Abstract
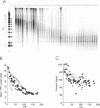
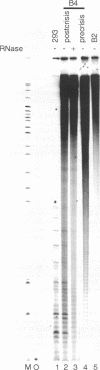
We have measured telomere length and telomerase activity throughout the life span of clones of human B lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Shortening of telomeres occurred at similar rates in all populations and persisted until chromosomes had little telomeric DNA remaining. At this stage, some of the clones entered a proliferative crisis and died. Only clones in which telomeres were stabilized, apparently by activation of telomerase, continued to proliferate indefinitely, i.e., became immortal. Since loss of telomeres impairs chromosome function, and may thus affect cell survival, we propose that telomerase activity is required for immortality. We have now detected this enzyme in a variety of immortal human cells transformed by different viruses, indicating that telomerase activation may be a common step in immortalization.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Dempster M., Hastie N. D. Human telomeres contain at least three types of G-rich repeat distributed non-randomly. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4611–4627. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsopp R. C., Vaziri H., Patterson C., Goldstein S., Younglai E. V., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W., Harley C. B. Telomere length predicts replicative capacity of human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10114–10118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):569–573. doi: 10.1038/350569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R. Molecular cloning of human telomeres in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):774–776. doi: 10.1038/338774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd P., Brown K. W., Gallimore P. H. Malignant transformation of human embryo retinoblasts by cloned adenovirus 12 DNA. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):69–71. doi: 10.1038/298069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K., Greider C. W. Tetrahymena telomerase catalyzes nucleolytic cleavage and nonprocessive elongation. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1364–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counter C. M., Avilion A. A., LeFeuvre C. E., Stewart N. G., Greider C. W., Harley C. B., Bacchetti S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1921–1929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. H., Allshire R. C., McKay S. J., McGill N. I., Cooke H. J. Cloning of human telomeres by complementation in yeast. Nature. 1989 Apr 27;338(6218):771–774. doi: 10.1038/338771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDI A. J., JENSEN F. C., KOPROWSKI H. SV40-INDUCED TRANFORMATION OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELLS: CRISIS AND RECOVERY. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Feb;65:69–83. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030650110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrini A. M., Camponeschi B., Ascenzioni F., Piccolella E., Donini P. Subtelomeric as well as telomeric sequences are lost from chromosomes in proliferating B lymphocytes. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):455–460. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):458–460. doi: 10.1038/345458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Telomere loss: mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat Res. 1991 Mar-Nov;256(2-6):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huschtscha L. I., Holliday R. Limited and unlimited growth of SV40-transformed cells from human diploid MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:77–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäger D., Philippsen P. Stabilization of dicentric chromosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by telomere addition to broken ends or by centromere deletion. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):247–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingelhutz A. J., Barber S. A., Smith P. P., Dyer K., McDougall J. K. Restoration of telomeres in human papillomavirus-immortalized human anogenital epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):961–969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M. Z., Allsopp R. C., Futcher A. B., Greider C. W., Harley C. B. Telomere end-replication problem and cell aging. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):951–960. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Duigou G. J., Hernandez E., Fisher P. B. Characterization of mutant human fibroblast cultures transformed with simian virus 40. J Cell Sci. 1988 Apr;89(Pt 4):481–493. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead P. S., Saksela E. The sequence of chromosome aberrations during SV 40 transformation of a human diploid cell strain. Hereditas. 1965;52(3):271–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1965.tb01960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin G. B. The human telomere terminal transferase enzyme is a ribonucleoprotein that synthesizes TTAGGG repeats. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prowse K. R., Avilion A. A., Greider C. W. Identification of a nonprocessive telomerase activity from mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1493–1497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radna R. L., Caton Y., Jha K. K., Kaplan P., Li G., Traganos F., Ozer H. L. Growth of immortal simian virus 40 tsA-transformed human fibroblasts is temperature dependent. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3093–3096. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray F. A., Peabody D. S., Cooper J. L., Cram L. S., Kraemer P. M. SV40 T antigen alone drives karyotype instability that precedes neoplastic transformation of human diploid fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Jan;42(1):13–31. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240420103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr Human cell transformation by simian virus 40--a review. In Vitro. 1981 Jan;17(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02618025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Wright W. E., Brasiskyte D., Van der Haegen B. A. E6 of human papillomavirus type 16 can overcome the M1 stage of immortalization in human mammary epithelial cells but not in human fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1407–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Wright W. E. Quantitation of the frequency of immortalization of normal human diploid fibroblasts by SV40 large T-antigen. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Sep;184(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90369-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Wright W. E., Werbin H. Defining the molecular mechanisms of human cell immortalization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternås L., Middleton T., Sugden B. The average number of molecules of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 per cell does not correlate with the average number of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA molecules per cell among different clones of EBV-immortalized cells. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2407–2410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2407-2410.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart N., Bacchetti S. Expression of SV40 large T antigen, but not small t antigen, is required for the induction of chromosomal aberrations in transformed human cells. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90008-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M., Griffin B. E. Cellular immortalization--an essential step or merely a risk factor in DNA virus-induced transformation? Cancer Cells. 1990 Nov;2(11):360–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M., Hering S., Lubbe L., Griffin B. E. Immortalization and transformation of human fibroblasts by regulated expression of polyoma virus T antigens. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Mark W. Clonal transformation of adult human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.503-508.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Phelps M., Domoradzki J. Epstein-Barr virus DNA is amplified in transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.590-595.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaziri H., Schächter F., Uchida I., Wei L., Zhu X., Effros R., Cohen D., Harley C. B. Loss of telomeric DNA during aging of normal and trisomy 21 human lymphocytes. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):661–667. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Lamb J., Harris P. C., Finney R. D., Higgs D. R. A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):868–871. doi: 10.1038/346868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G. L., Bradley J. D., Attardi L. D., Blackburn E. H. In vivo alteration of telomere sequences and senescence caused by mutated Tetrahymena telomerase RNAs. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):126–132. doi: 10.1038/344126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakian V. A. Structure and function of telomeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:579–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lange T., Shiue L., Myers R. M., Cox D. R., Naylor S. L., Killery A. M., Varmus H. E. Structure and variability of human chromosome ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):518–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]