Abstract
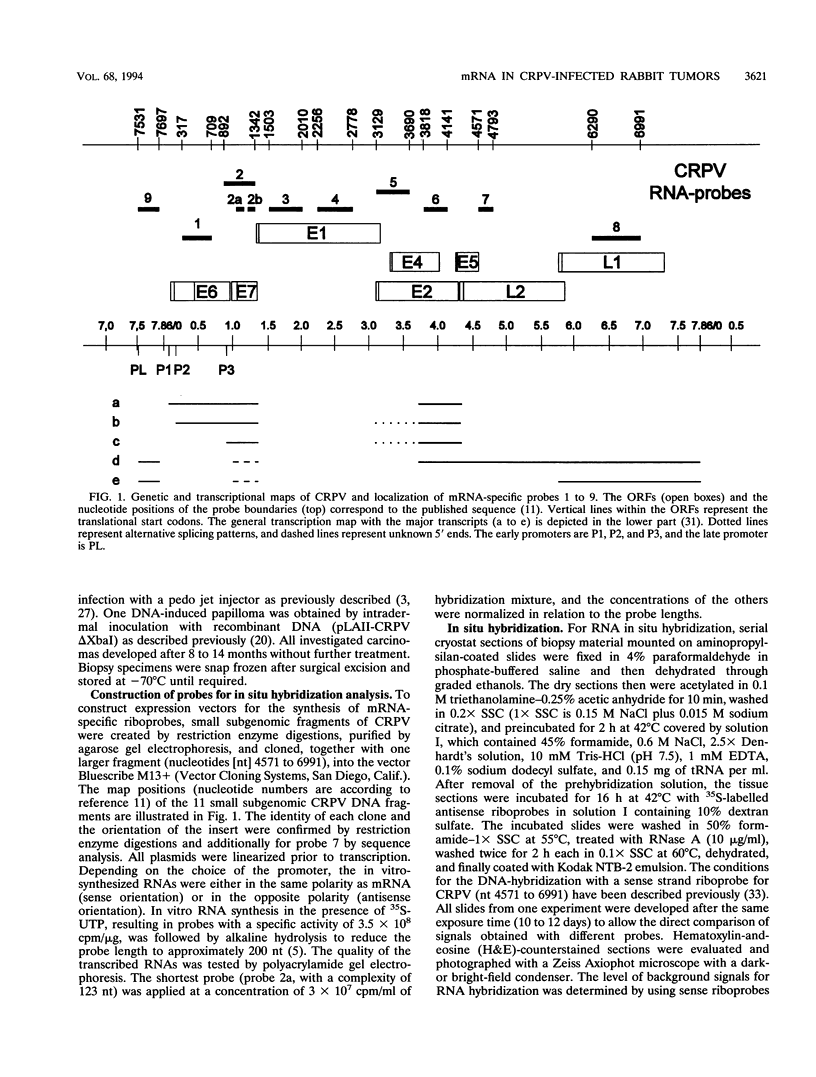
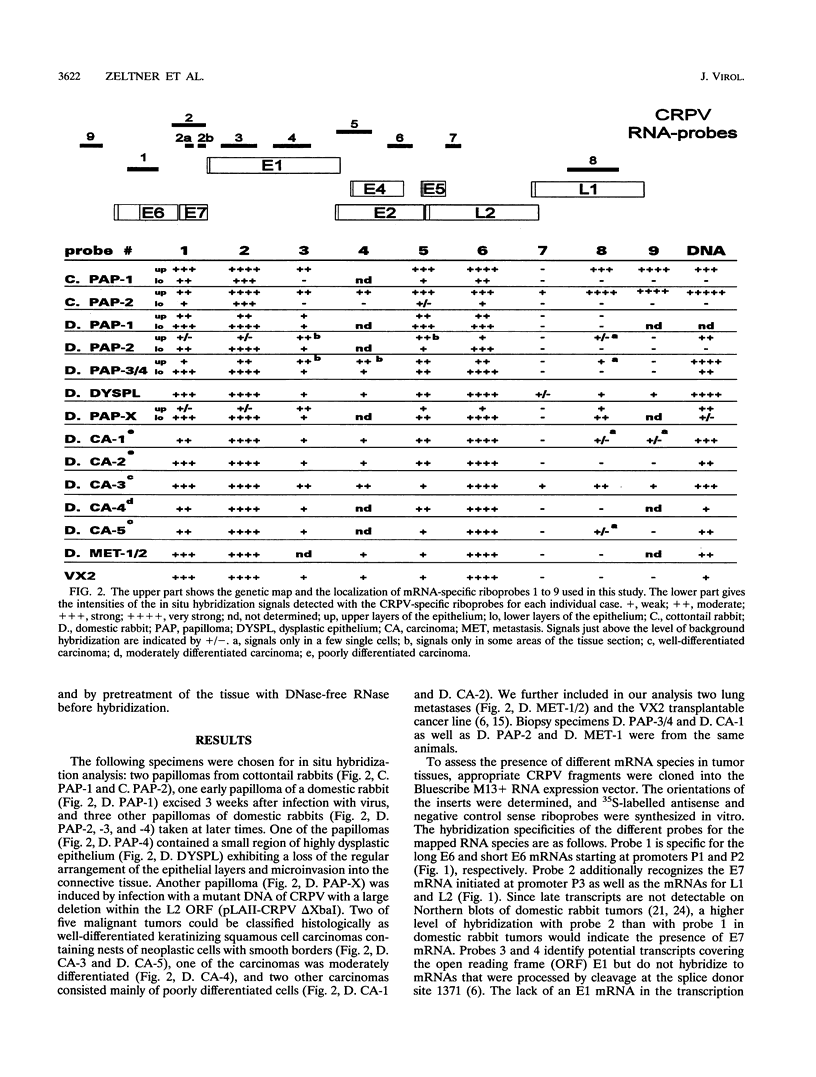
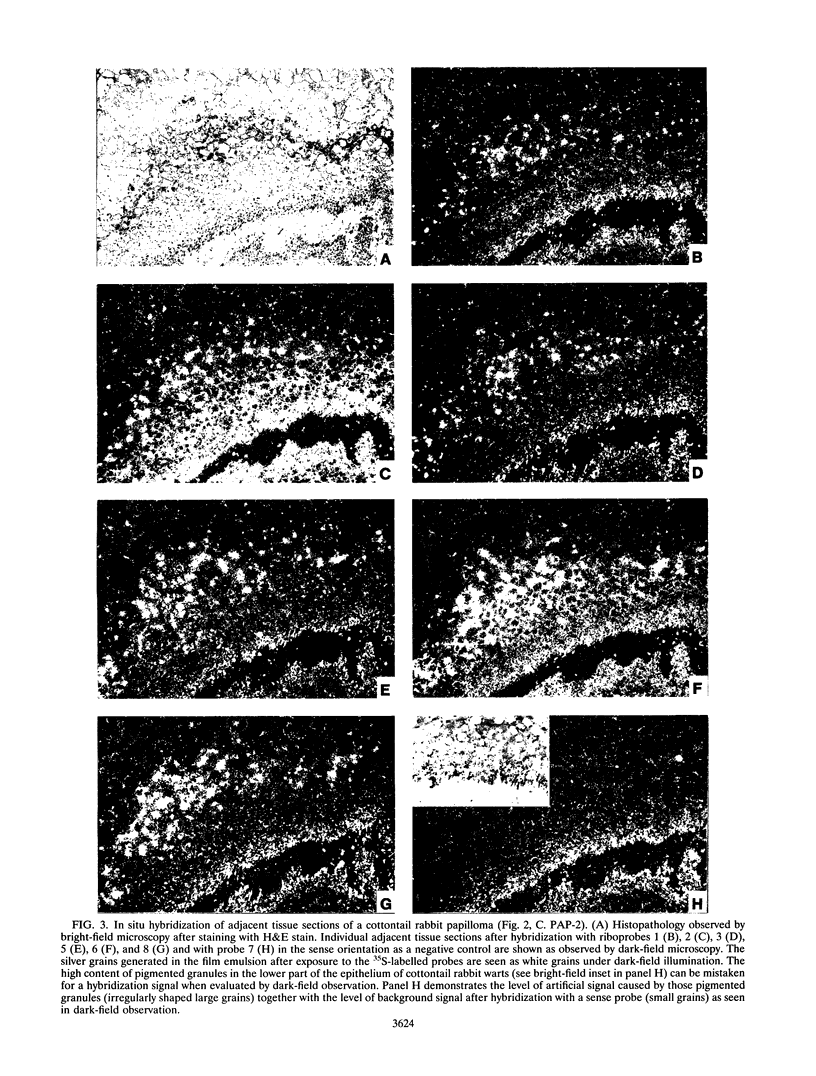
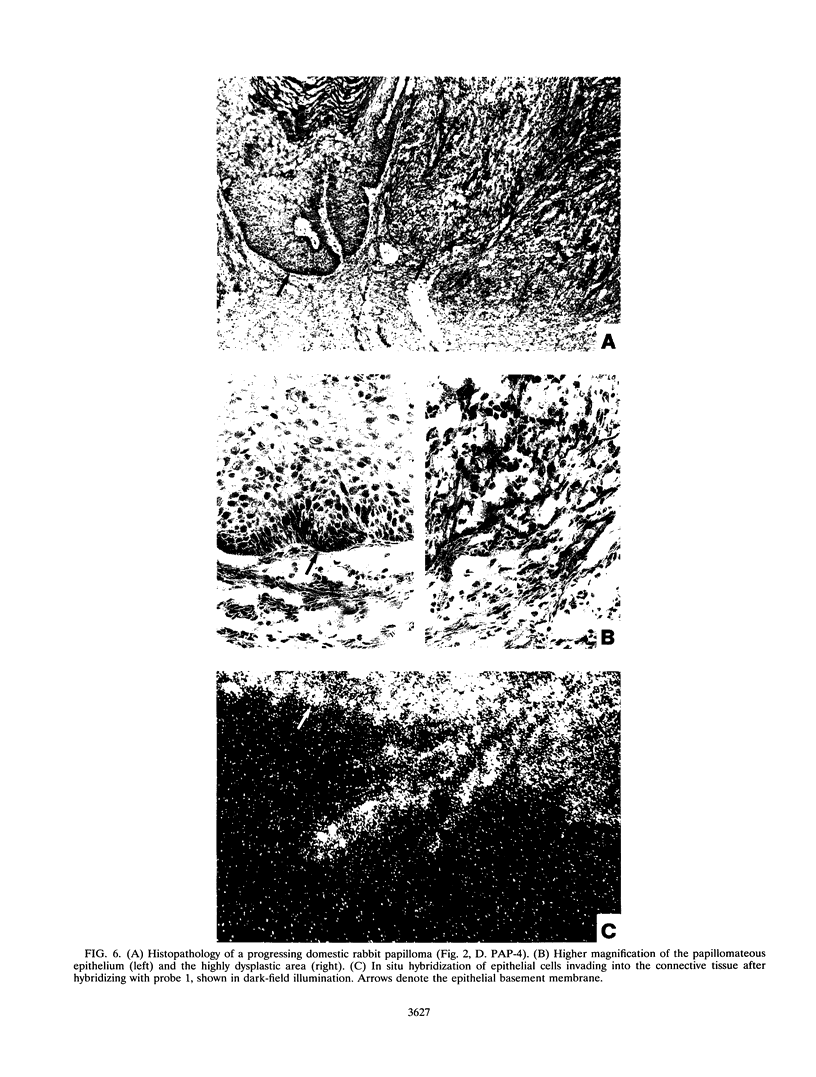
Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus induces strictly epithelial tumors in both cottontail and domestic rabbits. A high proportion of the initial benign papillomas progress within 8 to 14 months to invasive carcinomas. With the help of mRNA-specific riboprobes for E6, E7, E1, E2, L1 and L2, we investigated by in situ hybridization the RNA expression pattern of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus in tissue sections of biopsies from different stages of tumor development. Common features of all lesions were high levels of E6 and E7 mRNAs and low levels of E1 and E2 mRNAs. In agreement with earlier reports, there was no evidence for a major mRNA class equivalent to the prominent E1-E4 RNA of human papillomavirus types 6/11 and 16. In cottontail rabbit papillomas, high levels of E6 and E7 mRNAs were present in the upper differentiated epithelial layers. These layers also contained most of the E1 and E2 mRNAs and the viral DNA. In contrast, papillomas of domestic rabbits revealed the opposite differentiation-dependent expression pattern for the E6 and E7 mRNAs; there were strong signals in the basal layers, and these declined with increased differentiation. Transcripts encoding the L1 mRNA were detected only in a few isolated cells of the granular layer. There was no difference between the amounts of E6, E7, E1, and E2 mRNAs present in highly dysplastic tissue and those present in adjacent normal papillomatous epithelium within a progressing papilloma. However, late transcripts and viral DNA detectable only in the upper layers of the papilloma were present throughout the thickness of the dysplastic tissue, indicating a newly acquired permissiveness of the dysplastic cells for viral DNA replication and late transcription. Carcinomas in general had the same expression patterns for E6, E7, and E1 but were dissimilar in the levels of expression of E2 and late transcripts.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa M. S., Wettstein F. O. E2 of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus is a nuclear phosphoprotein translated from an mRNA encoding multiple open reading frames. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3242–3249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3242-3249.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J. L., Yang Z. H., Barthold S. W., Johnson E. A. Use of a rapid, efficient inoculation method to induce papillomas by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus DNA shows that the E7 gene is required. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4816–4820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsma J. L., Yang Z. H., DiMaio D., Barthold S. W., Johnson E., Xiao W. The putative E5 open reading frame of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus is dispensable for papilloma formation in domestic rabbits. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6204–6207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6204-6207.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm S., Wilczynski S. P., Pfister H., Iftner T. The predominant mRNA class in HPV16-infected genital neoplasias does not encode the E6 or the E7 protein. Int J Cancer. 1993 Nov 11;55(5):791–798. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox K. H., DeLeon D. V., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Detection of mrnas in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):485–502. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Georges E., Orth G., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the cottontail rabbit papillomavirus mRNAs expressed in the transplantable VX2 carcinoma. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):735–741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.735-741.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doorbar J., Parton A., Hartley K., Banks L., Crook T., Stanley M., Crawford L. Detection of novel splicing patterns in a HPV16-containing keratinocyte cell line. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):254–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90401-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Bosch F. X., Glitz D., Schneider A., zur Hausen H. Inverse relationship between human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 early gene expression and cell differentiation in nude mouse epithelial cysts and tumors induced by HPV-positive human cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.796-804.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Glitz D., Schneider A., zur Hausen H. Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV 16) gene expression and DNA replication in cervical neoplasia: analysis by in situ hybridization. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90688-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges E., Breitburd F., Jibard N., Orth G. Two Shope papillomavirus-associated VX2 carcinoma cell lines with different levels of keratinocyte differentiation and transplantability. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):246–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.246-250.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri I., Danos O., Yaniv M. Genomic structure of the cottontail rabbit (Shope) papillomavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1580–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri I., Yaniv M. Structural and mutational analysis of E2 trans-activating proteins of papillomaviruses reveals three distinct functional domains. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2823–2829. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. D., Uzelin D. M., Phillips G. E., McEvoy P., Marin R., Burrell C. J. Transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 16 in genital intraepithelial neoplasia: evidence for promoter usage within the E7 open reading frame during epithelial differentiation. J Gen Virol. 1992 Aug;73(Pt 8):2047–2057. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-8-2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftner T., Oft M., Böhm S., Wilczynski S. P., Pfister H. Transcription of the E6 and E7 genes of human papillomavirus type 6 in anogenital condylomata is restricted to undifferentiated cell layers of the epithelium. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4639–4646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4639-4646.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F. Papillomavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3417–3420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3417-3420.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Borenstein L. A., Selvakumar R., Ahmed R., Wettstein F. O. Progression from papilloma to carcinoma is accompanied by changes in antibody response to papillomavirus proteins. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.382-389.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers C., Harry J., Lin Y. L., Wettstein F. O. Identification of three transforming proteins encoded by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1655–1664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1655-1664.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Hirochika R., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. A human papilloma virus type 11 transcript encoding an E1--E4 protein. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Meyers C., Wettstein F. O. Genetic analysis of CRPV pathogenesis: the L1 open reading frame is dispensable for cellular transformation but is required for papilloma formation. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Wettstein F. O. Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus-specific transcripts in transplantable tumors with integrated DNA. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90362-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Wettstein F. O. Differences exist between viral transcripts in cottontail rabbit papillomavirus-induced benign and malignant tumors as well as non-virus-producing and virus-producing tumors. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):706–712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.706-712.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasseri M., Wettstein F. O., Stevens J. G. Two colinear and spliced viral transcripts are present in non-virus-producing benign and malignant neoplasms induced by the shope (rabbit) papilloma virus. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):263–268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.263-268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Leary S. L., Faras A. J. Shope papillomavirus transcription in benign and malignant rabbit tumors. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYVERTON J. T. The pathogenesis of the rabbit papilloma-to-carcinoma sequence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1952 Jul 10;54(6):1126–1140. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1952.tb39983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Prokoph H., Wettstein F. O. Oncogenic and nononcogenic human genital papillomaviruses generate the E7 mRNA by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1441-1447.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wettstein F. O. Multiple copies of Shope virus DNA are present in cells of benign and malignant non-virus-producing neoplasms. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):891–898. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.891-898.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Rhodes C. R., Whitbeck A., Wolinsky S. M., Chow L. T., Broker T. R. Human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 gene expression in cervical neoplasias. Hum Pathol. 1992 Feb;23(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90232-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Wolinsky S. M., Whitbeck A., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Differentiation-linked human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 transcription in genital condylomata revealed by in situ hybridization with message-specific RNA probes. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettstein F. O., Barbosa M. S., Nasseri M. Identification of the major cottontail rabbit papillomavirus late RNA cap site and mapping and quantitation of an E2 and minor E6 coding mRNA in papillomas and carcinomas. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilczynski S. P., Oft M., Cook N., Liao S. Y., Iftner T. Human papillomavirus type 6 in squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder and cervix. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jan;24(1):96–102. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90068-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Human papillomaviruses in the pathogenesis of anogenital cancer. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90816-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]