Abstract
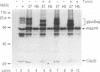
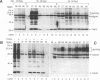
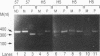
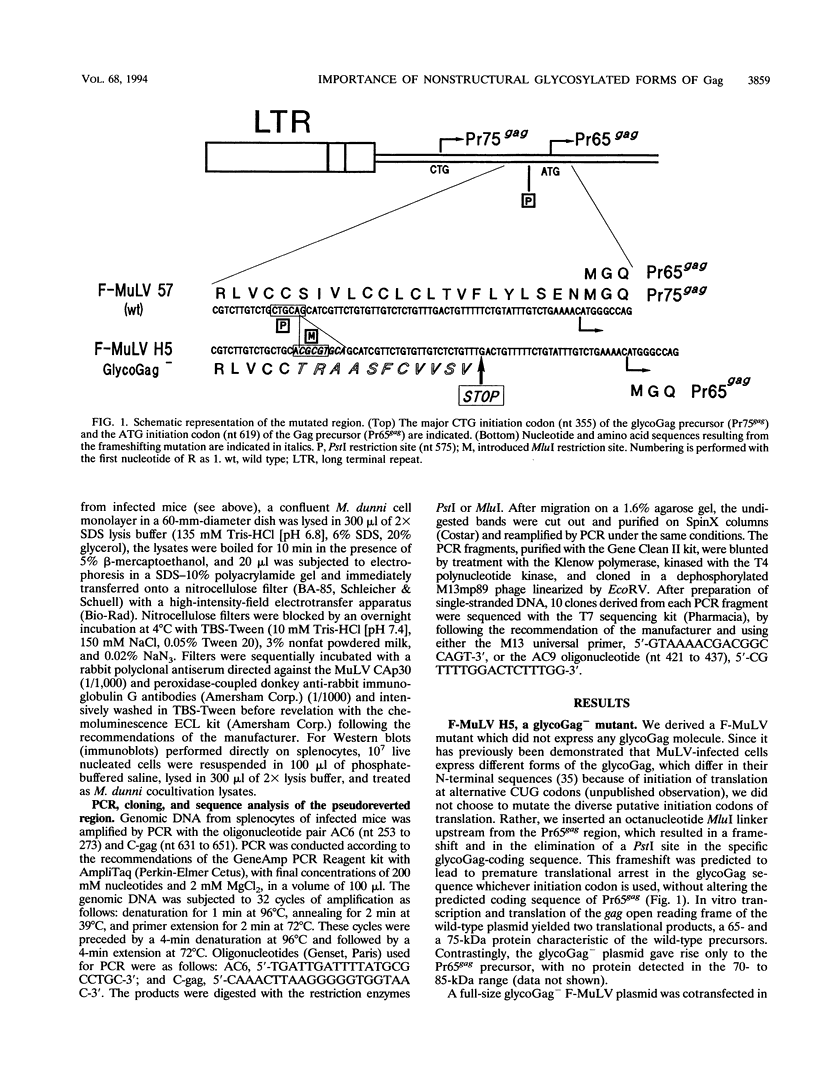
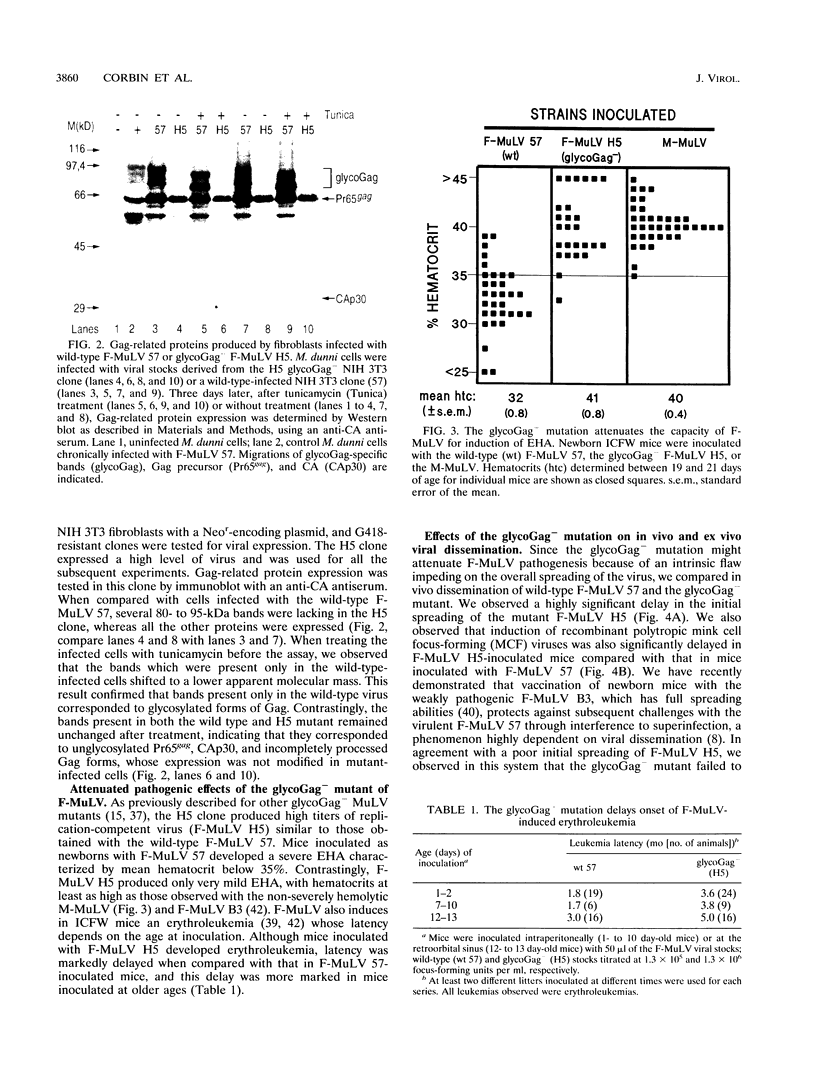
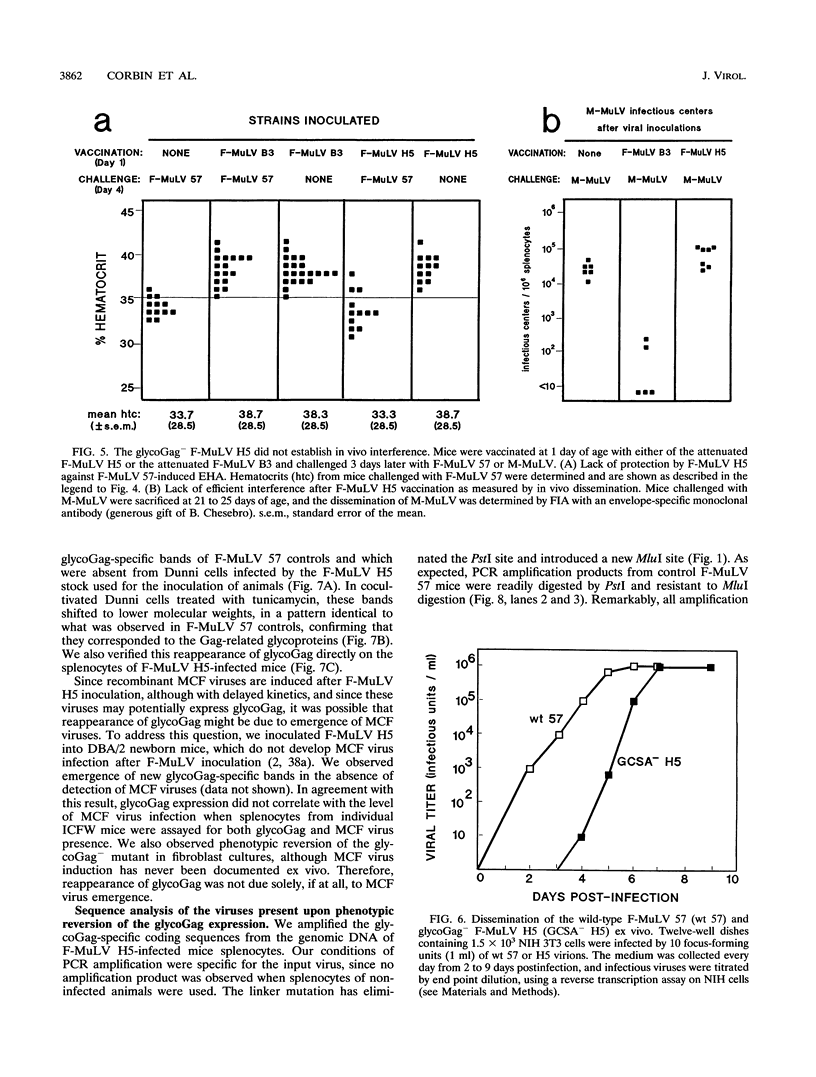
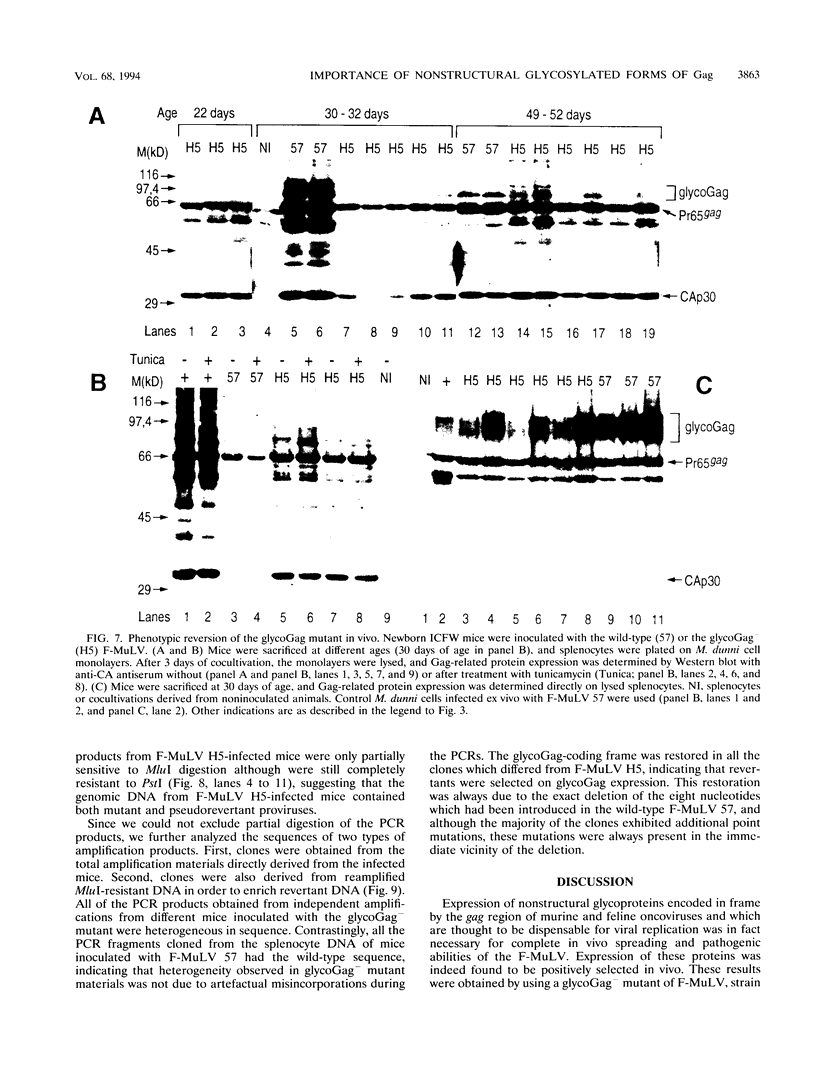
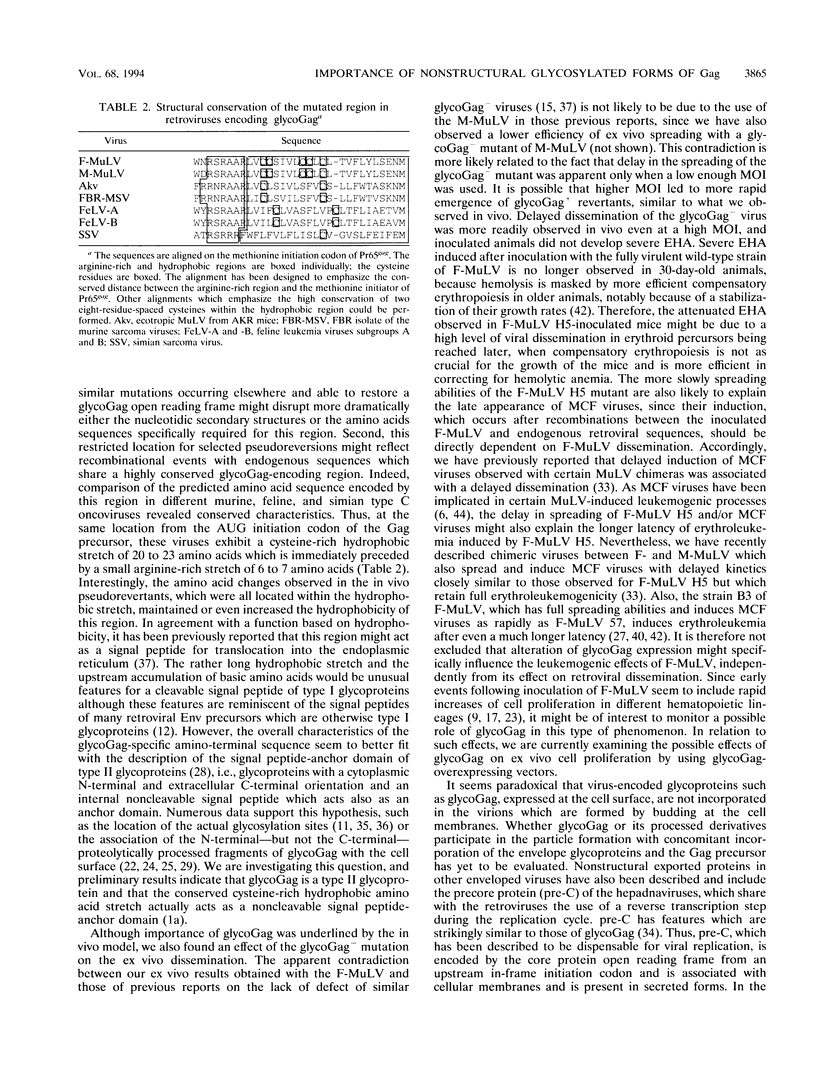
In addition to the Gag-Pol and Env precursors whose translation initiates at AUG codons, murine, feline, and simian type C oncoviruses also express glycosylated Gag-Pol precursors (glycoGag), glycoGag translation is initiated at CUG codons located upstream of the Gag AUG initiation codon. In contrast to Gag, glycoGag is translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum and is absent from virions. Since glycoGag has been described to be dispensable ex vivo, we investigated the in vivo effects of a glycoGag- mutation in the Friend murine leukemia virus (F-MuLV). F-MuLV induces severe early hemolytic anemia and subsequent erythroleukemia within 2 months after inoculation of newborn mice. We obtained a glycoGag- F-MuLV, strain H5, by inserting an octanucleotide linker downstream of the CUG codon leading to the reading of a stop codon in all reading frames upstream of the Gag AUG. F-MuLV H5 did not induce severe early hemolytic anemia, and latency of erythroleukemia was significantly increased most likely because of an approximately 1-week delay in the in vivo spreading. Accordingly, induction of recombinant polytropic viruses was also significantly delayed. Close examination of ex vivo spreading kinetics also showed a slower dissemination of F-MuLV H5. Western blot (immunoblot) performed after inoculation of newborn mice with this glycoGag- virus indicated the emergence of new glycoGag+ viruses. PCR analyses with F-MuLV-specific primers demonstrated in vivo pseudoreversions restoring the glycoGag reading frame. Our results demonstrated that glycoGag expression is positively selected and essential for full spreading and pathogenic abilities.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergholz C. M. Synthesis of virus-specific proteins in simian sarcoma virus-transformed primate cells. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. S., Sitbon M., Portis J. L. The endogenous mink cell focus-forming (MCF) gp70 linked to the Rmcf gene restricts MCF virus replication in vivo and provides partial resistance to erythroleukemia induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1535–1546. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Wehrly K., Nishio J. Effect of murine host genotype on MCF virus expression, latency, and leukemia cell type of leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia helper virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Evans L. Leukemia induction by a new strain of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: synergistic effect of Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):63–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.63-70.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin A., Sitbon M. Protection against retroviral diseases after vaccination is conferred by interference to superinfection with attenuated murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5146–5152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5146-5152.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Brightman B. K., Chandy K. G., Fan H. Characterization of a preleukemic state induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: evidence for two infection events during leukemogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4875–4879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. A., Fan H. Sequence relationship of glycosylated and unglycosylated gag polyproteins of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):41–51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.41-51.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards S. A., Fan H. gag-Related polyproteins of Moloney murine leukemia virus: evidence for independent synthesis of glycosylated and unglycosylated forms. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):551–563. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.551-563.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerbrok H., D'Auriol L., Vaquero C., Sitbon M. Functional tolerance of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope signal peptide to mutations in the amino-terminal and hydrophobic regions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5114–5118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5114-5118.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Dresler S., Kabat D. Synthesis and glycosylation of polyprotein precursors to the internal core proteins of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1977 Dec;24(3):865–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.3.865-874.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Morrison R. P., Malik F. G., Portis J., Britt W. J. A neutralizable epitope common to the envelope glycoproteins of ecotropic, polytropic, xenotropic, and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6176–6183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6176-6183.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Chute H., Chao E., Feuerman M. Construction and characterization of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants unable to synthesize glycosylated gag polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5965–5969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sudo T., Iizuka M., Kobayashi S., Nishio S., Kano S., Minato N. Generation of continuous large granular lymphocyte lines by interleukin 2 from the spleen cells of mice infected with Moloney leukemia virus. Involvement of interleukin 3. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):833–849. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Morita C., Miyake S., Ito T., Okabayashi M., Sano K., Nakai M., Hirai K., Kato S. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gag antigens on the surface of a cell line persistently infected with HIV-1 that highly expresses HIV-1 antigens. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Ringler D. J., Mori K., Panicali D. L., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90097-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J., Nowinski R. C., Emery S. Viral proteins expressed on the surface of murine leukemia cells. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):65–73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.65-73.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J., Nowinski R. C. Identification of the Gross cell surface antigen associated with murine leukemia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):315–322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.315-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. Increased hematopoiesis in mice soon after infection by Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3665–3670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3665-3670.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naso R. B., Stanker L. H., Kopchick J. J., Ng V. L., Karshin W. L., Arlinghaus R. B. Further studies on the glycosylated gag gene products of Rauscher murine leukemia virus: identification of an N-terminal 45,000-dalton cleavage product. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1200–1206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1200-1206.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Smart J. E., Hayman M. J., Jarrett O. Polypeptides of feline leukemia virus: a glycosylated gag-related protein is released into culture fluids. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Boyse E. A., Stockert E. The G (Gross) leukemia antigen. Cancer Res. 1965 Jul;25(6):813–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Topology of eukaryotic type II membrane proteins: importance of N-terminal positively charged residues flanking the hydrophobic domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90507-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillemer E. A., Kooistra D. A., Witte O. N., Weissman I. L. Monoclonal antibody to the amino-terminal L sequence of murine leukemia virus glycosylated gag polyproteins demonstrates their unusual orientation in the cell membrane. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):413–421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.413-421.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Revesz K., Herz R. Identification of large glycosylated proteins recognized by monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 gag proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Aug;8(8):1341–1344. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., De Billy G., Wang P., Darlix J. L. CUG initiation codon used for the synthesis of a cell surface antigen coded by the murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Roy C., Wang P. A., Erard M., Housset V., Gabus C., Paoletti C., Darlix J. L. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in dimer formation of murine leukemia virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.774-783.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J., Corbin A., Pozo F., Orsoni S., Sitbon M. Sequences responsible for the distinctive hemolytic potentials of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses are dispersed but confined to the psi-gag-PR region. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5478–5486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5478-5486.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., van Eenbergen J., Liskamp R. M., Bloemers H. P. Structure of glycosylated and unglycosylated gag and gag-pol precursor proteins of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):841–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.841-859.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Lockhart S. M., Rabin E. M., Oroszlan S. Structure of glycosylated and unglycosylated gag polyproteins of Rauscher murine leukemia virus: carbohydrate attachment sites. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):581–592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.581-592.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Deletion mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus which lack glycosylated gag protein are replication competent. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):538–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.538-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang F., Huang H., Revesz K., Chen H. C., Herz R., Pinter A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the human immunodeficiency virus matrix protein, p17gag: identification of epitopes exposed at the surfaces of infected cells. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4798–4804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4798-4804.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Evans L., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Analysis of two strains of Friend murine leukemia viruses differing in ability to induce early splenomegaly: lack of relationship with generation of recombinant mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):389–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.389-393.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., d'Auriol L., Ellerbrok H., André C., Nishio J., Perryman S., Pozo F., Hayes S. F., Wehrly K., Tambourin P. Substitution of leucine for isoleucine in a sequence highly conserved among retroviral envelope surface glycoproteins attenuates the lytic effect of the Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5932–5936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder H. W., Jr, Stockert E., Fleissner E. Characterization of molecular species carrying gross cell surface antigen. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):302–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.302-314.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Moroni C., Coffin J. M. Virological events leading to spontaneous AKR thymomas. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1273–1285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1273-1285.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tounekti N., Mougel M., Roy C., Marquet R., Darlix J. L., Paoletti J., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Effect of dimerization on the conformation of the encapsidation Psi domain of Moloney murine leukemia virus RNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90726-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Yoshiki T., Fleissner E. A core polyprotein of murine leukemia virus on the surface of mouse leukemia cells. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendling F., Moreau-Gachelin F., Tambourin P. Emergence of tumorigenic cells during the course of Friend virus leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]