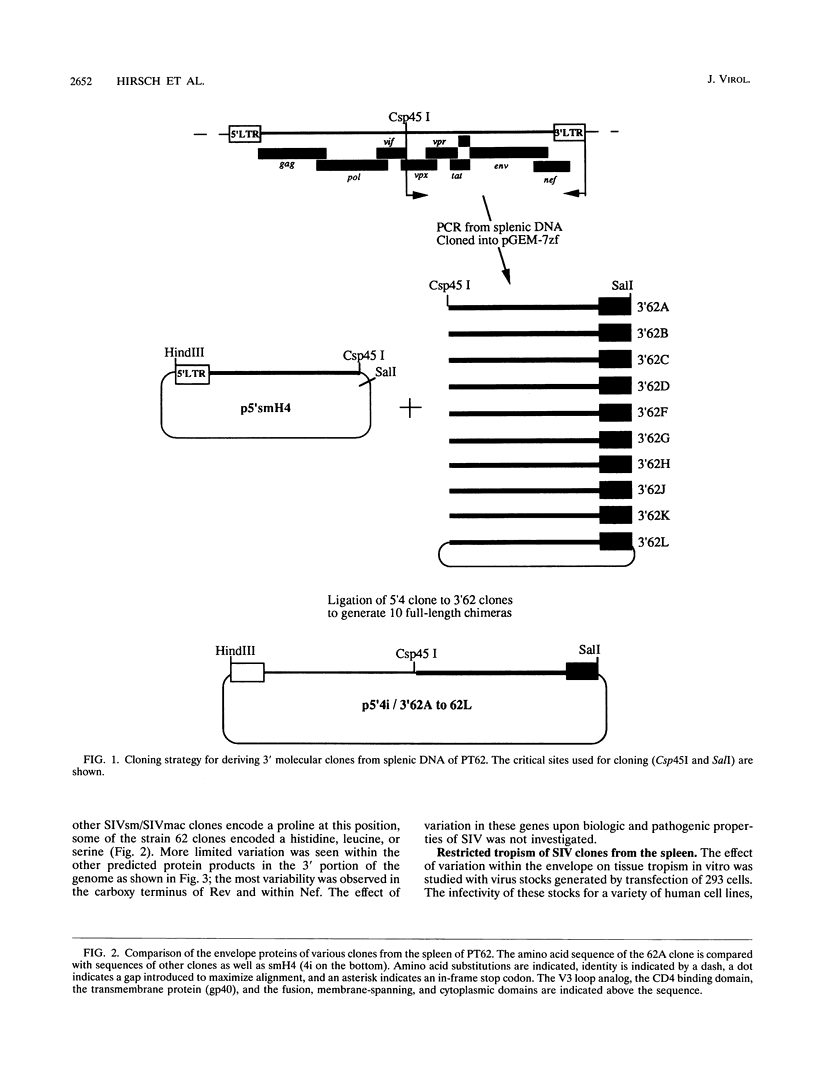
Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) exists within tissues of infected macaques as a mixture of diverse genotypes. The goal of this study was to investigate the biologic significance of this variation in terms of cellular tropism and pathogenicity. PCR was used to amplify and clone 3'-half genomes from the spleen of an immunodeficiency SIV-infected pig-tailed macaque (Macaca nemestrina). Eight infectious clones were generated by ligation of respective 3' clones into a related SIVsm 5' clone, and virus stocks were generated by transient transfection. Four of these viruses were infectious for macaque peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM). Three viruses with distinct tropism for macaque PBMC or MDM were tested for in vivo infectivity and pathogenicity. The ability of these three viruses to infect PBMC and macrophages correlated with differences in infectivity and pathogenicity. Thus, a virus that was infectious for both PBMC and MDM was highly infectious for macaques and induced AIDS in half of the inoculated animals. In contrast, virus that was less infectious for PBMC and not infectious for MDM induced only transient viremia. Finally, a virus that was not infectious for either primary cell type did not infect macaques. Chimeric clones exchanging portions of the envelope gene of the 62A and smH4 molecular clones and a series of point mutants were used to map the determinant of tropism to a 60-amino-acid region of gp120 encompassing the V3 analog of SIV. Naturally occurring mutations within this region were critical for determining tropism and, as a result, pathogenicity of these SIVsm clones.
Full text
PDF





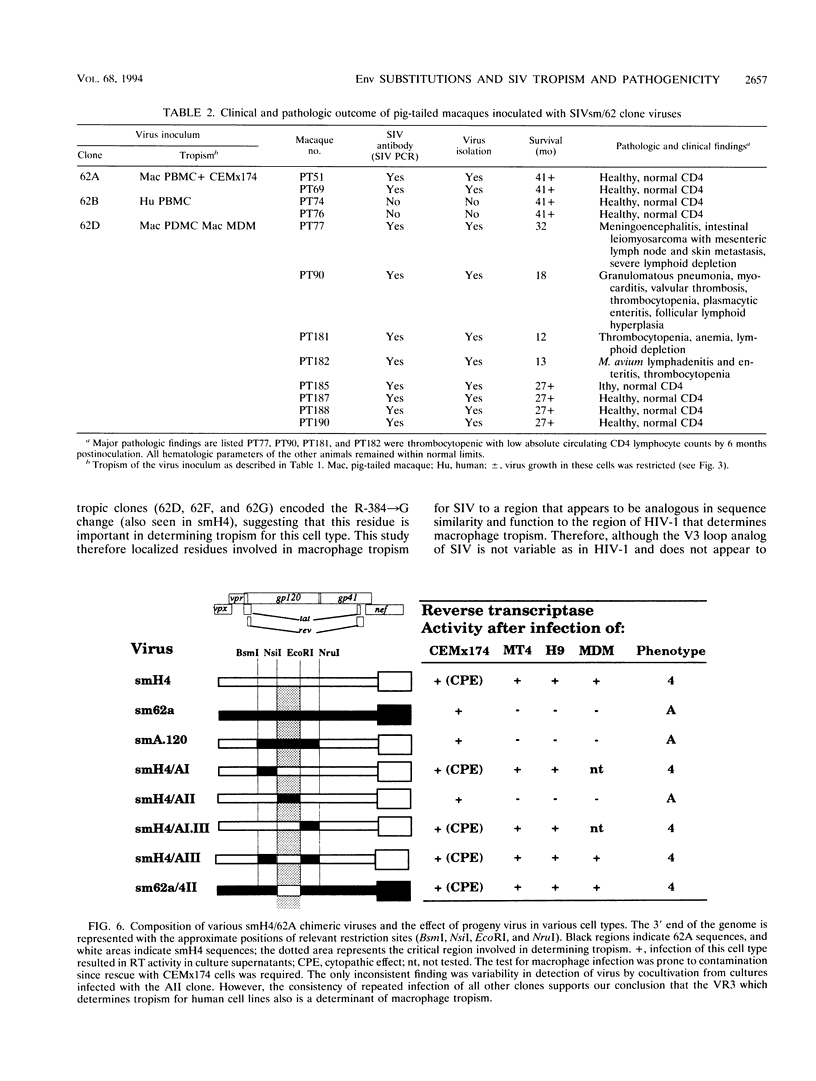



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond N., Jenkins A., Heath A. B., Kitchin P. Sequence variation in the env gene of simian immunodeficiency virus recovered from immunized macaques is predominantly in the V1 region. J Gen Virol. 1993 May;74(Pt 5):865–871. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-5-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almond N., Jenkins A., Heath A. B., Taffs L. F., Kitchin P. The genetic evolution of the envelope gene of simian immunodeficiency virus in cynomolgus macaques infected with a complex virus pool. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):996–1002. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. G., Hauer D., Sharma D. P., Joag S. V., Narayan O., Zink M. C., Clements J. E. Analysis of envelope changes acquired by SIVmac239 during neuroadaption in rhesus macaques. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):616–626. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banapour B., Marthas M. L., Ramos R. A., Lohman B. L., Unger R. E., Gardner M. B., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A. Identification of viral determinants of macrophage tropism for simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5798–5805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5798-5805.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeri E., Giri A., Lillo F., Ferrari G., Varnier O. E., Ferro A., Sabbatani S., Saxinger W. C., Franchini G. In vivo genetic variability of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 V3 region. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4546–4550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4546-4550.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. P., Desrosiers R. C. Selection of genetic variants of simian immunodeficiency virus in persistently infected rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1843–1854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1843-1854.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Quiroga M., Tung J. W., Dina D., Levy J. A. Viral determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 T-cell or macrophage tropism, cytopathogenicity, and CD4 antigen modulation. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4390–4398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4390-4398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Buller R., Portis J., Wehrly K. Failure of human immunodeficiency virus entry and infection in CD4-positive human brain and skin cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):215–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.215-221.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Blanc D., Weiss R. A. Specific cell surface requirements for the infection of CD4-positive cells by human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 and by Simian immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90904-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor R. I., Mohri H., Cao Y., Ho D. D. Increased viral burden and cytopathicity correlate temporally with CD4+ T-lymphocyte decline and clinical progression in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1772–1777. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1772-1777.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Hansen-Moosa A., Mori K., Bouvier D. P., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Ringler D. J. Macrophage-tropic variants of SIV are associated with specific AIDS-related lesions but are not essential for the development of AIDS. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. G., Kuiken C., Blumberg B. M., Hartman S., Sharer L. R., Clement M., Goudsmit J. HIV-1 V3 domain variation in brain and spleen of children with AIDS: tissue-specific evolution within host-determined quasispecies. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90072-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow M., Huet T., Saurin W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Wain-Hobson S. HIV-1 isolates are rapidly evolving quasispecies: evidence for viral mixtures and preferred nucleotide substitutions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaila R. J., Fuller B. A., Rennert P. D., Nelson M. B., Hammarskjöld M. L., Potts B., Murray M., Putney S. D., Gray G. Mutations in the principal neutralization determinant of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affect syncytium formation, virus infectivity, growth kinetics, and neutralization. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1875–1883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1875-1883.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori N., Michaels F., Fargnoli K., Marcon L., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. The human immunodeficiency virus type 2 vpr gene is essential for productive infection of human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8080–8084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Olmsted R. A., Murphey-Corb M., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. An African primate lentivirus (SIVsm) closely related to HIV-2. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):389–392. doi: 10.1038/339389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V. M., Zack P. M., Vogel A. P., Johnson P. R. Simian immunodeficiency virus infection of macaques: end-stage disease is characterized by widespread distribution of proviral DNA in tissues. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):976–988. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., Schmidt S., Kaufmann M., Cates N., Langedijk J. P., Meloen R. H., Desrosiers R. C., Burns D. P., Bolognesi D. P. The principal neutralization determinant of simian immunodeficiency virus differs from that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Hamm T. E., Goldstein S., Kitov S., Hirsch V. M. The genetic fate of molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus in experimentally infected macaques. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Mori K., Kawahara T., Ringler D. J., Desrosiers R. C. Analysis of simian immunodeficiency virus sequence variation in tissues of rhesus macaques with simian AIDS. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6522–6534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6522-6534.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Hirsch V. M., Olmsted R. A., Powell D., Maury W., Rabson A., Fauci A. S., Purcell R. H., Johnson P. R. Selective infection of human CD4+ cells by simian immunodeficiency virus: productive infection associated with envelope glycoprotein-induced fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W. Immunologic and pathologic manifestations of the infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(11):1023–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Hui H., Burgess C. J., Price R. W., Sharp P. M., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence, genome organization, and biological properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vivo: evidence for limited defectiveness and complementation. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6587–6600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6587-6600.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Cheynier R., Albert J., Seth M., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Temporal fluctuations in HIV quasispecies in vivo are not reflected by sequential HIV isolations. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Ringler D. J., Desrosiers R. C. Restricted replication of simian immunodeficiency virus strain 239 in macrophages is determined by env but is not due to restricted entry. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2807–2814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2807-2814.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Ringler D. J., Kodama T., Desrosiers R. C. Complex determinants of macrophage tropism in env of simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2067–2075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2067-2075.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison H. G., Kirchhoff F., Desrosiers R. C. Evidence for the cooperation of gp120 amino acids 322 and 448 in SIVmac entry. Virology. 1993 Jul;195(1):167–174. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Gulizia R. J., MacIsaac P. D., Torbett B. E., Levy J. A. Rapid loss of CD4+ T cells in human-PBL-SCID mice by noncytopathic HIV isolates. Science. 1993 Apr 30;260(5108):689–692. doi: 10.1126/science.8097595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novembre F. J., Hirsch V. M., McClure H. M., Johnson P. R. Molecular diversity of SIVsmm/PBj and a cognate variant, SIVsmm/PGg. J Med Primatol. 1991 Jun;20(4):188–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak M. A., May R. M., Anderson R. M. The evolutionary dynamics of HIV-1 quasispecies and the development of immunodeficiency disease. AIDS. 1990 Nov;4(11):1095–1103. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199011000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbaugh J., Rudensey L. M. Alterations in potential sites for glycosylation predominate during evolution of the simian immunodeficiency virus envelope gene in macaques. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5937–5948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5937-5948.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbaugh J., Rudensey L. M., Papenhausen M. D., Benveniste R. E., Morton W. R. Variation in simian immunodeficiency virus env is confined to V1 and V4 during progression to simian AIDS. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):7025–7031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.7025-7031.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang S., Vinters H. V., Akashi T., O'Brien W. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 env sequence variation in brain tissue of patients with AIDS-related neurologic disease. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(11):1082–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Matthews T. J., Robey W. G., Lynn D. L., Robert-Guroff M., Mueller W. T., Langlois A. J., Ghrayeb J., Petteway S. R., Jr, Weinhold K. J. HTLV-III/LAV-neutralizing antibodies to an E. coli-produced fragment of the virus envelope. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1392–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2431482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Hahn B. H., Gibbons J., Li Y., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Shaw G. M. Extensive variation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in vivo. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):440–444. doi: 10.1038/334440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpless N. E., O'Brien W. A., Verdin E., Kufta C. V., Chen I. S., Dubois-Dalcq M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tropism for brain microglial cells is determined by a region of the env glycoprotein that also controls macrophage tropism. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2588–2593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2588-2593.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Macrophage and T cell-line tropisms of HIV-1 are determined by specific regions of the envelope gp120 gene. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):167–169. doi: 10.1038/349167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Small amino acid changes in the V3 hypervariable region of gp120 can affect the T-cell-line and macrophage tropism of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9434–9438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Trowbridge D. B., Epstein L. G., Blumberg B. M., Li Y., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Price R. W., Ratner L. Macrophage tropism determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2577–2582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2577-2582.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Rutledge R. A., Dias S., Folks T., Theodore T., Buckler C. E., Martin M. A. Identification of conserved and divergent domains within the envelope gene of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]