Abstract
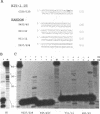
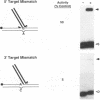
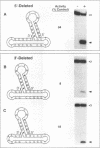
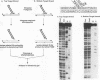
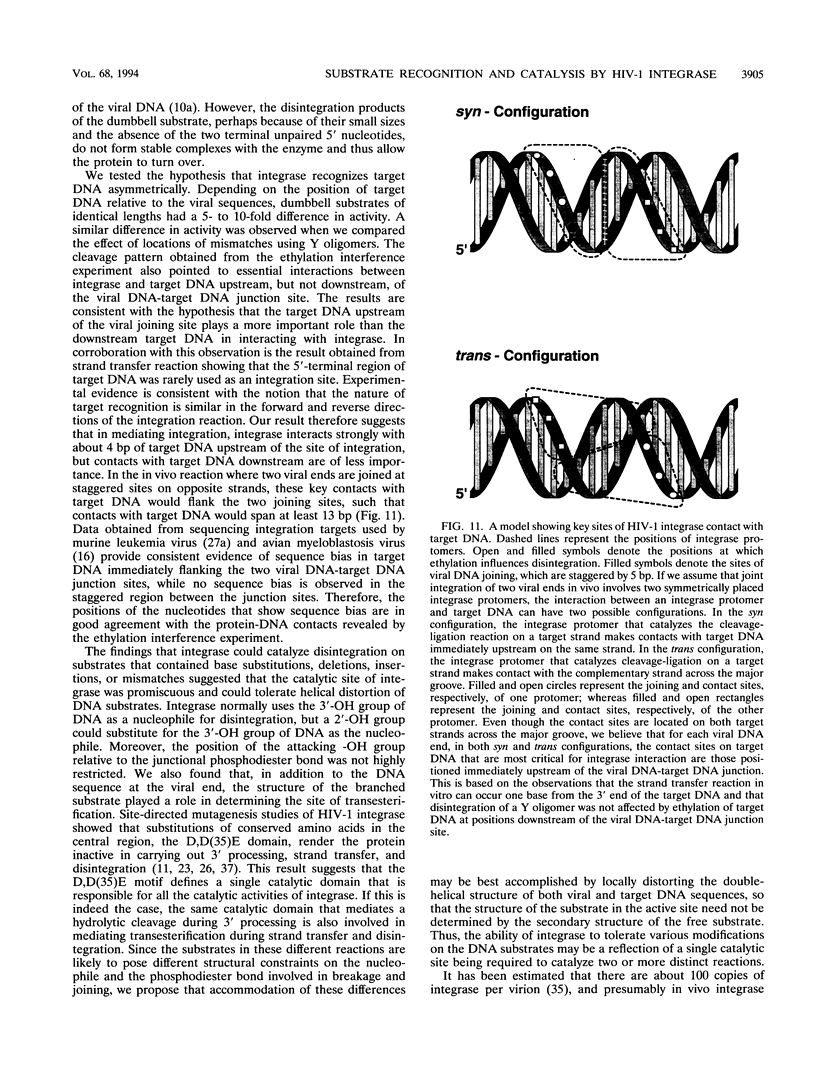
The integrase encoded by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is required for integration of viral DNA into the host cell chromosome. In vitro, integrase mediates a concerted cleavage-ligation reaction (strand transfer) that results in covalent attachment of viral DNA to target DNA. With a substrate that mimics the strand transfer product, integrase carries out disintegration, the reverse of the strand transfer reaction, resolving this integration intermediate into its viral and target DNA parts. We used a set of disintegration substrates to study the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 integrase and the interaction between the protein and the viral and target DNA sequence. One substrate termed dumbbell consists of a single oligonucleotide that can fold to form a structure that mimics the integration intermediate. Kinetic analysis using the dumbbell substrate showed that integrase turned over, establishing that HIV-1 integrase is an enzyme. Analysis of the disintegration activity on the dumbbell substrate and its derivatives showed that both the viral and target DNA parts of the molecule were required for integrase recognition. Integrase recognized target DNA asymmetrically: the target DNA upstream of the viral DNA joining site played a much more important role than the downstream target DNA in protein-DNA interaction. The site of transesterification was determined by both the DNA sequence of the viral DNA end and the structure of the branched substrate. Using a series of disintegration substrates with various base modifications, we found that integrase had relaxed structural specificity for the hydroxyl group used in transesterification and could tolerate distortion of the double-helical structure of these DNA substrates.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blommers M. J., Walters J. A., Haasnoot C. A., Aelen J. M., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Hilbers C. W. Effects of base sequence on the loop folding in DNA hairpins. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7491–7498. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O. Integration of retroviral DNA. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Integration of human immunodeficiency virus DNA: adduct interference analysis of required DNA sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3458–3462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Engelman A., Palmer I., Wingfield P., Craigie R. Domains of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for polynucleotidyl transfer and zinc binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K., Bushman F. D., Engelman A. A rapid in vitro assay for HIV DNA integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2729–2734. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison V., Abrams H., Roe T., Lifson J., Brown P. Human immunodeficiency virus integration in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2711–2715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2711-2715.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Craigie R. Identification of conserved amino acid residues critical for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase function in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6361–6369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6361-6369.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Mizuuchi K., Craigie R. HIV-1 DNA integration: mechanism of viral DNA cleavage and DNA strand transfer. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1211–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Integration of mini-retroviral DNA: a cell-free reaction for biochemical analysis of retroviral integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gates C. A., Cox M. M. FLP recombinase is an enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4628–4632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Inman R. B., Vora A. C., Fitzgerald M. L. Comparison of DNA binding and integration half-site selection by avian myeloblastosis virus integrase. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2628–2636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2628-2636.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Mumm S. R. Unraveling retrovirus integration. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90707-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirao I., Nishimura Y., Naraoka T., Watanabe K., Arata Y., Miura K. Extraordinary stable structure of short single-stranded DNA fragments containing a specific base sequence: d(GCGAAAGC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2223–2231. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirao I., Nishimura Y., Tagawa Y., Watanabe K., Miura K. Extraordinarily stable mini-hairpins: electrophoretical and thermal properties of the various sequence variants of d(GCGAAAGC) and their effect on DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3891–3896. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. S., Coleman J., Merkel G. W., Laue T. M., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase functions as a multimer and can turn over catalytically. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16037–16040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R. A., Merkel G., Kulkosky J., Leis J., Skalka A. M. The avian retroviral IN protein is both necessary and sufficient for integrative recombination in vitro. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90290-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Jones K. S., Katz R. A., Mack J. P., Skalka A. M. Residues critical for retroviral integrative recombination in a region that is highly conserved among retroviral/retrotransposon integrases and bacterial insertion sequence transposases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2331–2338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Schneider C. L., Robbins H. L., Callahan P. L., LeGrow K., Roth E., Schleif W. A., Emini E. A. Requirement of active human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase enzyme for productive infection of human T-lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7414–7419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7414-7419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Rose R. B., Varmus H. E. Both substrate and target oligonucleotide sequences affect in vitro integration mediated by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase protein produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2359–2368. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2359-2368.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Shiue L., Varmus H. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of HIV-1 integrase demonstrates differential effects on integrase functions in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2113–2119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Sil A., Varmus H. E. Retroviral integration into minichromosomes in vitro. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):291–303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Billich A. The N-terminal region of HIV-1 integrase is required for integration activity, but not for DNA-binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91708-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Dickson M. L., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integration protein: DNA sequence requirements for cleaving and joining reactions. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3593–3601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3593-3601.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Chow S. A., Brown P. O. Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase expressed in Escherichia coli and analysis of variants with amino-terminal mutations. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):425–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.425-437.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Oude Groeneger A. M., Plasterk R. H. Identification of the catalytic and DNA-binding region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Yeheskiely E., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Plasterk R. H. Site-specific hydrolysis and alcoholysis of human immunodeficiency virus DNA termini mediated by the viral integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6691–6698. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Bolk M. W., Vink C., Plasterk R. H. DNA binding properties of the integrase proteins of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3821–3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Mutational analysis of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9598–9602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]