Abstract
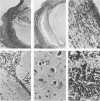
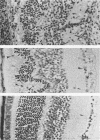
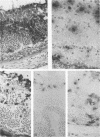
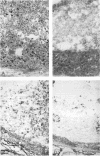
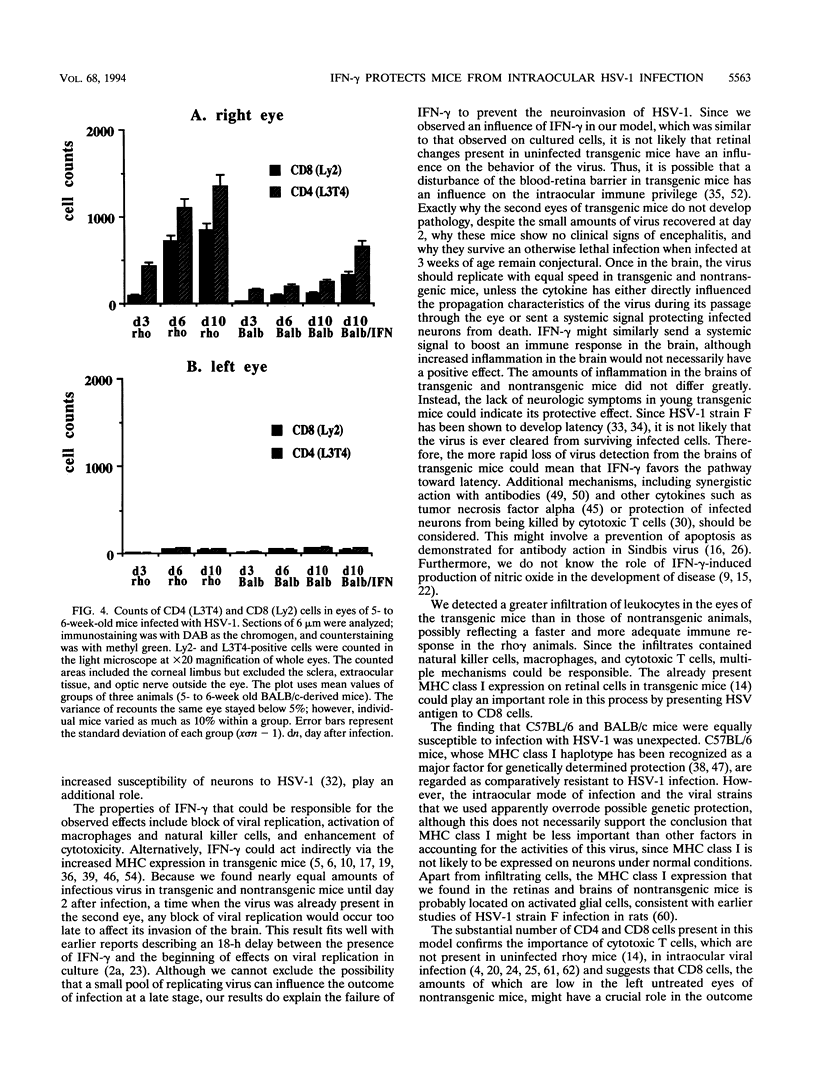
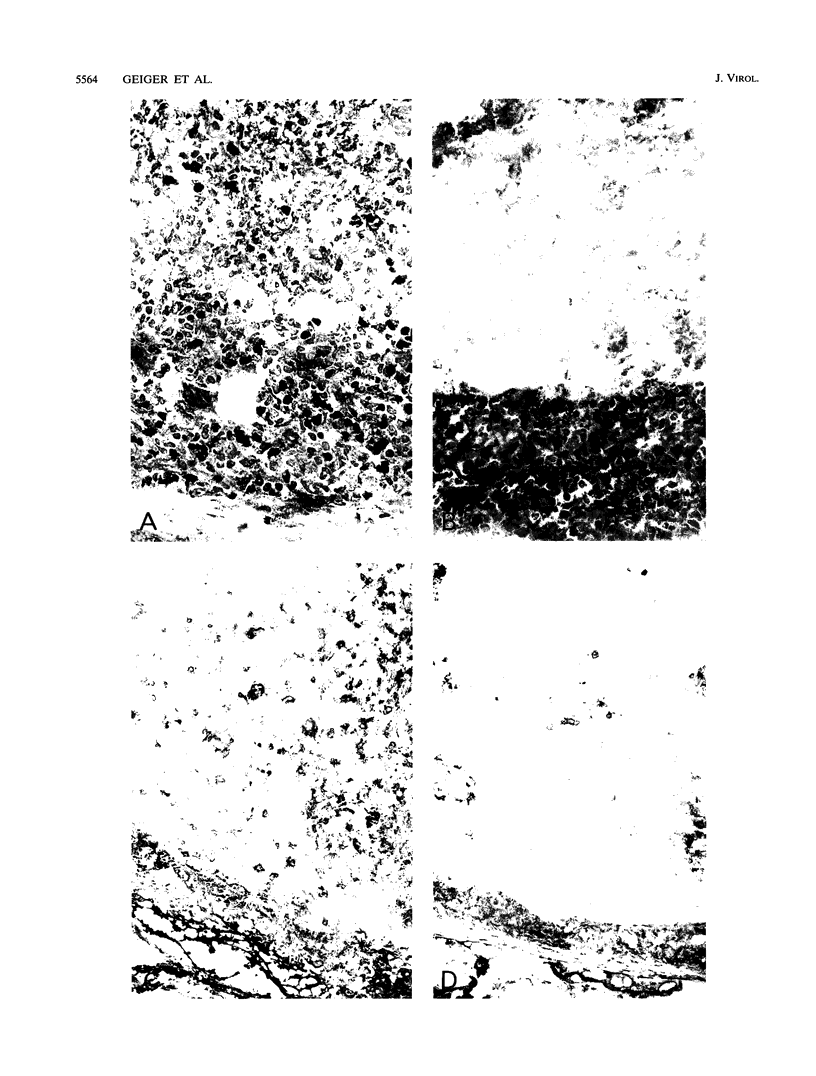
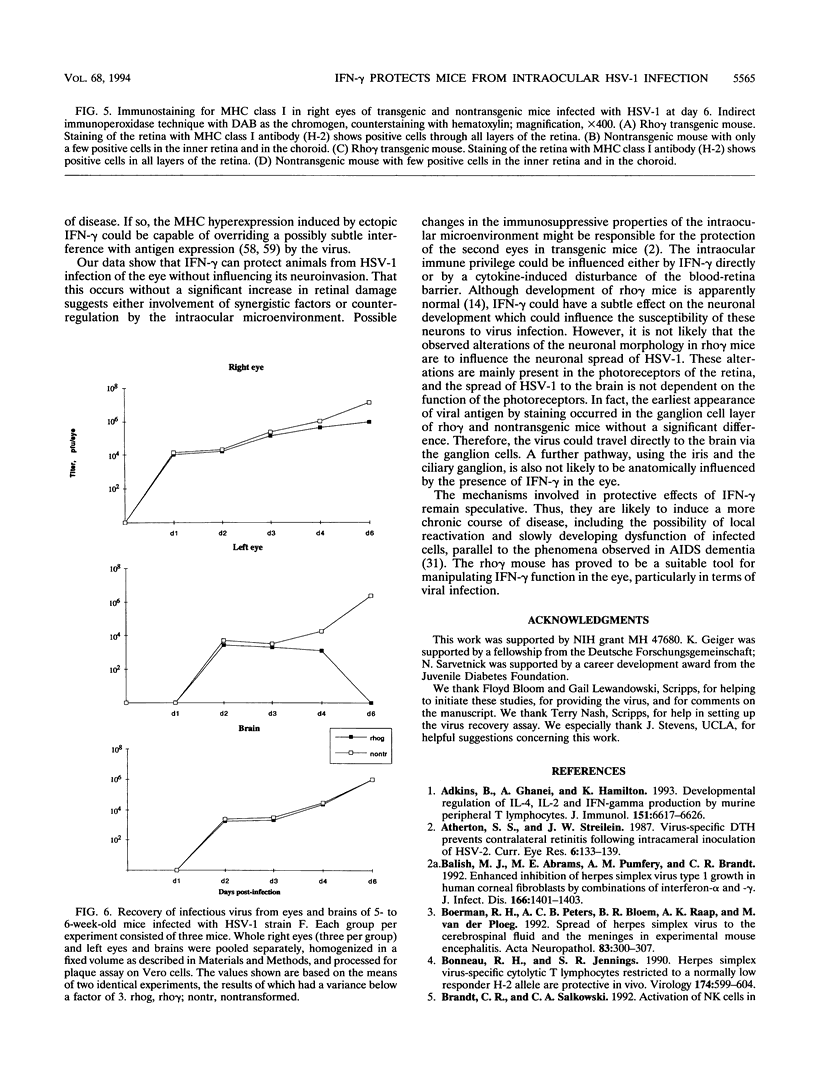
Transgenic (rho gamma) mice provide a model for studying the influence of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) produced in the eye on ocular and cerebral viral infection. To establish this model, we injected BALB/c- and C57BL/6-derived transgenic and nontransgenic mice of different ages intravitreally with herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) strain F. Eye and brain tissues of these mice were assessed for pathological and immunocytochemical changes. HSV-1 infection induced severe retinitis of the injected eyes and infection of the brain in all mice. In transgenic mice inoculated with HSV-1, the left, nontreated eyes were protected from retinitis, whereas nontransgenic mice developed bilateral retinitis. Additional intravitreal injection of IFN-gamma with the virus protected the noninoculated eyes of nontransgenic mice. Three-week-old nontransgenic mice died from HSV-1 infection, whereas transgenic mice of the same age and nontransgenic mice intravitreally treated with IFN-gamma survived. Ocular IFN-gamma production increased the extent of inflammation in transgenic mice but did not have a significant influence on the growth of HSV-1 until day 3 after inoculation and did not influence the neuroinvasion of this virus. Thus, the effects of IFN-gamma were not caused by an early block of viral replication. Possible mechanisms of IFN-gamma action include activation of the immune response, alteration of the properties of the virus, and direct protection of neurons.
Full text
PDF

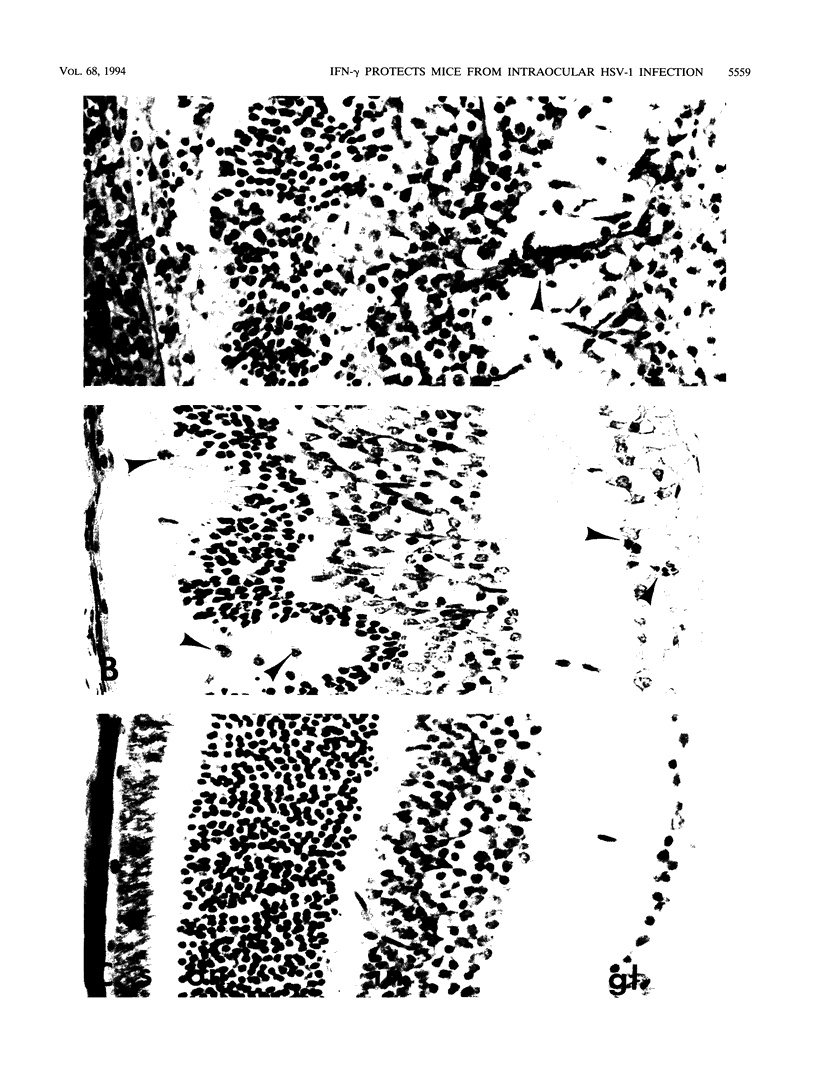
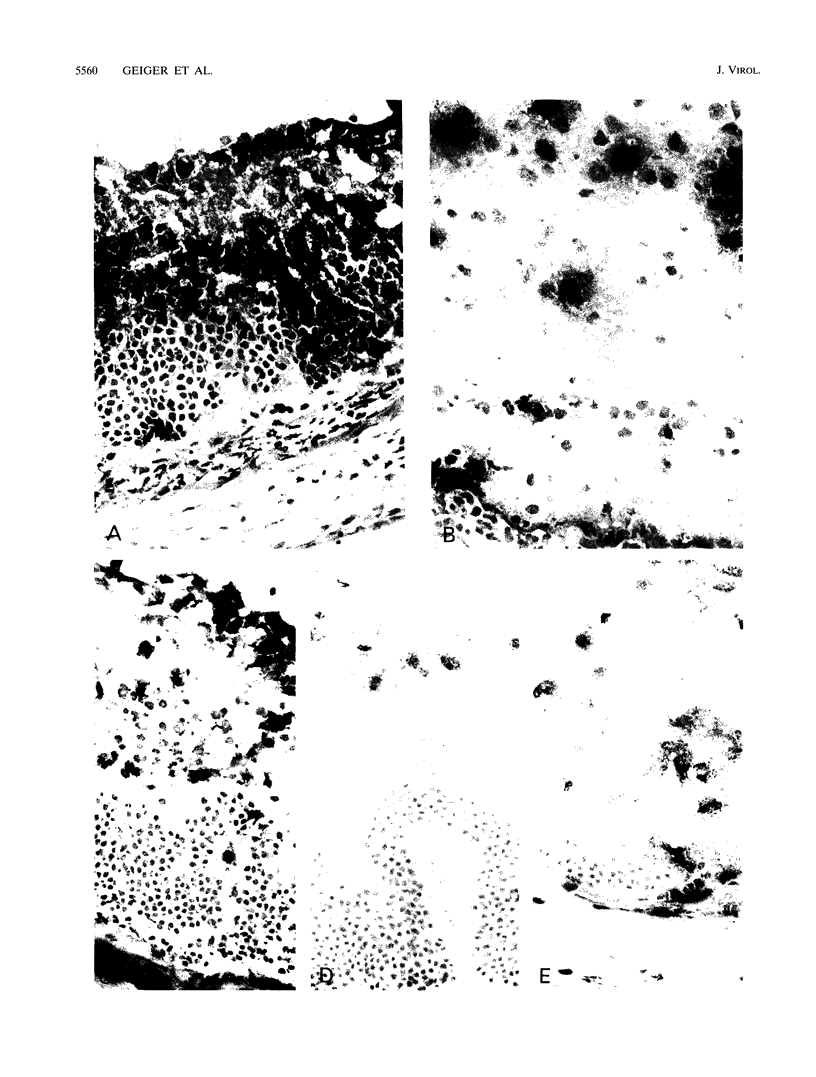



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Ghanei A., Hamilton K. Developmental regulation of IL-4, IL-2, and IFN-gamma production by murine peripheral T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6617–6626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton S. S., Streilein J. W. Virus-specific DTH prevents contralateral retinitis following intracameral inoculation of HSV-2. Curr Eye Res. 1987 Jan;6(1):133–139. doi: 10.3109/02713688709020080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balish M. J., Abrams M. E., Pumfery A. M., Brandt C. R. Enhanced inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 growth in human corneal fibroblasts by combinations of interferon-alpha and -gamma. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1401–1403. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerman R. H., Peters A. C., Bloem B. R., Raap A. K., van der Ploeg M. Spread of herpes simplex virus to the cerebrospinal fluid and the meninges in experimental mouse encephalitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(3):300–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00296793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau R. H., Jennings S. R. Herpes simplex virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocytes restricted to a normally low responder H-2 allele are protective in vivo. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):599–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charteris D. G., Lightman S. L. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) production in vivo in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis. Immunology. 1992 Mar;75(3):463–467. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousins S. W., McCabe M. M., Danielpour D., Streilein J. W. Identification of transforming growth factor-beta as an immunosuppressive factor in aqueous humor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1991 Jul;32(8):2201–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D. Evidence for antiviral effect of nitric oxide. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2446–2452. doi: 10.1172/JCI116479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Role of immune interferon in the monocytic differentiation of human promyelocytic cell lines induced by leukocyte conditioned medium. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):583–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denkins Y. M., Kripke M. L. Effect of UV irradiation on lethal infection of mice with Candida albicans. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 Feb;57(2):266–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb02285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Singer E. J., Graves M. C., Tourtellotte W. W., Stewart J. A., Schable C. A., Rhodes R. H., Vinters H. V. AIDS dementia complex complicated by cytomegalovirus encephalopathy. J Neurol. 1993;240(4):223–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00818709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartry D. S., Spalton D. J., Tilzey A., Hykin P. G. Acute retinal necrosis syndrome. Br J Ophthalmol. 1991 May;75(5):292–297. doi: 10.1136/bjo.75.5.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger K., Howes E., Gallina M., Huang X. J., Travis G. H., Sarvetnick N. Transgenic mice expressing IFN-gamma in the retina develop inflammation of the eye and photoreceptor loss. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994 May;35(6):2667–2681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goureau O., Lepoivre M., Courtois Y. Lipopolysaccharide and cytokines induce a macrophage-type of nitric oxide synthase in bovine retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):854–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90824-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin D. E., Levine B., Tyor W. R., Irani D. N. The immune response in viral encephalitis. Semin Immunol. 1992 Apr;4(2):111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel C. P., Detrick B., Hooks J. J. Evaluation of Ia expression in rat ocular tissues following inoculation with interferon-gamma. Exp Eye Res. 1990 Feb;50(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(90)90228-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks R. L., Tumpey T. M., Finnegan A. IFN-gamma and IL-2 are protective in the skin but pathologic in the corneas of HSV-1-infected mice. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3023–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. C., Male D. K., Lantos P. L. Adhesion of lymphocytes to cerebral microvascular cells: effects of interferon-gamma, tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):677–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inatsuki A., Yasukawa M., Kobayashi Y. Functional alterations of herpes simplex virus-specific CD4+ multifunctional T cell clones following infection with human T lymphotropic virus type I. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1327–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang L. Q., Jorquera M., Streilein J. W. Subretinal space and vitreous cavity as immunologically privileged sites for retinal allografts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Nov;34(12):3347–3354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karupiah G., Xie Q. W., Buller R. M., Nathan C., Duarte C., MacMicking J. D. Inhibition of viral replication by interferon-gamma-induced nitric oxide synthase. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1445–1448. doi: 10.1126/science.7690156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotzbücher A., Mittnacht S., Kirchner H., Jacobsen H. Different effects of IFN gamma and IFN alpha/beta on "immediate early" gene expression of HSV-1. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):487–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90322-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolaitis G., Doymaz M., Rouse B. T. Demonstration of MHC class II-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mice against herpes simplex virus. Immunology. 1990 Sep;71(1):101–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzushima K., Isobe K., Morishima T., Takatsuki A., Nakashima I. Inhibitory effect of herpes simplex virus infection to target cells on recognition of minor histocompatibility antigens by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4536–4540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Hardwick J. M., Trapp B. D., Crawford T. O., Bollinger R. C., Griffin D. E. Antibody-mediated clearance of alphavirus infection from neurons. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):856–860. doi: 10.1126/science.1658936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski G. A., Lo D., Bloom F. E. Interference with major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted antigen presentation in the brain by herpes simplex virus type 1: a possible mechanism of evasion of the immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2005–2009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchiari M. A., Pereira C. A. A major role of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma during mouse hepatitis virus type 3 infection. II. Age-dependent resistance. Immunobiology. 1990 Aug;181(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80163-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. J. Ocular manifestations of AIDS. Br J Hosp Med. 1989 Sep;42(3):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E., Gamble S. R. How do CTL control virus infections? Evidence for prelytic halt of herpes simplex. Viral Immunol. 1992 Spring;5(1):81–91. doi: 10.1089/vim.1992.5.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Achim C. L., Ge N., DeTeresa R., Terry R. D., Wiley C. A. Spectrum of human immunodeficiency virus-associated neocortical damage. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R., Woo W. Possible neural basis for age-dependent resistance to neurologic disease from herpes simplex virus. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Nov;81(2-3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignier B., Norrild B., Roizman B. Colonization of murine ganglia by a superinfecting strain of herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):702–708. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.702-708.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesburn A. B., Dickinson R., Radnoti M., Green M. J. Experimental reactivation of ocular herpes simplex in rabbits. Surv Ophthalmol. 1976 Sep-Oct;21(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(76)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederkorn J. Y. Immune privilege and immune regulation in the eye. Adv Immunol. 1990;48:191–226. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. H., Latina M. A. Effects of gamma-interferon on human trabecular meshwork cell phagocytosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Jun;34(7):2228–2236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepose J. S., Whittum-Hudson J. A. An immunogenetic analysis of resistance to herpes simplex virus retinitis in inbred strains of mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1549–1552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percopo C. M., Hooks J. J., Shinohara T., Caspi R., Detrick B. Cytokine-mediated activation of a neuronal retinal resident cell provokes antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4101–4107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack I. F., Lund R. D. The blood-brain barrier protects foreign antigens in the brain from immune attack. Exp Neurol. 1990 May;108(2):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(90)90017-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B. J., Rosenblum M. The AIDS dementia complex and HIV-1 brain infection: a pathogenetic model of virus-immune interaction. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1990;68:269–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provinciali M., Muzzioli M., Fabris N. Timing of appearance and disappearance of IFN and IL-2 induced natural immunity during ontogenetic development and aging. Exp Gerontol. 1989;24(3):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(89)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossol-Voth R., Rossol S., Schütt K. H., Corridori S., de Cian W., Falke D. In vivo protective effect of tumour necrosis factor alpha against experimental infection with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jan;72(Pt 1):143–147. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons A. H-2-linked genes influence the severity of herpes simplex virus infection of the peripheral nervous system. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1503–1507. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan D. J., Wood M. J., Charlton H. M. The immune response to intracerebral neural grafts. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Aug;14(8):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90159-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiezia K. V., Dille B. J., Mushahwar I. K., Kifle L., Okasinski G. F. Prevalence of specific antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 2 as revealed by an enzyme-linked immunoassay and western blot analysis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1990;278:231–242. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5853-4_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staats H. F., Oakes J. E., Lausch R. N. Anti-glycoprotein D monoclonal antibody protects against herpes simplex virus type 1-induced diseases in mice functionally depleted of selected T-cell subsets or asialo GM1+ cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6008–6014. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6008-6014.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W. Anterior chamber associated immune deviation: the privilege of immunity in the eye. Surv Ophthalmol. 1990 Jul-Aug;35(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(90)90048-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W. Immune privilege as the result of local tissue barriers and immunosuppressive microenvironments. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):428–432. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90064-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W., Wilbanks G. A., Cousins S. W. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of the eye. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Aug;39(3):185–200. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90253-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streilein J. W., Wilbanks G. A., Taylor A., Cousins S. Eye-derived cytokines and the immunosuppressive intraocular microenvironment: a review. Curr Eye Res. 1992;11 (Suppl):41–47. doi: 10.3109/02713689208999510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao D. S., Grogan J. B. Host response to tissues placed in the anterior chamber of the eye: demonstration of migration inhibition factor and serum blocking activity. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba Rao D. S., Grogan J. B. Suppression of graft-versus-host reactions in rats bearing implants in the anterior chamber of the eye. Transplantation. 1979 Feb;27(2):75–78. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197902000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessella R. L., Raju S., Cockrell J. V., Grogan J. B. Host response to allogeneic implants in the anterior chamber of the rat eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978 Feb;17(2):140–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walev I., Kunkel J., Schwaeble W., Weise K., Falke D. Relationship between HLA I surface expression and different cytopathic effects produced after herpes simplex virus infection in vitro. Arch Virol. 1992;126(1-4):303–311. doi: 10.1007/BF01309703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Selby M., Erickson A., Cataldo D., Valensi J. P., Van Nest G. V. Cationic lipids direct a viral glycoprotein into the class I major histocompatibility complex antigen-presentation pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7915–7918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Walker D. G., Akiyama H., McGeer P. L. Herpes simplex virus type I infection of the CNS induces major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):55–65. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum-Hudson J. A., Pepose J. S. Immunologic modulation of virus-induced pathology in a murine model of acute herpetic retinal necrosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1541–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa M., Inatsuki A., Horiuchi T., Kobayashi Y. Functional heterogeneity among herpes simplex virus-specific human CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1341–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]