Abstract
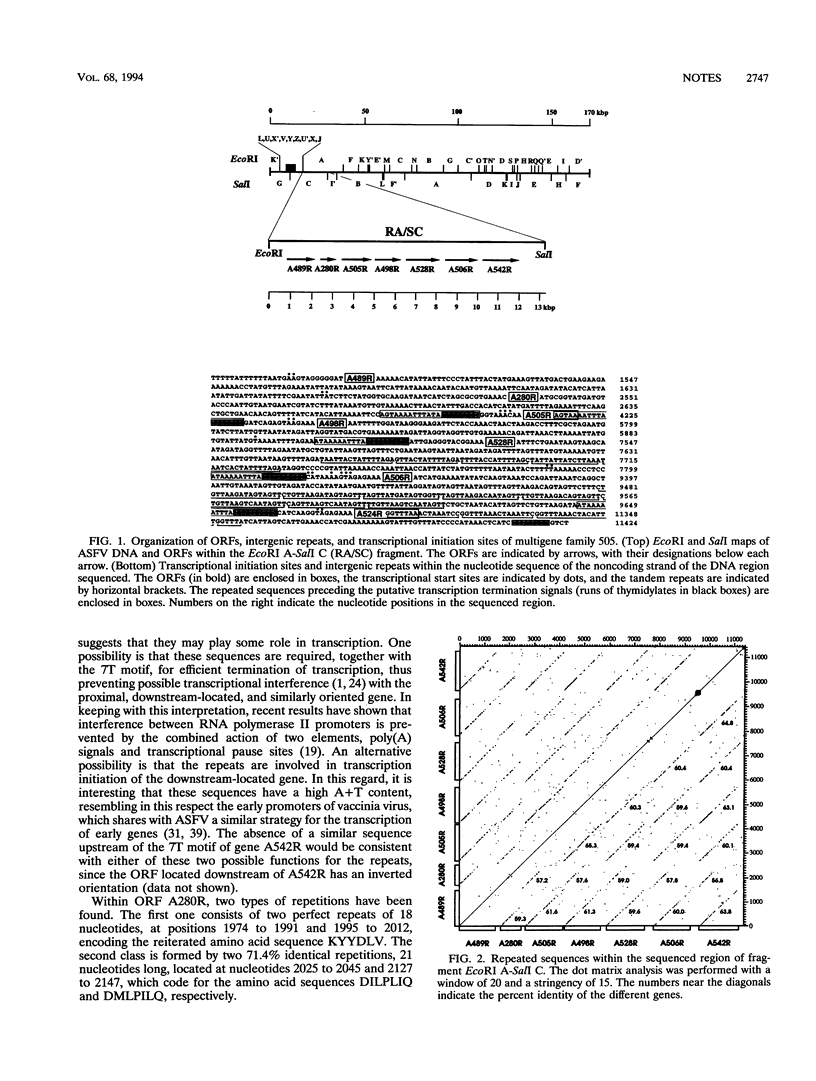
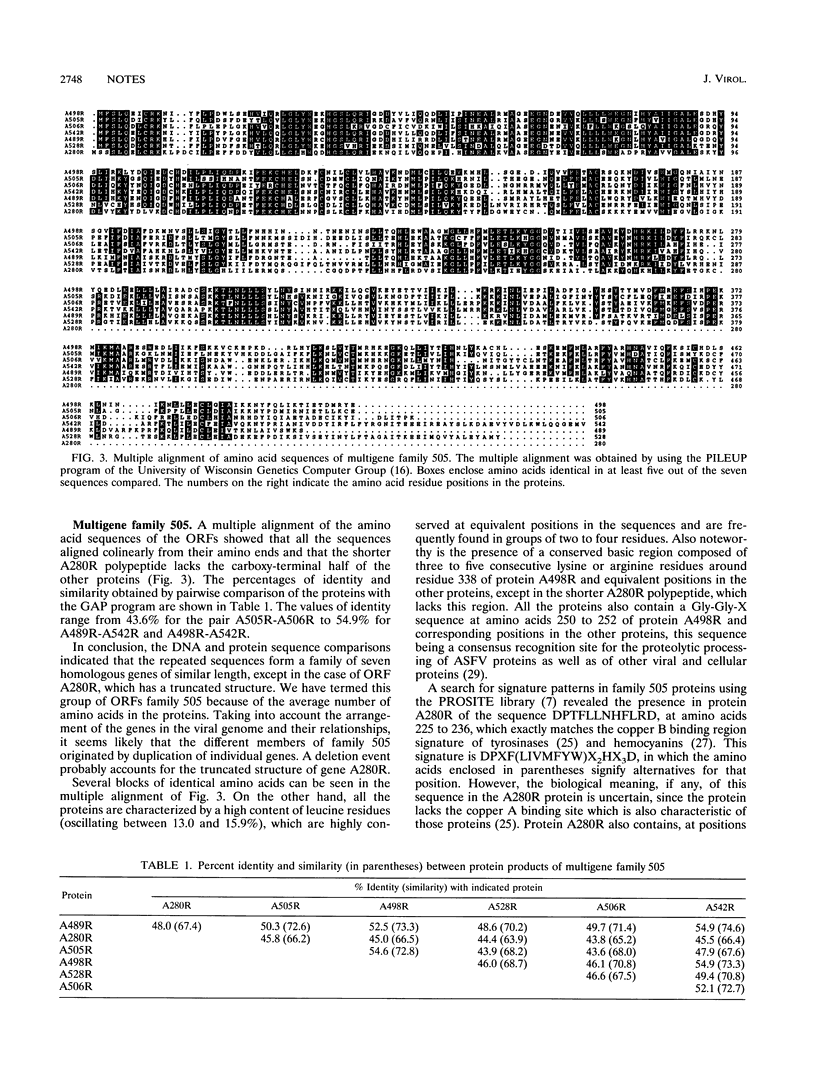
Sequencing of restriction fragment EcoRI A-SalI C of African swine fever virus has revealed the existence of a multigene family, designated family 505 because of the average number of amino acids in the proteins, composed of seven homologous and tandemly arranged genes. All the genes of family 505 are expressed during infection. Primer extension analysis showed that transcription is initiated a short distance (3 to 62 nucleotides) from the start codon of the corresponding open reading frame. The proteins of family 505 showed similarity to those of family 360 from African swine fever virus. In particular, a striking conservation of three regions at the amino terminus of the polypeptides was observed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agüero M., Blasco R., Wilkinson P., Viñuela E. Analysis of naturally occurring deletion variants of African swine fever virus: multigene family 110 is not essential for infectivity or virulence in pigs. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90244-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almazán F., Rodríguez J. M., Andrés G., Pérez R., Viñuela E., Rodriguez J. F. Transcriptional analysis of multigene family 110 of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6655–6667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6655-6667.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almazán F., Rodríguez J. M., Angulo A., Viñuela E., Rodriguez J. F. Transcriptional mapping of a late gene coding for the p12 attachment protein of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):553–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.553-556.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almendral J. M., Almazán F., Blasco R., Viñuela E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: family 110. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2064–2072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2064-2072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angulo A., Viñuela E., Alcamí A. Comparison of the sequence of the gene encoding African swine fever virus attachment protein p12 from field virus isolates and viruses passaged in tissue culture. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3869–3872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3869-3872.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A. PROSITE: a dictionary of sites and patterns in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19 (Suppl):2241–2245. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.suppl.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., Agüero M., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Variable and constant regions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., de la Vega I., Almazán F., Agüero M., Viñuela E. Genetic variation of African swine fever virus: variable regions near the ends of the viral DNA. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R., Wild F. Leucine zipper motif extends. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):547–547. doi: 10.1038/338547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Bristow C., Wilkinson P. J., Sumption K. J. Identification of a variable region of the African swine fever virus genome that has undergone separate DNA rearrangements leading to expansion of minisatellite-like sequences. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):677–688. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90391-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon L. K., Wilkinson P. J. Genetic diversity of African swine fever virus isolates from soft ticks (Ornithodoros moubata) inhabiting warthog burrows in Zambia. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2981–2993. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggermont J., Proudfoot N. J. Poly(A) signals and transcriptional pause sites combine to prevent interference between RNA polymerase II promoters. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2539–2548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05909.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Barreno B., Sanz A., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies of African swine fever virus: antigenic differences among field virus isolates and viruses passaged in cell culture. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.385-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Beato R., Freije J. M., López-Otín C., Blasco R., Viñuela E., Salas M. L. A gene homologous to topoisomerase II in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):938–947. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Calvo V., Almazán F., Almendral J. M., Ramírez J. C., de la Vega I., Blasco R., Viñuela E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: family 360. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2073–2081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2073-2081.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Talavera A., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Hairpin loop structure of African swine fever virus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6835–6844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausler B., Somerville R. L. Interaction in vivo between strong closely spaced constitutive promoters. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackman M. P., Hajnal A., Lerch K. Albino mutants of Streptomyces glaucescens tyrosinase. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):707–713. doi: 10.1042/bj2740707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang W. H., van Holde K. E. Cloning and sequencing of Octopus dofleini hemocyanin cDNA: derived sequences of functional units Ode and Odf. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):244–248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leucine-zipper motif update. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):103–104. doi: 10.1038/340103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leucine-zipper motif update. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):103–104. doi: 10.1038/340103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Almendral J. M., Carbonero P., Beloso A., Viñuela E., Talavera A. Molecular cloning of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Otín C., Simón-Mateo C., Martínez L., Viñuela E. Gly-Gly-X, a novel consensus sequence for the proteolytic processing of viral and cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9107–9110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Regulation of vaccinia virus transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:661–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. M., Salas M. L., Viñuela E. Genes homologous to ubiquitin-conjugating proteins and eukaryotic transcription factor SII in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):40–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Almendral J. M., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Terminal and internal inverted repetitions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumption K. J., Hutchings G. H., Wilkinson P. J., Dixon L. K. Variable regions on the genome of Malawi isolates of African swine fever virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Oct;71(Pt 10):2331–2340. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-10-2331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yáez R. J., Boursnell M., Nogal M. L., Yuste L., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus encodes two genes which share significant homology with the two largest subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2423–2427. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yáez R. J., Rodríguez J. M., Rodríguez J. F., Salas M. L., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus thymidylate kinase gene: sequence and transcriptional mapping. J Gen Virol. 1993 Aug;74(Pt 8):1633–1638. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-8-1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega I., Viñuela E., Blasco R. Genetic variation and multigene families in African swine fever virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90293-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




