Abstract
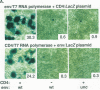
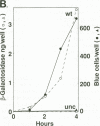
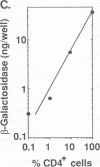
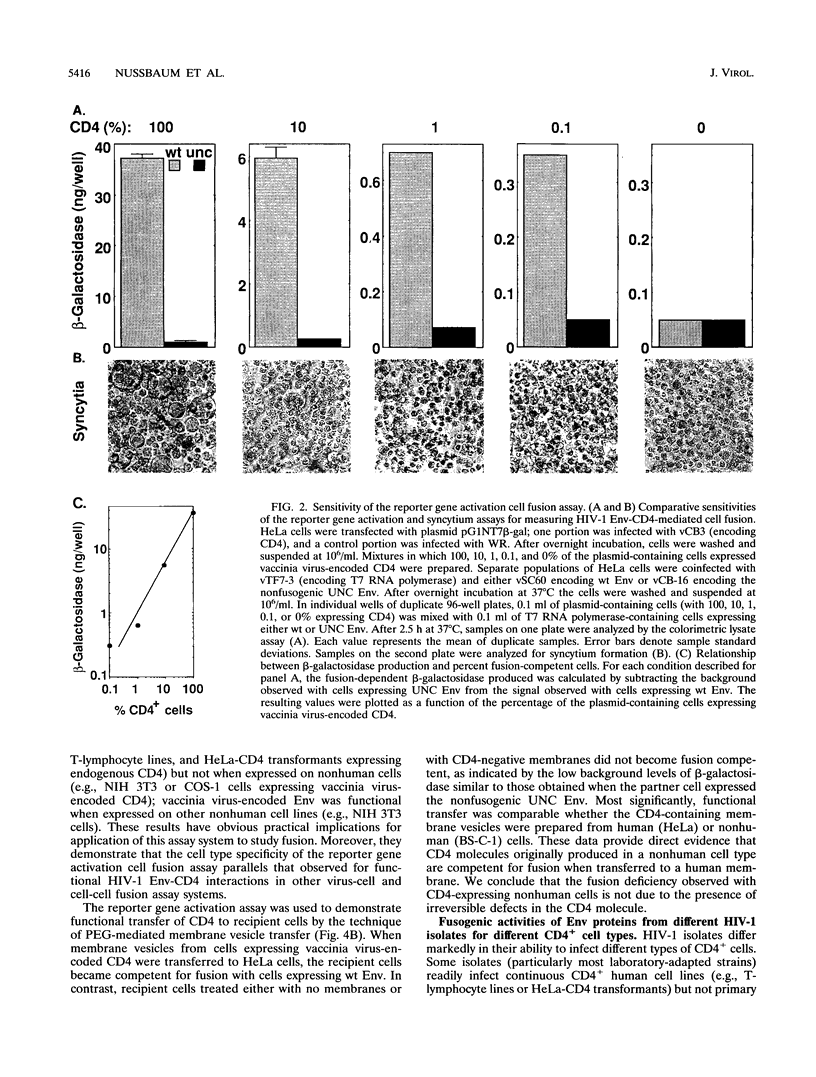
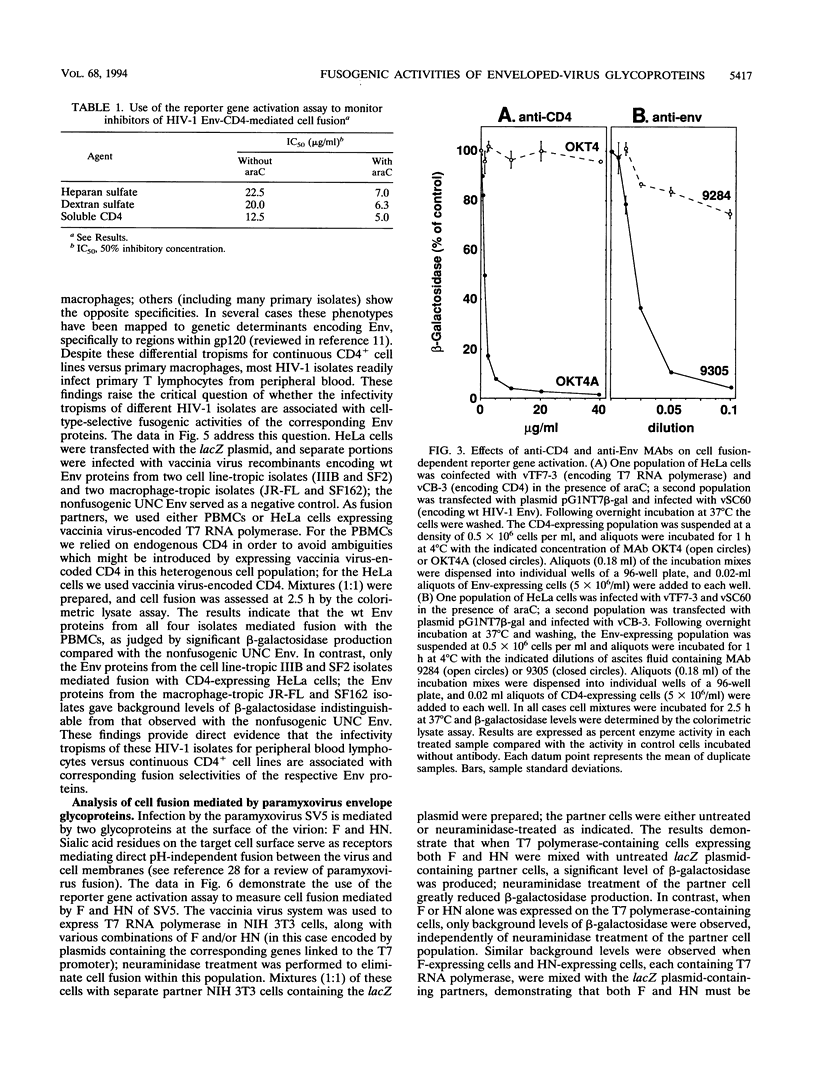
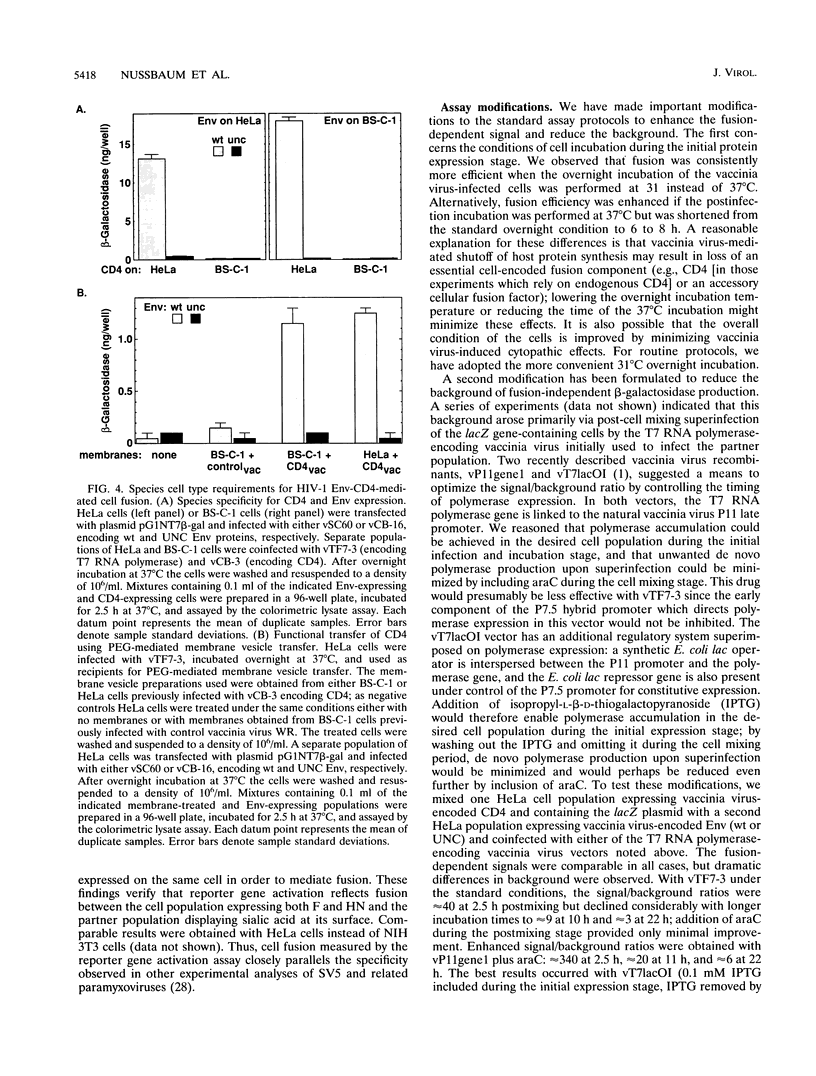
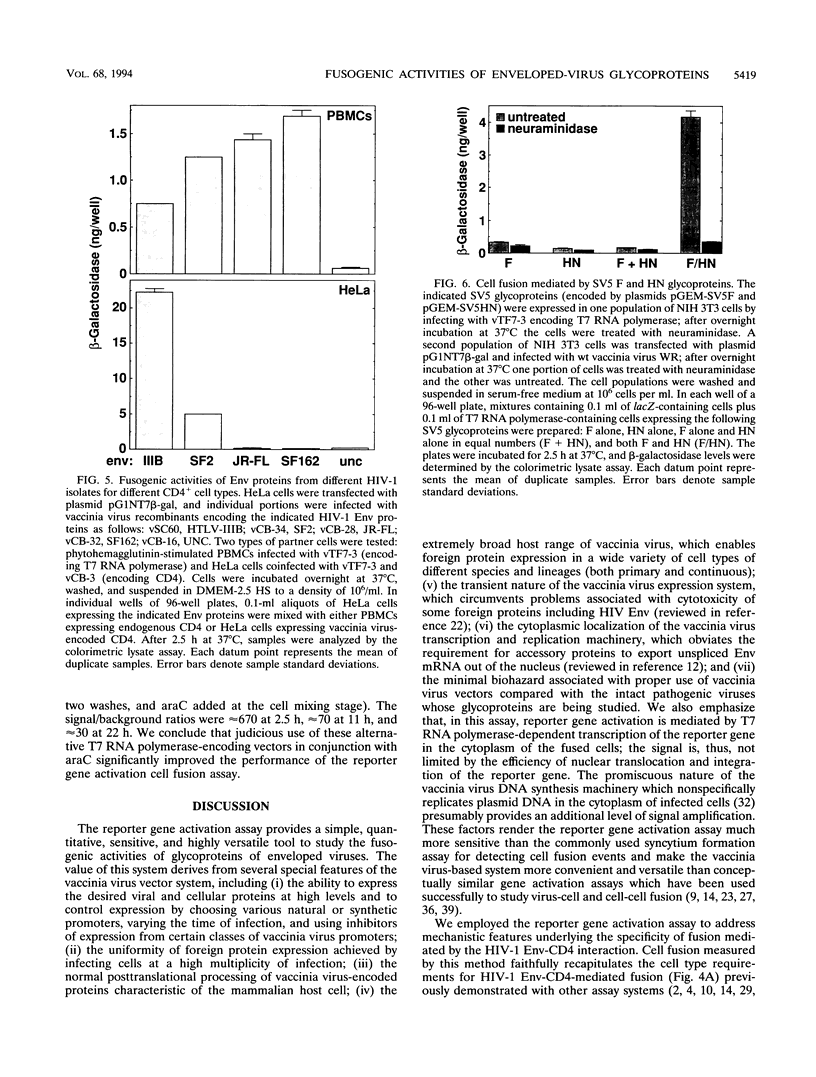
The fusogenic activities of enveloped-virus glycoproteins were analyzed by using a quantitative, sensitive, rapid, and highly versatile recombinant vaccinia virus-based assay measuring activation of a reporter gene upon fusion of two distinct cell populations. One population uniformly expressed vaccinia virus-encoded viral glycoproteins mediating specific binding and fusion activities; the other expressed the corresponding cellular receptor(s). The cytoplasm of one population also contained vaccinia virus-encoded bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase; the cytoplasm of the other contained a transfected plasmid with the Escherichia coli lacZ gene linked to the T7 promoter. When the two populations were mixed, cell fusion resulted in activation of the LacZ gene in the cytoplasm of the fused cells; beta-galactosidase activity was assessed by colorimetric assay of detergent cell lysates or by in situ staining. We applied this approach to study the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein (Env)-CD4 interaction. Beta-Galactosidase was detected within 1 h after cell mixing and accumulated over the next several hours. Cell fusion dependence was demonstrated by the strict requirement for both CD4 and functional Env expression and by the inhibitory effects of known fusion-blocking monoclonal antibodies and pharmacological agents. Quantitative measurements indicated much higher sensitivity compared with analysis of syncytium formation. The assay was used to probe mechanisms of the cell type specificity for Env-CD4-mediated fusion. In agreement with known restrictions, cell fusion occurred only when CD4 was expressed on a human cell type. Membrane vesicle transfer experiments indicated that CD4 initially produced in either human or nonhuman cells was functional when delivered to human cells, suggesting that the fusion deficiency with nonhuman cells was not associated with irreversible defects in CD4. We also demonstrated that the infectivity specificities of different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates for peripheral blood lymphocytes versus continuous CD4+ cell lines were associated with corresponding fusion selectivities of the respective recombinant Env proteins. The assay enabled analysis of the fusogenic activity of the fusion glycoprotein/hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5. This system provides a powerful tool to study fusion mechanisms mediated by enveloped-virus glycoproteins, as well as to screen fusion-blocking antibodies and pharmacological agents.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander W. A., Moss B., Fuerst T. R. Regulated expression of foreign genes in vaccinia virus under the control of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase and the Escherichia coli lac repressor. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2934–2942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2934-2942.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashorn P. A., Berger E. A., Moss B. Human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein/CD4-mediated fusion of nonprimate cells with human cells. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2149–2156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2149-2156.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Dimitrov D. S., Blumenthal R., Berger E. A. The block to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion in animal cells expressing human CD4 can be overcome by a human cell component(s). Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):483–491. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Kennedy P. E., Michaels F., Berger E. A. Expression of foreign genes in cultured human primary macrophages using recombinant vaccinia virus vectors. Gene. 1994 May 16;142(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder C. C., Nussbaum O., Gutheil W. G., Bachovchin W. W., Berger E. A. CD26 antigen and HIV fusion? Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1156–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.7909959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callebaut C., Krust B., Jacotot E., Hovanessian A. G. T cell activation antigen, CD26, as a cofactor for entry of HIV in CD4+ cells. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2045–2050. doi: 10.1126/science.7903479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Quiroga M., Tung J. W., Dina D., Levy J. A. Viral determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 T-cell or macrophage tropism, cytopathogenicity, and CD4 antigen modulation. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4390–4398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4390-4398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciminale V., Felber B. K., Campbell M., Pavlakis G. N. A bioassay for HIV-1 based on Env-CD4 interaction. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Nov;6(11):1281–1287. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Blanc D., Weiss R. A. Specific cell surface requirements for the infection of CD4-positive cells by human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 and by Simian immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90904-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Garrett E. D. A comparison of regulatory features in primate lentiviruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):387–393. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragic T., Charneau P., Clavel F., Alizon M. Complementation of murine cells for human immunodeficiency virus envelope/CD4-mediated fusion in human/murine heterokaryons. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4794–4802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4794-4802.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durda P. J., Bacheler L., Clapham P., Jenoski A. M., Leece B., Matthews T. J., McKnight A., Pomerantz R., Rayner M., Weinhold K. J. HIV-1 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies induced by a synthetic peptide. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Sep;6(9):1115–1123. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Koenig S., Moss B. Biological and immunological properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein: analysis of proteins with truncations and deletions expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):31–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.31-41.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eustice D. C., Feldman P. A., Colberg-Poley A. M., Buckery R. M., Neubauer R. H. A sensitive method for the detection of beta-galactosidase in transfected mammalian cells. Biotechniques. 1991 Dec;11(6):739-40, 742-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helseth E., Kowalski M., Gabuzda D., Olshevsky U., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Rapid complementation assays measuring replicative potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein mutants. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2416-2420.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Baba M., Sato A., Pauwels R., De Clercq E., Shigeta S. Inhibitory effect of dextran sulfate and heparin on the replication of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1987 Jul;7(6):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimpton J., Emerman M. Detection of replication-competent and pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus with a sensitive cell line on the basis of activation of an integrated beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2232-2239.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A. Paramyxovirus fusion: a hypothesis for changes. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):1–11. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munzer J. S., Silvius J. R., Blostein R. Delivery of ion pumps from exogenous membrane-rich sources into mammalian red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5202–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page K. A., Landau N. R., Littman D. R. Construction and use of a human immunodeficiency virus vector for analysis of virus infectivity. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5270–5276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5270-5276.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter Z., Reiter Y., Fishelson Z., Shinitzky M., Kessler A., Loyter A., Nussbaum O., Rubinstein M. Resistance to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity (in K-562 cells) does not correlate with class I MHC antigen levels. Immunobiology. 1991 Sep;183(1-2):23–39. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80183-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocancourt D., Bonnerot C., Jouin H., Emerman M., Nicolas J. F. Activation of a beta-galactosidase recombinant provirus: application to titration of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and HIV-infected cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2660–2668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2660-2668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Ting R., Langlois A. J., Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Javaherian K., Matthews T. J. Characteristics of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody to the HIV envelope glycoprotein. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Jun;4(3):187–197. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usdin T. B., Brownstein M. J., Moss B., Isaacs S. N. SP6 RNA polymerase containing vaccinia virus for rapid expression of cloned genes in tissue culture. Biotechniques. 1993 Feb;14(2):222–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]