Abstract
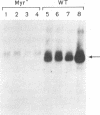
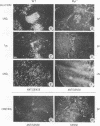
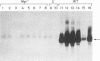
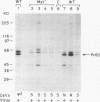
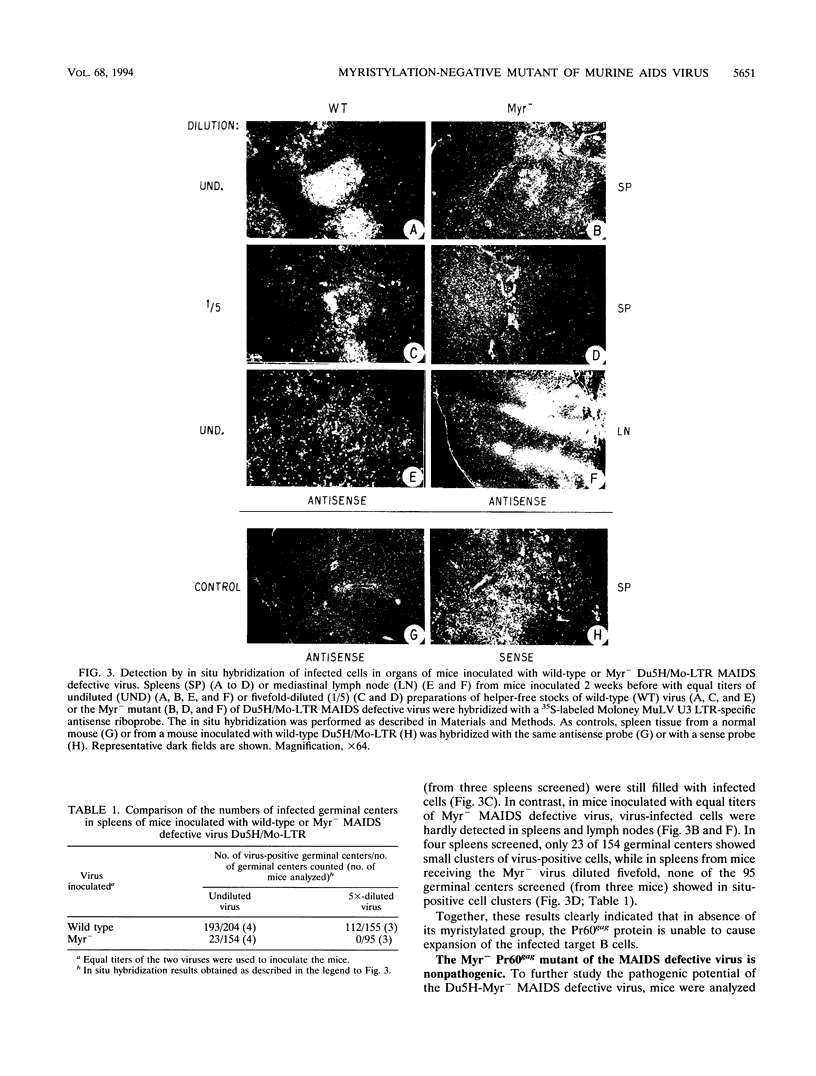
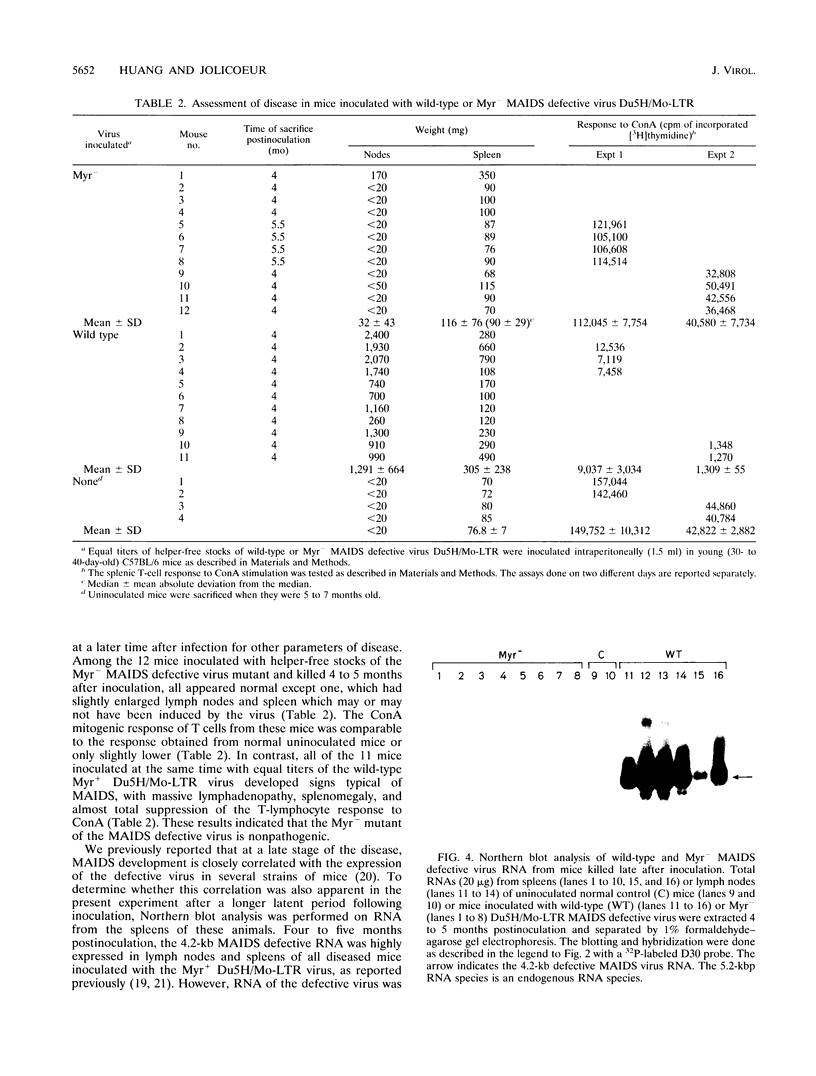
Murine AIDS (MAIDS) is characterized by severe lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. The proliferation of the infected target B cells is also an important manifestation of the disease (M. Huang, C. Simard, D. G. Kay, and P. Jolicoeur, J. Virol. 65:6562-6571, 1991). The etiologic agent of MAIDS is a defective murine leukemia virus that is deleted of most of its pol and env genes and appears to encode a single protein, the Gag precursor Pr60gag protein. Pr60gag is myristylated and attached to the plasma membrane. To study the role myristylation on the function of Pr60gag, we have generated a myristylation-negative (Myr-) mutant of the MAIDS defective virus. We found that Myr- Pr60gag interacted less tightly with the plasma membrane. In addition, the Myr- MAIDS defective virus mutant was unable to induce expansion of infected cells and was nonpathogenic. These results emphasize the essential role of Pr60gag in the disease process. Our data also suggest that Pr60gag, once recruited to the cell membrane through its myristylation, interacts with other membrane-bound effectors to send signals to induce proliferation of the infected cells and to initiate immune dysfunctions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham N., Veillette A. Activation of p56lck through mutation of a regulatory carboxy-terminal tyrosine residue requires intact sites of autophosphorylation and myristylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5197–5206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisenberg A. C. Malignant lymphoma. 1. N Engl J Med. 1973 Apr 26;288(17):883–890. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197304262881705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aziz D. C., Hanna Z., Jolicoeur P. Severe immunodeficiency disease induced by a defective murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):505–508. doi: 10.1038/338505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia S., Taylor S. J., Shalloway D. Myristylation is required for Tyr-527 dephosphorylation and activation of pp60c-src in mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1464–1470. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kamps M. P., Gould K., Sefton B. M. The absence of myristic acid decreases membrane binding of p60src but does not affect tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.468-474.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron L., Abraham N., Pawson T., Veillette A. Structural requirements for enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2720–2729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Hügin A. W., Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Zinkernagel R. M., Makino M., Morse H. C., 3rd B cells are required for induction of T cell abnormalities in a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):315–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd, Makino M., Ruscetti S. K., Hartley J. W. Defective virus is associated with induction of murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Sengupta D. N., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Characteristics and contributions of defective, ecotropic, and mink cell focus-inducing viruses involved in a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome of mice. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4232–4241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4232-4241.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desforges J. F., Rutherford C. J., Piro A. Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 29;301(22):1212–1222. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911293012205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore G. L., Cowing C., Mosier D. E. LP-BM5 murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease in allogeneic SCID chimeric mice. Inability to recognize a putative viral superantigen does not prevent induction of disease. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Jolicoeur P. Characterization of the gag/fusion protein encoded by the defective Duplan retrovirus inducing murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5764–5772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5764-5772.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Simard C., Jolicoeur P. Immunodeficiency and clonal growth of target cells induced by helper-free defective retrovirus. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1614–1617. doi: 10.1126/science.2480643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Simard C., Kay D. G., Jolicoeur P. The majority of cells infected with the defective murine AIDS virus belong to the B-cell lineage. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6562–6571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6562-6571.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügin A. W., Vacchio M. S., Morse H. C., 3rd A virus-encoded "superantigen" in a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome of mice. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):424–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1850169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Laperrière A., Beaulieu N. Efficient production of human immunodeficiency virus proteins in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3904–3908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3904-3908.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P. Murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (MAIDS): an animal model to study the AIDS pathogenesis. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2398–2405. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen E. C., Kjeldgaard N. O., Pedersen F. S., Jørgensen P. A nucleotide substitution in the gag N terminus of the endogenous ecotropic DBA/2 virus prevents Pr65gag myristylation and virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3217-3223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Yucel J. K., Malhotra V. ARF signaling: a potential role for phospholipase D in membrane traffic. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90314-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata N., Jotte R. M., Holt J. T. Myristylation alters DNA-binding activity and transactivation of FBR (gag-fos) protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):765–772. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., Drumm M., Saulino A., Collins F. S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1154–1154. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Chattopadhyay S. K., Makino M., Fredrickson T. N., Hügin A. W., Hartley J. W. Retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in the mouse: MAIDS as a model for AIDS. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):607–621. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. Animal models for retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease. Immunol Invest. 1986 May;15(3):233–261. doi: 10.3109/08820138609026687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Functional T lymphocytes are required for a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease (MAIDS). J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1737–1742. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozols J., Carr S. A., Strittmatter P. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase as myristic acid and the complete amino acid sequence of the membrane-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13349–13354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Kay D. G., Rassart E., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Substitution of the U3 long terminal repeat region of the neurotropic Cas-Br-E retrovirus affects its disease-inducing potential. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3742–3752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3742-3752.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozsgay J. M., Beilharz M. W., Wines B. D., Hess A. D., Pitha P. M. The MA (p15) and p12 regions of the gag gene are sufficient for the pathogenicity of the murine AIDS virus. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):5989–5999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.5989-5999.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange R., Clemen A., Streeck R. E. Myristylation is involved in intracellular retention of hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3919–3923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3919-3923.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvey L. A., Morse H. C., 3rd, Granger L. G., Hodes R. J. Preferential expansion and activation of V beta 5+ CD4+ T cells in murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1712–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard C., Huang M., Jolicoeur P. Murine AIDS is initiated in the lymph nodes draining the site of inoculation, and the infected B cells influence T cells located at distance, in noninfected organs. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1903–1912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1903-1912.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simard C., Jolicoeur P. The effect of anti-neoplastic drugs on murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.1987646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yetter R. A., Buller R. M., Lee J. S., Elkins K. L., Mosier D. E., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ T cells are required for development of a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome (MAIDS). J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):623–635. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., McGlone M. L., Taylor S. S. N-myristylation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase conveys structural stability. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2348–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]