Abstract
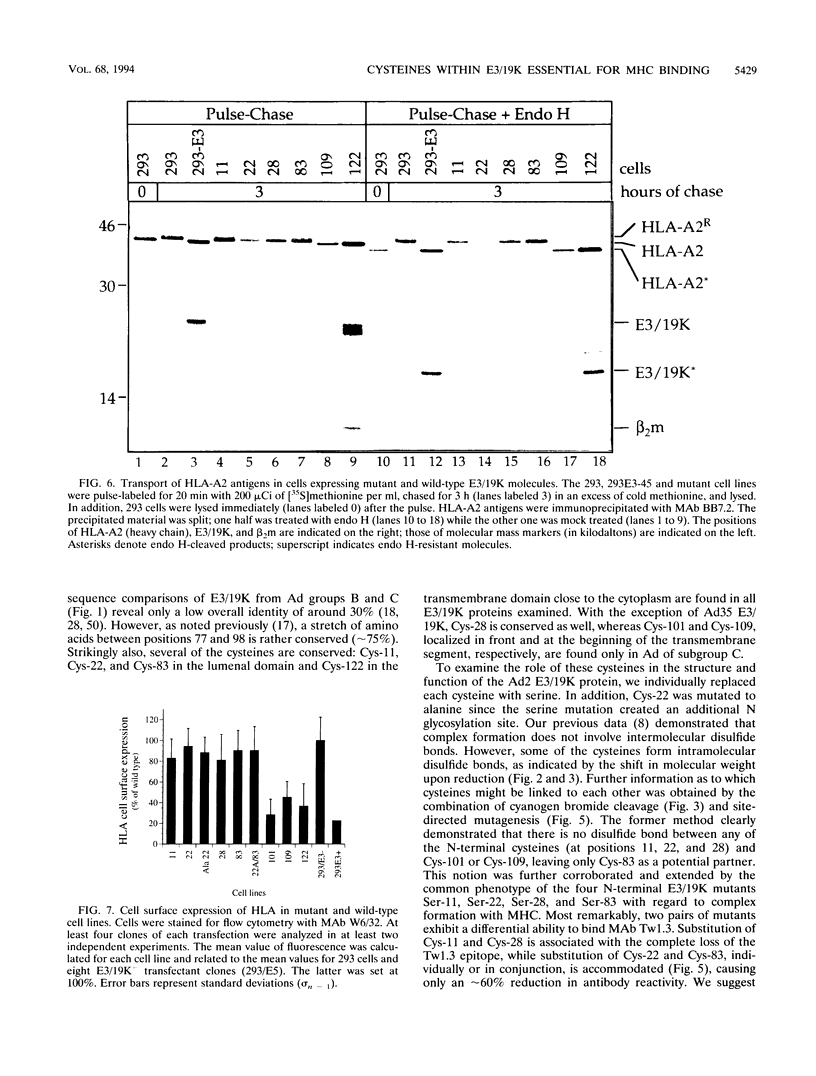
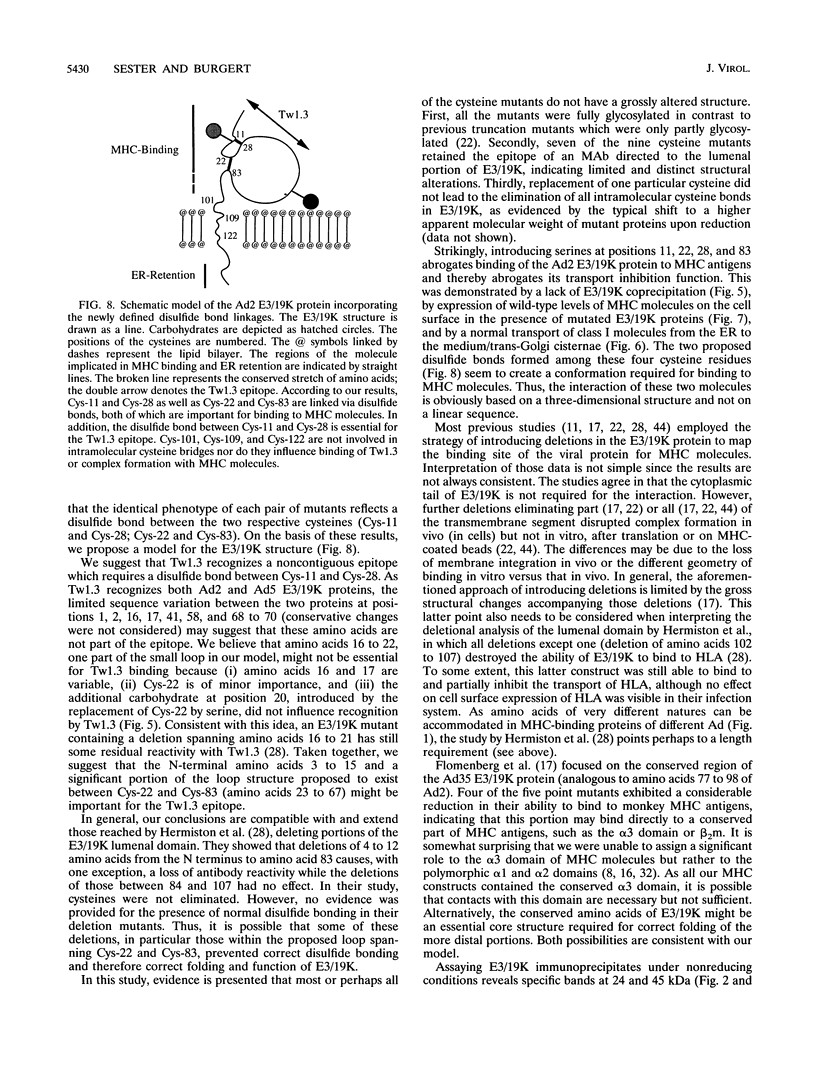
The E3/19K protein of human adenovirus type 2 is a resident transmembrane glycoprotein of the endoplasmic reticulum. Its capacity to associate with class I histocompatibility (MHC) antigens abrogates cell surface expression and the antigen presentation function of MHC antigens. At present, it is unclear exactly which structure of the E3/19K protein mediates binding to MHC molecules. Apart from a stretch of approximately 20 conserved amino acids in front of the transmembrane segment, E3/19K molecules from different adenovirus subgroups (B and C) share little homology. Remarkably, the majority of cysteines are conserved. In this report, we examined the importance of cysteine residues for the structure and function of E3/19K. We show that E3/19K contains intramolecular disulfide bonds. By using site-directed mutagenesis, individual cysteines were replaced by serines and mutant proteins were stably expressed in 293 cells. On the basis of the differential binding of monoclonal antibody Tw1.3 and cyanogen bromide cleavage experiments, a structural model of E3/19K is proposed, in which Cys-11 and Cys-28 as well as Cys-22 and Cys-83 are linked by disulfide bonds. Both disulfide bonds (all four cysteines) are absolutely critical for the interaction with human MHC antigens. This was demonstrated by three criteria: loss of E3/19K coprecipitation, lack of transport inhibition, and normal cell surface expression of MHC molecules. Mutation of the three other cysteines had no effect. This indicates that a conformational determinant based on two disulfide bonds is crucial for the function of the E3/19K molecule, namely, to bind and to inhibit transport of MHC antigens.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., McMichael A., Peterson P. A. Reduced allorecognition of adenovirus-2 infected cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3960–3966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M., Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Parham P. Structure, function, and diversity of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:253–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braciale T. J., Braciale V. L. Antigen presentation: structural themes and functional variations. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):124–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90096-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. The E3/19K protein of adenovirus type 2 binds to the domains of histocompatibility antigens required for CTL recognition. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2019–2026. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Maryanski J. L., Kvist S. "E3/19K" protein of adenovirus type 2 inhibits lysis of cytolytic T lymphocytes by blocking cell-surface expression of histocompatibility class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cladaras C., Wold W. S. DNA sequence of the early E3 transcription unit of adenovirus 5. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):28–43. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Bennink J. R., Yewdell J. W. Retention of adenovirus E19 glycoprotein in the endoplasmic reticulum is essential to its ability to block antigen presentation. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1629–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Yewdell J. W., Eisenlohr L. C., Johnson P. R., Bennink J. R. Antigen presentation requires transport of MHC class I molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):715–718. doi: 10.1126/science.2137259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen E., Cohen-Doyle M. F., Williams D. B. Efficient dissociation of the p88 chaperone from major histocompatibility complex class I molecules requires both beta 2-microglobulin and peptide. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1653–1661. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O. Consensus motifs and peptide ligands of MHC class I molecules. Semin Immunol. 1993 Apr;5(2):81–94. doi: 10.1006/smim.1993.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerbach D., Burgert H. G. Novel proteins associated with MHC class I antigens in cells expressing the adenovirus protein E3/19K. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3153–3161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Horwitz M. S. Sequence and genetic organization of adenovirus type 35 early region 3. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4431–4437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4431-4437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P., Szmulewicz J., Gutierrez E., Lupatkin H. Role of the adenovirus E3-19k conserved region in binding major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4778–4783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4778-4783.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Hall C. E., Cooney M. K. The Seattle Virus Watch. VII. Observations of adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Apr;105(4):362–386. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremont D. H., Matsumura M., Stura E. A., Peterson P. A., Wilson I. A. Crystal structures of two viral peptides in complex with murine MHC class I H-2Kb. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):919–927. doi: 10.1126/science.1323877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabathuler R., Kvist S. The endoplasmic reticulum retention signal of the E3/19K protein of adenovirus type 2 consists of three separate amino acid segments at the carboxy terminus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1803–1810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabathuler R., Lévy F., Kvist S. Requirements for the association of adenovirus type 2 E3/19K wild-type and mutant proteins with HLA antigens. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3679–3685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3679-3685.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. P., Saper M. A., Bjorkman P. J., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA-Aw68. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):692–696. doi: 10.1038/342692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Margulies D. H. The biochemistry and cell biology of antigen processing and presentation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:403–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Lundholm-Beauchamp U., Horswood R. L., Pernis B., Wold W. S., Chanock R. M., Prince G. A. Role of early region 3 (E3) in pathogenesis of adenovirus disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3823–3827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Tripp R. A., Sparer T., Gooding L. R., Wold W. S. Deletion mutation analysis of the adenovirus type 2 E3-gp19K protein: identification of sequences within the endoplasmic reticulum lumenal domain that are required for class I antigen binding and protection from adenovirus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5289–5298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5289-5298.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstenbach F., David V., Watkins S., Brenner M. B. Endoplasmic reticulum resident protein of 90 kilodaltons associates with the T- and B-cell antigen receptors and major histocompatibility complex antigens during their assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies W. A., Burgert H. G. E3/19K from adenovirus 2 is an immunosubversive protein that binds to a structural motif regulating the intracellular transport of major histocompatibility complex class I proteins. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1653–1664. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Lévy F. Early events in the assembly of MHC class I antigens. Semin Immunol. 1993 Apr;5(2):105–116. doi: 10.1006/smim.1993.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Ostberg L., Persson H., Philipson L., Peterson P. A. Molecular association between transplantation antigens and cell surface antigen in adenovirus-transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner H., Burgert H. G. Down-regulation of HLA antigens by the adenovirus type 2 E3/19K protein in a T-lymphoma cell line. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1442–1448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1442-1448.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Körner H., Fritzsche U., Burgert H. G. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates expression of adenovirus early region 3 proteins: implications for viral persistence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11857–11861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Srivastava P. K. Tumor rejection antigen gp96/grp94 is an ATPase: implications for protein folding and antigen presentation. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3143–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The three-dimensional structure of HLA-B27 at 2.1 A resolution suggests a general mechanism for tight peptide binding to MHC. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei Y. F., Wadell G. The nucleotide sequence of adenovirus type 11 early 3 region: comparison of genome type Ad11p and Ad11a. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90173-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J. A molecular model of MHC class-I-restricted antigen processing. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90122-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Brodsky F. M. Partial purification and some properties of BB7.2. A cytotoxic monoclonal antibody with specificity for HLA-A2 and a variant of HLA-A28. Hum Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(4):277–299. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Hall C., Rühlmann A., Sancho J., Terhorst C. The T-cell receptor zeta chain contains a GTP/GDP binding site. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):933–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Bhat B. M., Wold W. S., Peterson P. A. A short sequence in the COOH-terminus makes an adenovirus membrane glycoprotein a resident of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90226-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Adenoviruses of subgenera B, C, D, and E modulate cell-surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9665–9669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Nilsson T., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Structural and functional dissection of an MHC class I antigen-binding adenovirus glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1921–1927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawle F. C., Tollefson A. E., Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Mouse anti-adenovirus cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Inhibition of lysis by E3 gp19K but not E3 14.7K. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2031–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Martens I., Peterson P. A. Differential association between two human MHC class I antigens and an adenoviral glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):1003–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Williams J. Genetic analysis of adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;111:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69549-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Akusjärvi G., Pettersson U. Region E3 of human adenoviruses; differences between the oncogenic adenovirus-3 and the non-oncogenic adenovirus-2. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Katze M. G., Persson H., Philipson L. An adenovirus glycoprotein binds heavy chains of class I transplantation antigens from man and mouse. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):175–178. doi: 10.1038/299175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Tevethia S. S. Differential effect of adenovirus 2 E3/19K glycoprotein on the expression of H-2Kb and H-2Db class I antigens and H-2Kb- and H-2Db-restricted SV40-specific CTL-mediated lysis. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Deutscher S. L., Kapoor Q. S. The 19-kDa glycoprotein coded by region E3 of adenovirus. Purification, characterization, and structural analysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2424–2431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Gooding L. R. Region E3 of adenovirus: a cassette of genes involved in host immunosurveillance and virus-cell interactions. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90815-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. Cell biology of antigen processing and presentation to major histocompatibility complex class I molecule-restricted T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:1–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]