Abstract
We have devised an enrichment scheme for the isolation of export-competent derivatives of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII signal peptide mutants. Enrichment is based upon a growth advantage imparted upon gIII-containing virions compared with virions lacking the glycoprotein. Each of identified derivatives suppressed the gIII signal peptide defect by fusing the gIII gene in frame to the prv43 gene that lay immediately upstream; the result was the synthesis of a Prv43-gIII hybrid protein. The deduced Prv43 protein is predicted to span a membrane multiple times, and it appeared that the gIII portion of each hybrid used a hydrophobic domain of Prv43 protein to initiate its export. For at least two of the isolates, the hybrid protein was efficiently translocated across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane but appeared to be poorly exported out of the endoplasmic reticulum. Nonetheless, the prv43-gIII fusions encoded a gIII species that was localized to the virus envelope. Because the gIII portion of each hybrid protein must be exposed on the virion surface to provide a growth advantage, our results also suggest a preliminary membrane topology for wild-type Prv43 protein.
Full text
PDF

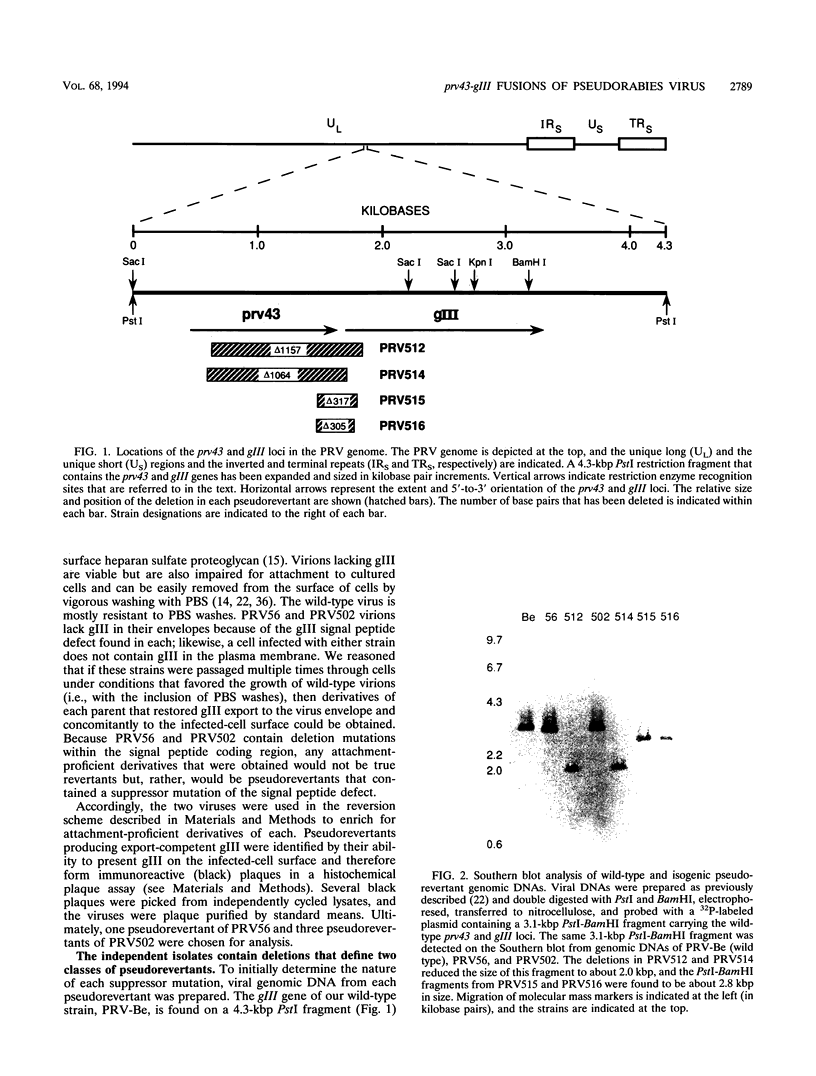

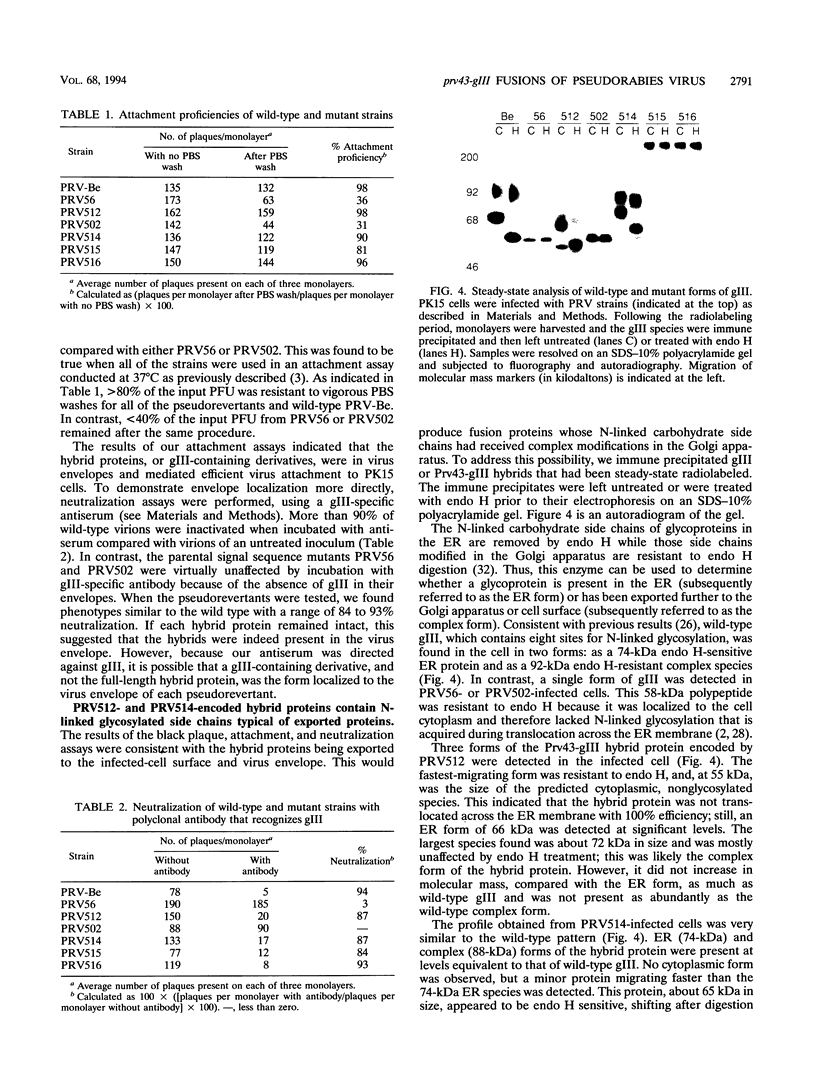



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos T. J., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. NH2-terminal hydrophobic region of influenza virus neuraminidase provides the signal function in translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2327–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Keeler C. L., Jr, Robbins A. K., Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E. An amino-terminal deletion mutation of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII affects protein localization and RNA accumulation. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3565–3573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3565-3573.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn S. J., Burgett B. L., Stein D. S., Wilkinson K. S., Ryan P. The amino-terminal one-third of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII contains a functional attachment domain, but this domain is not required for the efficient penetration of Vero cells. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2646–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2646-2654.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampl H., Ben-Porat T., Ehrlicher L., Habermehl K. O., Kaplan A. S. Characterization of the envelope proteins of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):583–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.583-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Antigenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.672-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Holland L. E., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Physical mapping of the mutation in an antigenic variant of herpes simplex virus type 1 by use of an immunoreactive plaque assay. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.649-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Topography of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:999–1027. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. A., Efstathiou S., Elliott M. L., Jamieson F. E., McGeoch D. J. Investigation of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes encoding multiply inserted membrane proteins. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C. Analysis of membrane protein topology using alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase gene fusions. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;34:61–75. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61676-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Glycoprotein gIII deletion mutants of pseudorabies virus are impaired in virus entry. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):623–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90635-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Kern H., Ben-Porat T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.278-286.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., von Heijne G. Fine-tuning the topology of a polytopic membrane protein: role of positively and negatively charged amino acids. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90390-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers L., Wilkinson K. S., Ryan P. Characterization of the prv43 gene of pseudorabies virus and demonstration that it is not required for virus growth in cell culture. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):81–88. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy R., Holland T. C. In vitro characterization of the HSV-1 UL53 gene product. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90024-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Enquist L. W. The gene encoding the gIII envelope protein of pseudorabies virus vaccine strain Bartha contains a mutation affecting protein localization. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):250–258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.250-258.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Watson R. J., Whealy M. E., Hays W. W., Enquist L. W. Characterization of a pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gene with homology to herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):339–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.339-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Watson R. J., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus gene encoding glycoprotein gIII is not essential for growth in tissue culture. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):635–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.635-645.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Duncan M. C., Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Intragenic reversion mutations that improve export of maltose-binding protein in Escherichia coli malE signal sequence mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P., Robbins A., Whealy M., Enquist L. W. Overall signal sequence hydrophobicity determines the in vivo translocation efficiency of a herpesvirus glycoprotein. Virus Genes. 1993 Feb;7(1):5–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01702345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Maher P. A., Yaffe M. P. On the transfer of integral proteins into membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1960–1964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon K. A., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Mutations in the C-terminal hydrophobic domain of pseudorabies virus gIII affect both membrane anchoring and protein export. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5952–5960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5952-5960.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsak L., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T., Robbins A. K., Whealy M. E., Enquist L. W. The gIII glycoprotein of pseudorabies virus is involved in two distinct steps of virus attachment. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4317–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4317-4324.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Membrane protein structure prediction. Hydrophobicity analysis and the positive-inside rule. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90934-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. The signal peptide. J Membr Biol. 1990 May;115(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01868635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





