Abstract
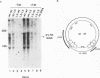
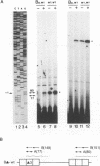
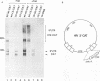
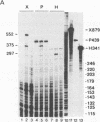
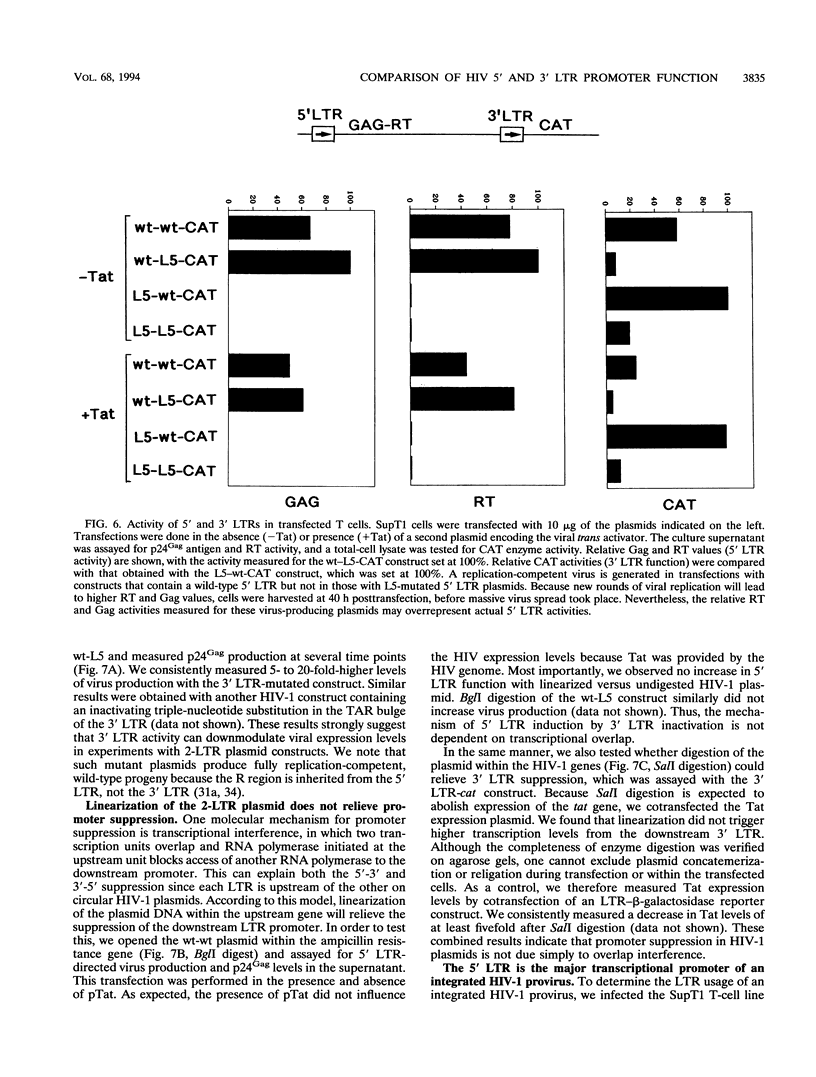
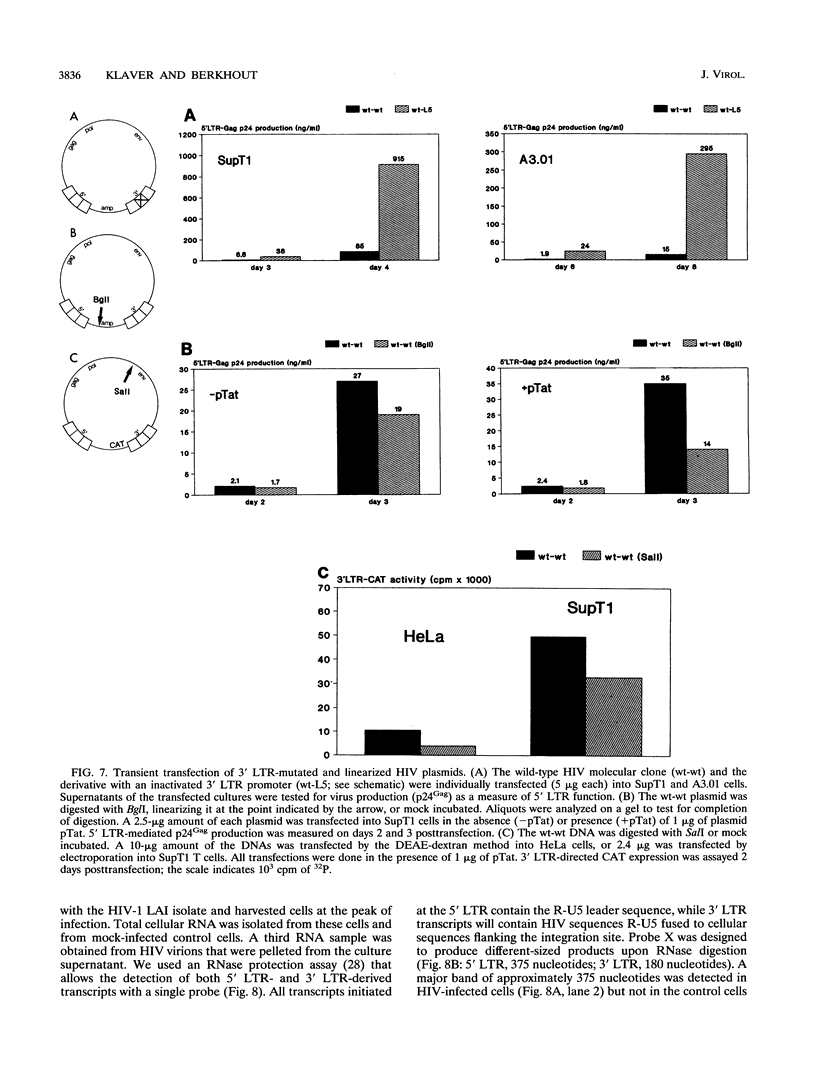
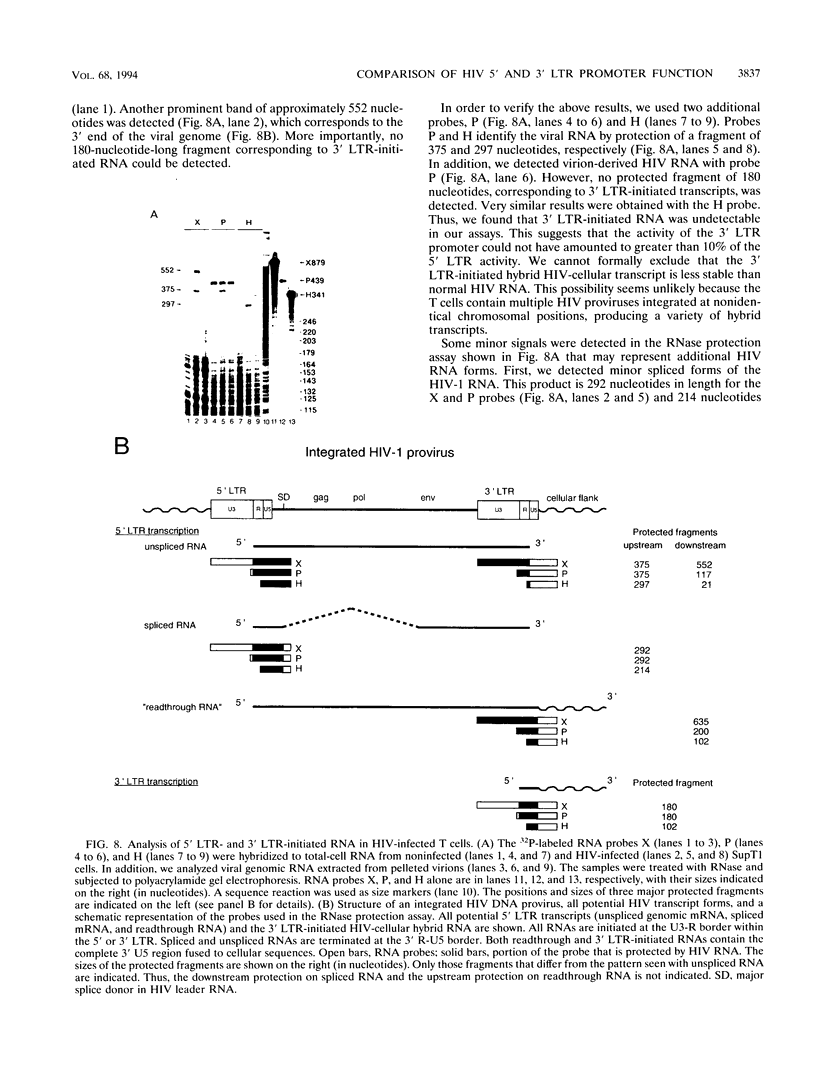
The architecture of a retroviral genome presents some unusual features for transcriptional regulation because of duplication of the transcriptional control sequences in the 5' and 3' long terminal repeats (LTRs). We have studied the transcriptional activity of the 5' and 3' LTRs of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vectors. Using full-length HIV molecular clones, we demonstrate that both LTRs function as Tat-inducible promoters. However, the absolute levels of transcription were found to be much higher for the 5' LTR than for the 3' LTR promoter. When transcription was assayed for an integrated HIV-1 provirus, we also found that the upstream 5' LTR element was the major transcriptional promoter. 3' LTR transcription, however, can be triggered by inactivation of the 5' LTR promoter. Likewise, 5' LTR transcription is induced in constructs lacking a functional 3' LTR promoter. This phenomenon of promoter suppression may have important implications for the design of HIV-based retrovirus vectors.
Full text
PDF
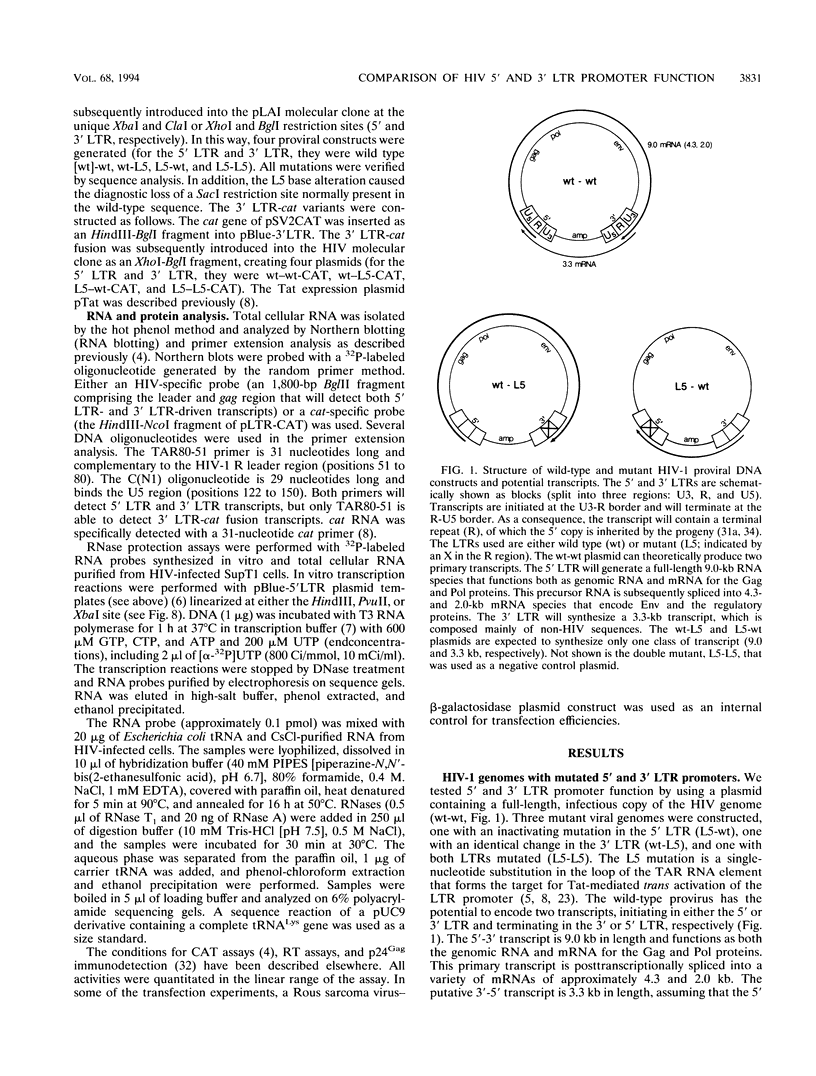
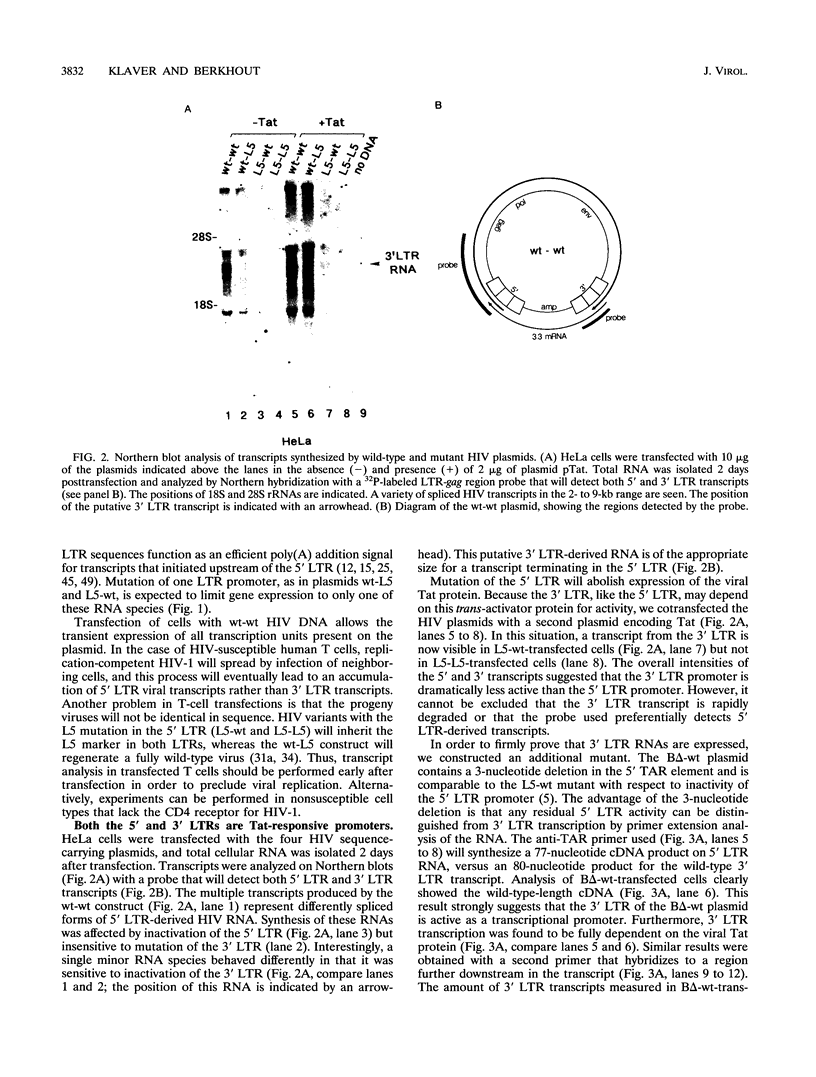
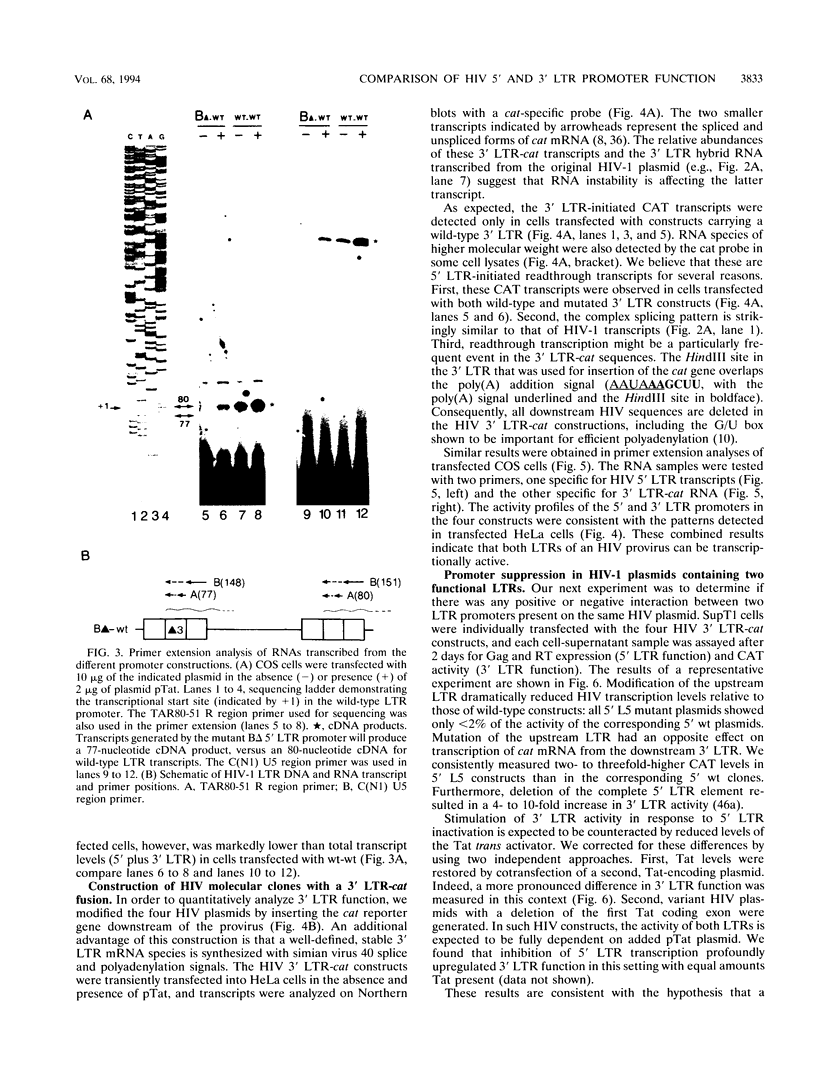
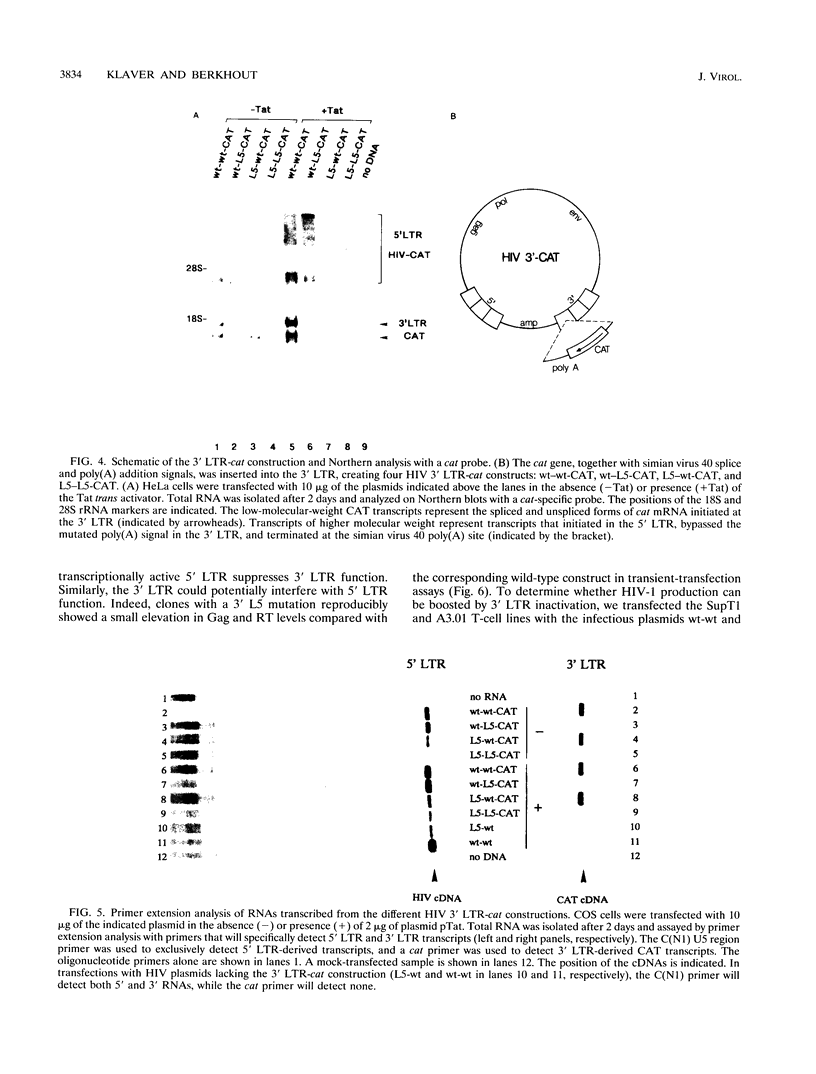



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Y. F., Gilmartin G. M., Hanly S. M., Nevins J. R., Greene W. C. The HTLV-I Rex response element mediates a novel form of mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):727–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90502-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Essink B. B., Schoneveld I. In vitro dimerization of HIV-2 leader RNA in the absence of PuGGAPuA motifs. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):181–187. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Silver J., Jeang K. T. Efficient trans-activation by the HIV-2 Tat protein requires a duplicated TAR RNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1839–1846. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. trans activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is sequence specific for both the single-stranded bulge and loop of the trans-acting-responsive hairpin: a quantitative analysis. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5501–5504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5501-5504.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Klaver B. In vivo selection of randomly mutated retroviral genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5020–5024. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerkoel C. F., Kung H. J. Transcriptional interaction between retroviral long terminal repeats (LTRs): mechanism of 5' LTR suppression and 3' LTR promoter activation of c-myc in avian B-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4814–4823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4814-4823.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchschacher G. L., Jr, Panganiban A. T. Human immunodeficiency virus vectors for inducible expression of foreign genes. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2731–2739. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2731-2739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Identification of a U5-specific sequence required for efficient polyadenylation within the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):421–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.421-424.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J., Ganem D. Regulation of polyadenylation in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): contributions of promoter proximity and upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1513–1524. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeZazzo J. D., Kilpatrick J. E., Imperiale M. J. Involvement of long terminal repeat U3 sequences overlapping the transcription control region in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mRNA 3' end formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1624–1630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A., Valerio R. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 tat protein binds trans-activation-responsive region (TAR) RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. A promoterless retroviral vector indicates that there are sequences in U3 required for 3' RNA processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1197–1201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann D. M., Dollard C., Winston F. SPT15, the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding factor TFIID, is required for normal transcription initiation in vivo. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Comparison of promoter suppression in avian and murine retrovirus vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9381–9396. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Quantitative analysis of gene suppression in integrated retrovirus vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Fleming E. S., Oetjen J. Activation of HIV-1 pre-mRNA 3' processing in vitro requires both an upstream element and TAR. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4419–4428. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. TAR independent activation of the human immunodeficiency virus in phorbol ester stimulated T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4417–4423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausler B., Somerville R. L. Interaction in vivo between strong closely spaced constitutive promoters. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90335-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S. A., Coffin J. M. Differential transcription from the long terminal repeats of integrated avian leukosis virus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):497–505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.497-505.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J. E., Durbin K. J., Winston F. Genetic evidence for promoter competition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4608–4615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju G., Cullen B. R. The role of avian retroviral LTRs in the regulation of gene expression and viral replication. Adv Virus Res. 1985;30:179–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60451-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadesch T., Berg P. Effects of the position of the simian virus 40 enhancer on expression of multiple transcription units in a single plasmid. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2593–2601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaver B., Berkhout B. Premature strand transfer by the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase during strong-stop DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 25;22(2):137–144. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken S. E., van Wamel J. L., Goudsmit J., Berkhout B., Geelen J. L. Natural variants of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat: analysis of promoters with duplicated DNA regulatory motifs. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):968–972. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90274-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Goff S. P. Reverse transcription of retroviral genomes: mutations in the terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):447–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.447-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P., Temin H. M., Dornburg R. Unusually high frequency of reconstitution of long terminal repeats in U3-minus retrovirus vectors by DNA recombination or gene conversion. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1336–1343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1336-1343.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Emerman M., Montagnier L. Changes in growth properties on passage in tissue culture of viruses derived from infectious molecular clones of HIV-1LAI, HIV-1MAL, and HIV-1ELI. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):661–672. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90537-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. Poly(A) signals. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):671–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90495-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raineri I., Senn H. P. HIV-1 promotor insertion revealed by selective detection of chimeric provirus-host gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6261–6266. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Blais B. M., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. At least two regions of the viral genome determine the oncogenic potential of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain A., Coffin J. M. Polyadenylation at correct sites in genome RNA is not required for retrovirus replication or genome encapsidation. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3301–3306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3301-3306.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Itoh M., Inoue J., Seiki M., Takaku F., Yoshida M. Secondary structure of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 rex-responsive element is essential for rex regulation of RNA processing and transport of unspliced RNAs. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2825–2832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2825-2832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Donehower L., Hager G., Zeller N., Malavarca R., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Sequence comparison in the crossover region of an oncogenic avian retrovirus recombinant and its nononcogenic parent: genetic regions that control growth rate and oncogenic potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1331–1338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valsamakis A., Schek N., Alwine J. C. Elements upstream of the AAUAAA within the human immunodeficiency virus polyadenylation signal are required for efficient polyadenylation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3699–3705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valsamakis A., Zeichner S., Carswell S., Alwine J. C. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 polyadenylylation signal: a 3' long terminal repeat element upstream of the AAUAAA necessary for efficient polyadenylylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdin E., Becker N., Bex F., Droogmans L., Burny A. Identification and characterization of an enhancer in the coding region of the genome of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4874–4878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdin E. DNase I-hypersensitive sites are associated with both long terminal repeats and with the intragenic enhancer of integrated human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6790–6799. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6790-6799.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weichs an der Glon C., Monks J., Proudfoot N. J. Occlusion of the HIV poly(A) site. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):244–253. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., von Rüden T., Kantoff P. W., Garber C., Seiberg M., Rüther U., Anderson W. F., Wagner E. F., Gilboa E. Self-inactivating retroviral vectors designed for transfer of whole genes into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3194–3198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]