Abstract
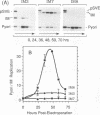
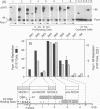
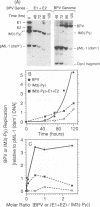
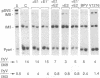
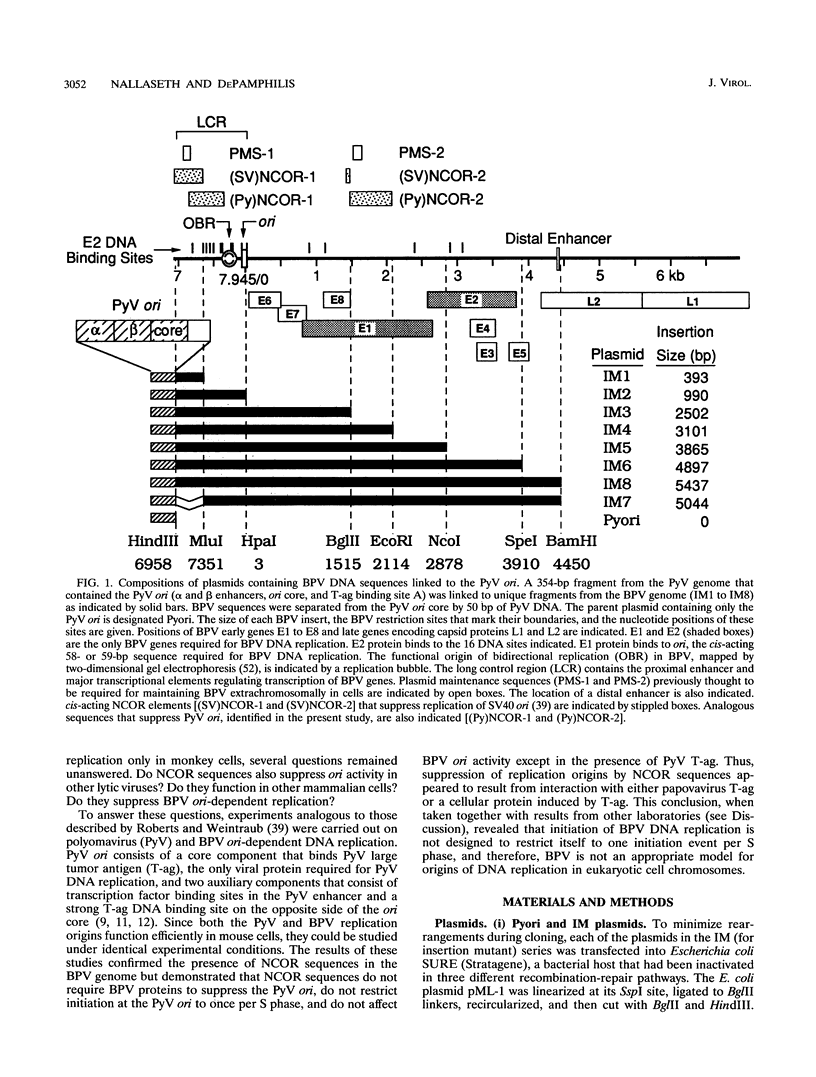
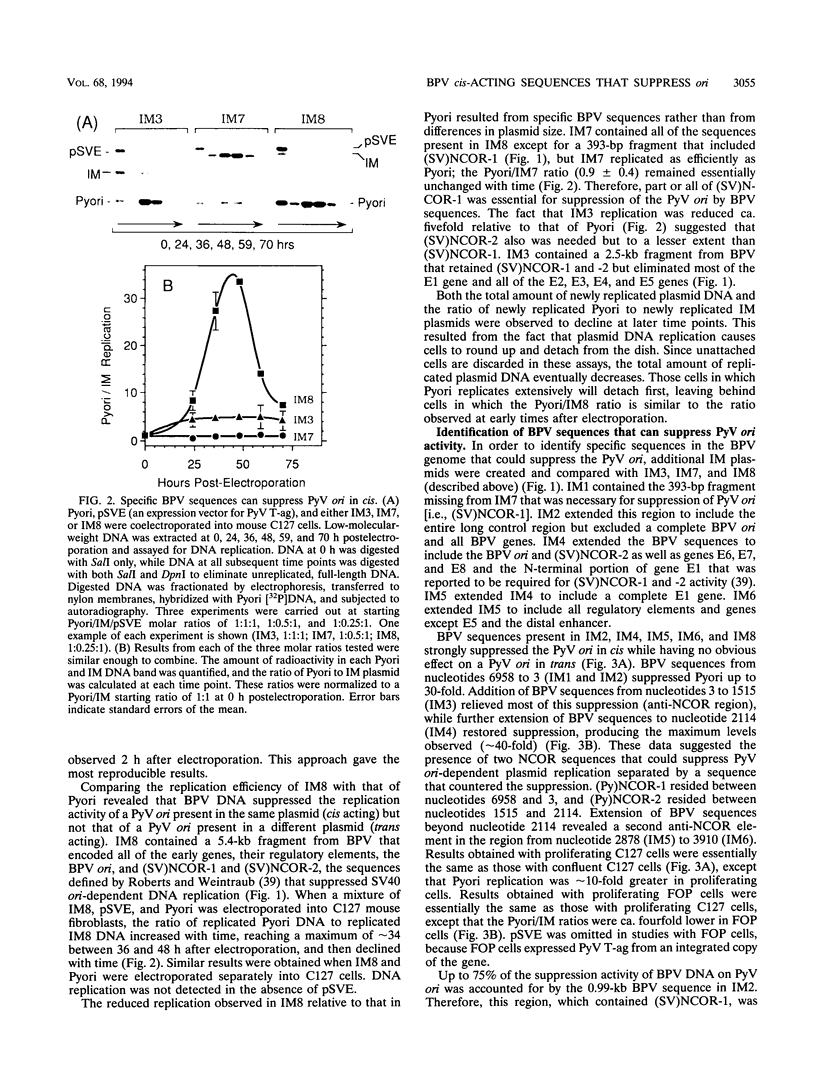
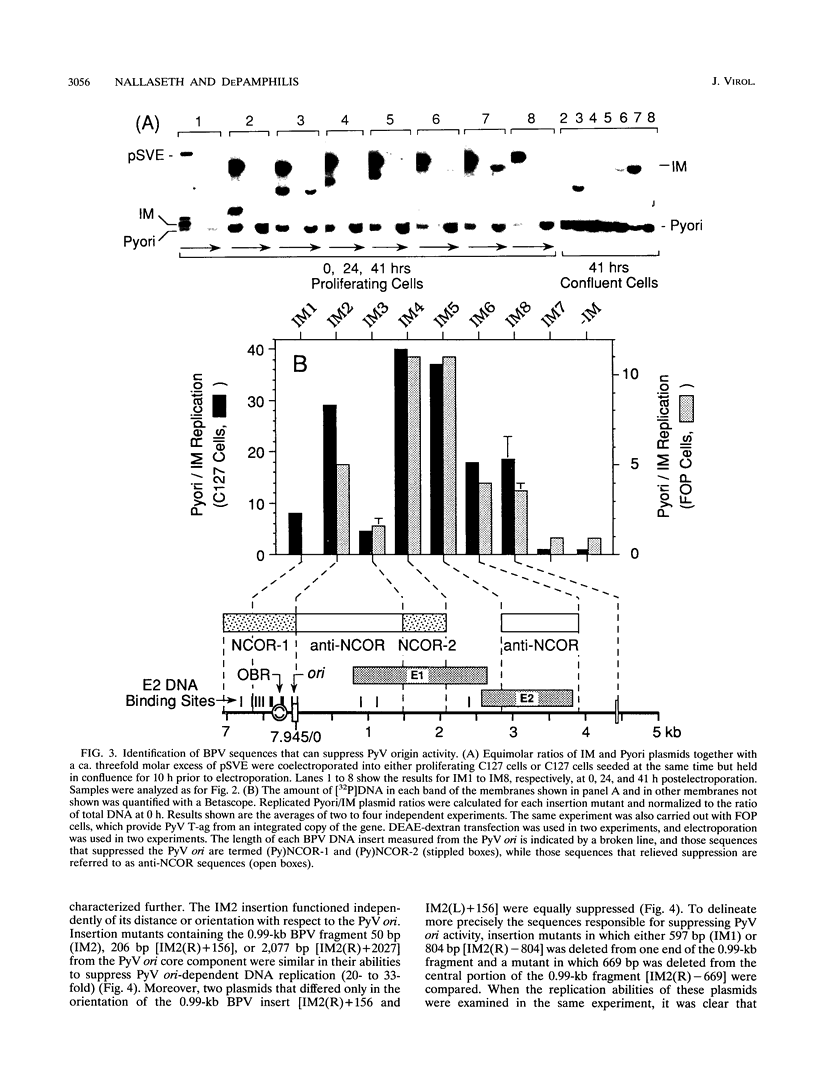
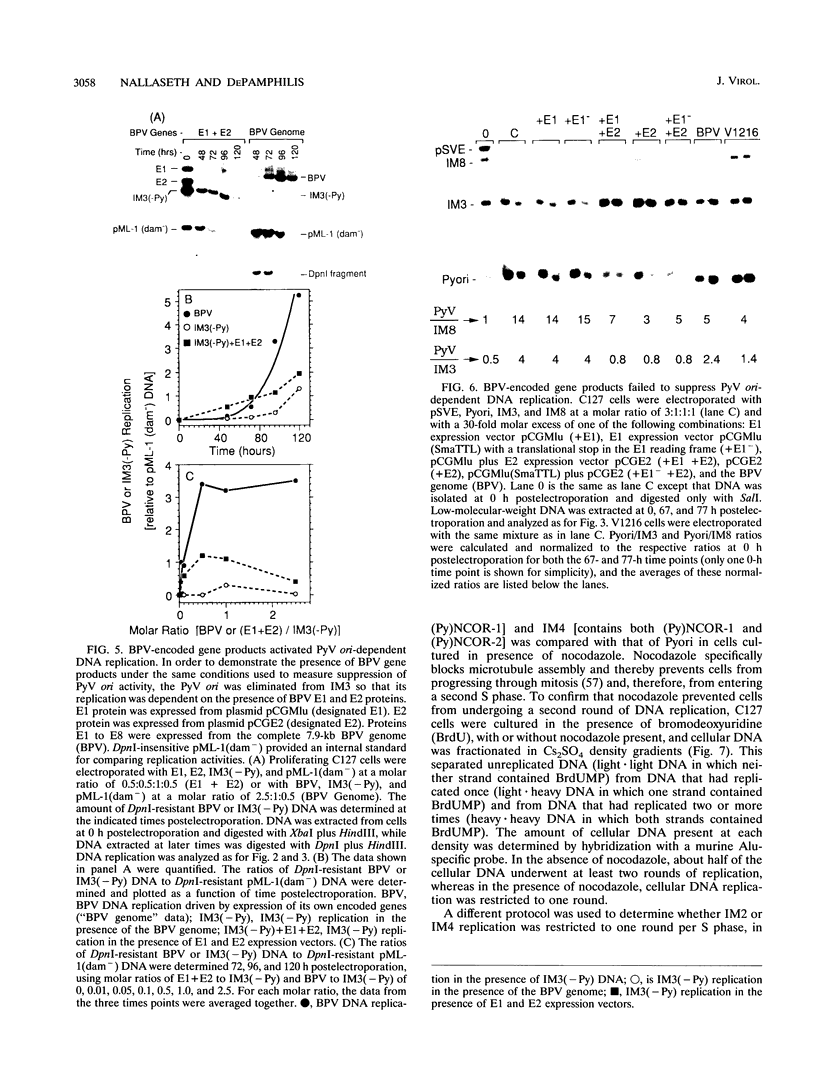
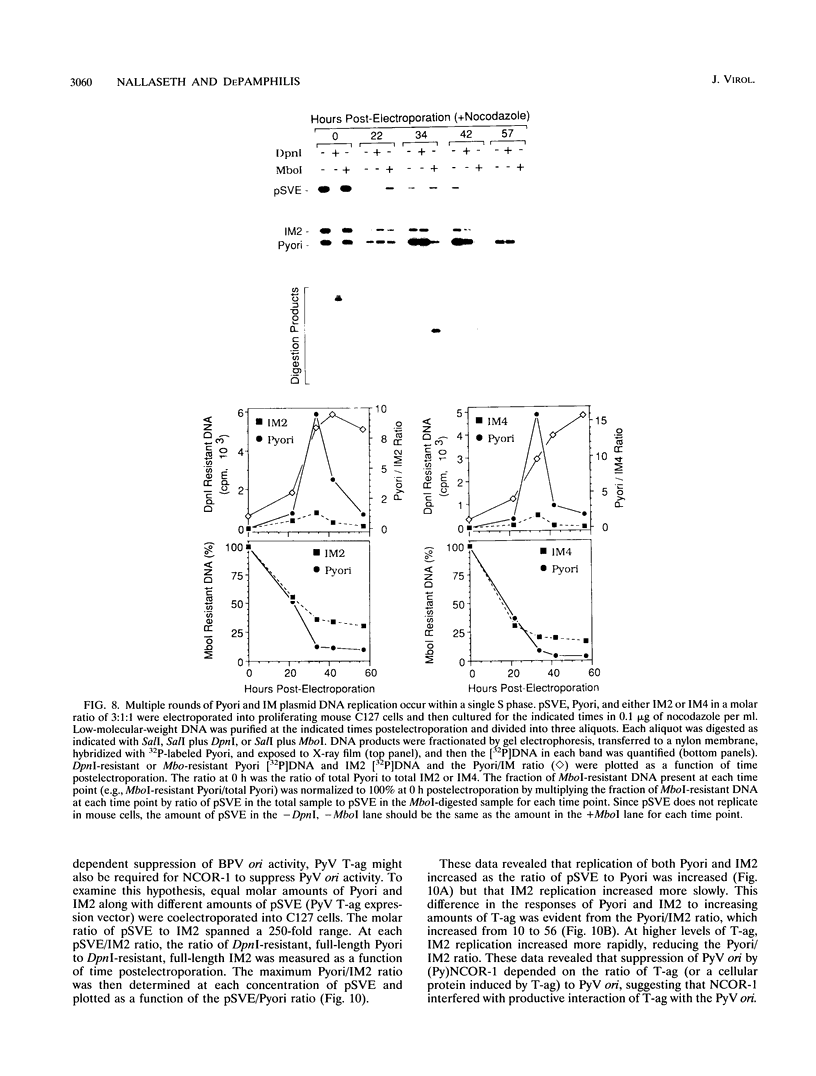
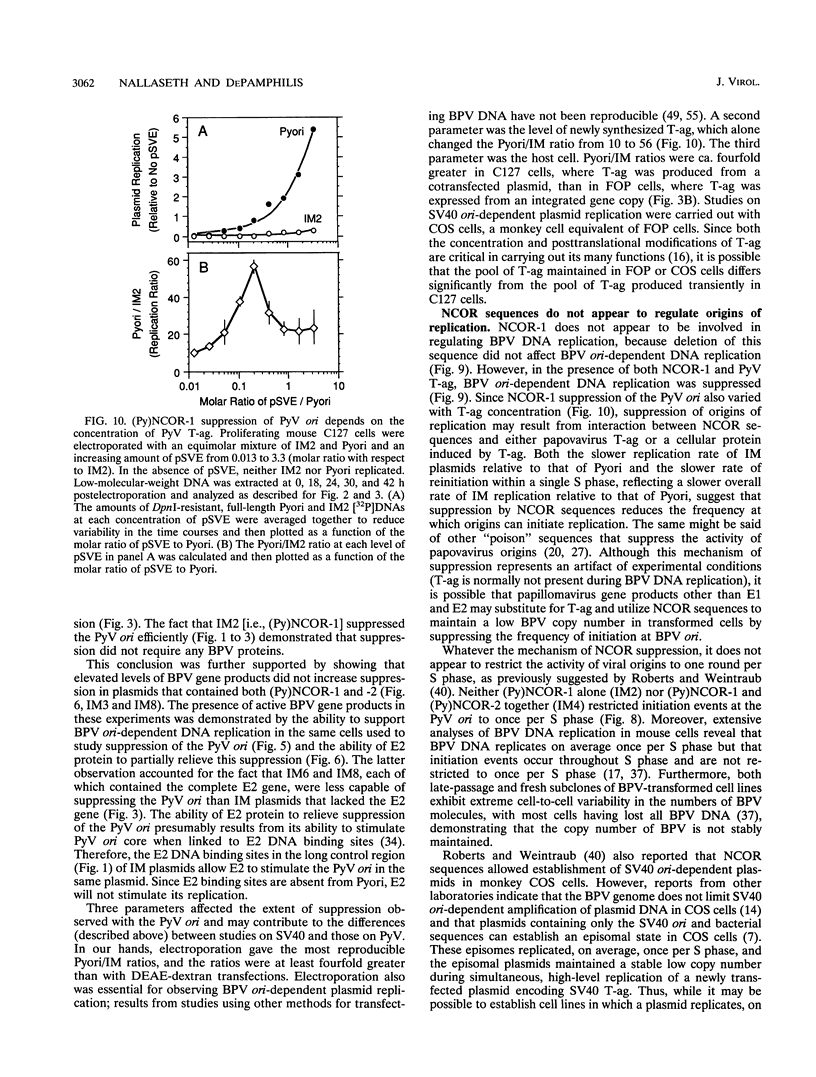
Bovine papillomavirus (BPV) DNA has been reported to restrict its own replication and that of the lytic simian virus 40 (SV40) origin to one initiation event per molecule per S phase, which suggests BPV DNA replication as a model for cellular chromosome replication. Suppression of the SV40 origin required two cis-acting BPV sequences (NCOR-1 and -2) and one trans-acting BPV protein. The results presented in this paper confirm the presence of two NCOR sequences in the BPV genome that can suppress polyomavirus (PyV) as well as SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication as much as 40-fold. However, in contrast to results of previous studies on SV40, most of the suppression of the PyV origin was due to NCOR-1, a 512-bp sequence that functioned independently of distance or orientation with respect to the PyV origin and that was not required for BPV DNA replication. Moreover, NCOR-1 alone or together with NCOR-2 did not restrict the ability of the PyV ori to reinitiate replication within a single S phase and did not require any BPV protein to exert suppression. Furthermore, NCOR-1 did not suppress BPV origin-dependent DNA replication except in the presence of PyV large tumor antigen (T-ag). Since NCOR-1 suppression of PyV origin activity also varied with T-ag concentration, suppression of origins by NCOR sequences appeared to require papovavirus T-ag. Therefore, it is unlikely that NCOR sequences are involved in regulating BPV DNA replication. When these results are taken together with those from other laboratories, BPV appears to be a slowly replicating version of papovaviruses rather than a model for origins of DNA replication in eukaryotic cell chromosomes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett-Cook E. R., Hassell J. A. Activation of polyomavirus DNA replication by yeast GAL4 is dependent on its transcriptional activation domains. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):959–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L., Lusky M., Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. Repression of bovine papilloma virus replication is mediated by a virally encoded trans-acting factor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitz I. L., Laimins L. A. The 68-kilodalton E1 protein of bovine papillomavirus is a DNA binding phosphoprotein which associates with the E2 transcriptional activator in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):649–656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.649-656.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Berg L., Reynolds J., Lusky M. The bovine papillomavirus replicon. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;120:53–67. doi: 10.1002/9780470513309.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Dong G., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Control of human papillomavirus type 11 origin of replication by the E2 family of transcription regulatory proteins. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5224–5231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5224-5231.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Frey A., Levine A. J. Regulated replication of an episomal simian virus 40 origin plasmid in COS7 cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5944–5951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5944-5951.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clertant P., Seif I. A common function for polyoma virus large-T and papillomavirus E1 proteins? Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):276–279. doi: 10.1038/311276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphili M. L. How transcription factors regulate origins of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 May;3(5):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90137-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication that function in eukaryotic cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90008-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Lusky M., Botchan M. R., Calos M. P. Amplification of a bovine papillomavirus-simian virus 40 chimera. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):625–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.625-627.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Cohen S. N. Bovine papilloma virus plasmids replicate randomly in mouse fibroblasts throughout S phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90662-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M., Miyazawa H., Nallaseth F. S., Ortega J. M., Blow J. J., DePamphilis M. L. Site-specific initiation of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes and the role of nuclear organization. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:475–485. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase S. B., Calos M. P. Replication control of autonomously replicating human sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):5053–5058. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.5053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl M., Willnow T., Fanning E. cis-active elements from mouse chromosomal DNA suppress simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2884–2894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2884-2894.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 E1 replication-defective mutants are altered in their transcriptional regulation. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4009–4015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4009-4015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Monk B. C., Howley P. M. Phenotypic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 repressor mutants. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):950–956. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.950-956.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F. Papillomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3417–3420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3417-3420.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Fairman M. P., Blow J. J. S phase of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):609–614. doi: 10.1126/science.2683076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. R. Characterization of the bovine papilloma virus plasmid maintenance sequences. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Romanczuk H., Howley P. M. The papillomavirus E2 regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18411–18414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Clark R., Sun S., Androphy E. J., MacPherson P., Botchan M. R. Targeting the E1 replication protein to the papillomavirus origin of replication by complex formation with the E2 transactivator. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1694–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2176744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Naujokas M. A., Hassell J. A. Isolation of large T antigen-producing mouse cell lines capable of supporting replication of polyomavirus-plasmid recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2406–2412. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nallaseth F. S. Sequence instability and functional inactivation of murine Y chromosomes can occur on a specific genetic background. Mol Biol Evol. 1992 Mar;9(2):331–365. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary K., DiMaio D. Open reading frames E6 and E7 of bovine papillomavirus type 1 are both required for full transformation of mouse C127 cells. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.259-266.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M., Forsberg M., You Z. Y., Westin G., Magnusson G. Enhancer effect of bovine papillomavirus E2 protein in replication of polyomavirus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7061–7065. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravnan J. B., Gilbert D. M., Ten Hagen K. G., Cohen S. N. Random-choice replication of extrachromosomal bovine papillomavirus (BPV) molecules in heterogeneous, clonally derived BPV-infected cell lines. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6946–6952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6946-6952.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riese D. J., 2nd, Settleman J., Neary K., DiMaio D. Bovine papillomavirus E2 repressor mutant displays a high-copy-number phenotype and enhanced transforming activity. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):944–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.944-949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
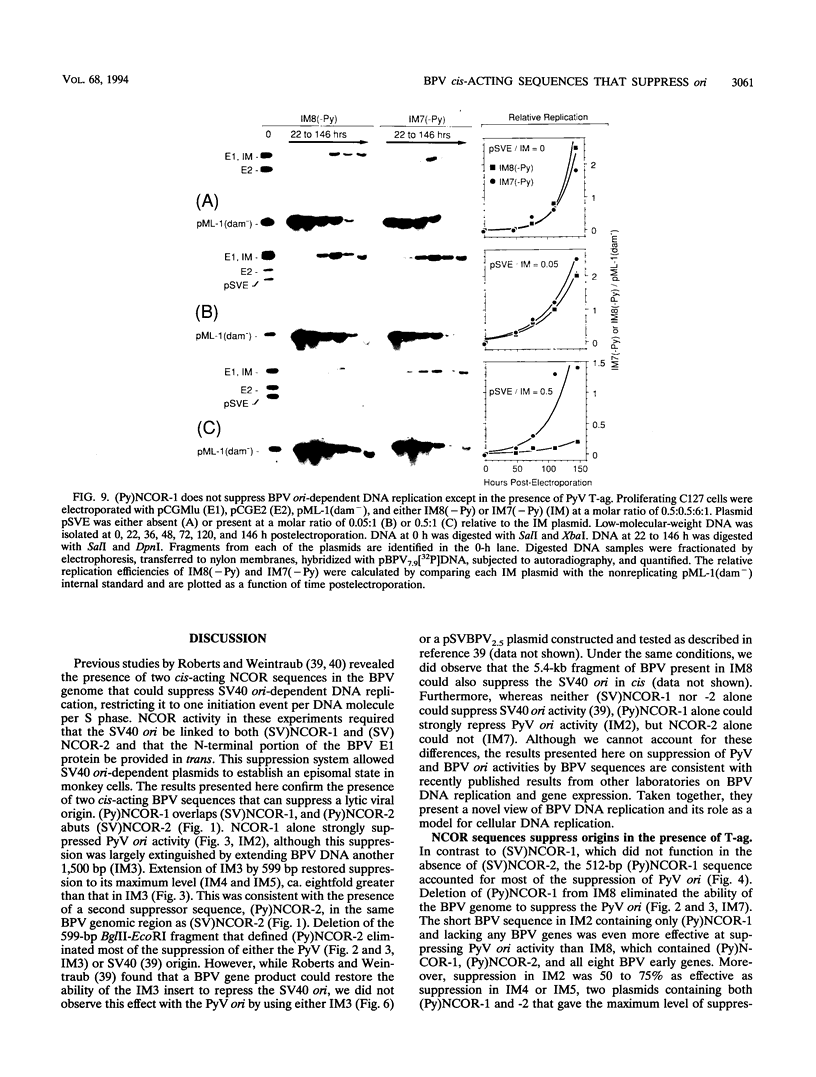
- Roberts J. M., Weintraub H. Cis-acting negative control of DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):397–404. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Weintraub H. Negative control of DNA replication in composite SV40-bovine papilloma virus plasmids. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Kleiner E., Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Pfister H. Identification of bovine papillomavirus E1 mutants with increased transforming and transcriptional activity. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1775–1782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1775-1782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Müller F., Lusky M., Gibbs E., Kim H. Y., Phillips B., Hurwitz J. Bovine papilloma virus (BPV)-encoded E2 protein enhances binding of E1 protein to the BPV replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2865–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo Y. S., Müller F., Lusky M., Hurwitz J. Bovine papilloma virus (BPV)-encoded E1 protein contains multiple activities required for BPV DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):702–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Regulation of early gene expression from the bovine papillomavirus genome in transiently transfected C127 cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5710–5720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5710-5720.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorner L., Bucay N., Choe J., Botchan M. The product of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 modulator gene (M) is a phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2474–2482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2474-2482.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tlsty T. D. Normal diploid human and rodent cells lack a detectable frequency of gene amplification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3132–3136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav E., Ustav M., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. The bovine papillomavirus origin of replication requires a binding site for the E2 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):898–902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Stenlund A. Transient replication of BPV-1 requires two viral polypeptides encoded by the E1 and E2 open reading frames. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):449–457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Ustav E., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Identification of the origin of replication of bovine papillomavirus and characterization of the viral origin recognition factor E1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4321–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Prives C. DNA helicase and duplex DNA fragment unwinding activities of polyoma and simian virus 40 large T antigen display similarities and differences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12668–12675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel R., Schweizer J., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 T-antigen DNA helicase is a hexamer which forms a binary complex during bidirectional unwinding from the viral origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):804–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.804-815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Botchan M. Replication of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA initiates within an E2-responsive enhancer element. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5903–5911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5903-5911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Guan N. Epstein-Barr virus-derived plasmids replicate only once per cell cycle and are not amplified after entry into cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):483–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.483-488.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Turnbull D., Mullins J. M., McIntosh J. R. Production of large numbers of mitotic mammalian cells by use of the reversible microtubule inhibitor nocodazole. Nocodazole accumulated mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):397–405. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]