Abstract
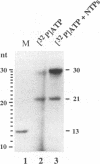
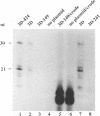
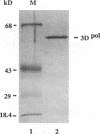
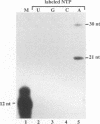
A terminal adenylyl transferase (TATase) activity has been identified in preparations of purified poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (3Dpol). Highly purified 3Dpol is capable of adding [32P]AMP to the 3' ends of chemically synthesized 12-nucleotide (nt)-long RNAs. The purified 52-kDa polypeptide, isolated after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and renatured, retained the TATase activity. Two 3Dpol mutants, purified from Escherichia coli expression systems, displayed no detectable polymerase activity and were unable to catalyze TATase activity. Likewise, extracts from the parental E. coli strain that harbored no expression plasmid were unable to catalyze formation of the TATase products. With the RNA oligonucleotide 5'-CCUGCUUUUGCA-3' used as an acceptor, the products formed by wild-type 3Dpol were 9 and 18 nt longer than the 12-nt oligomer. GTP, CTP, and UTP did not serve as substrates for transfer to this RNA, either by themselves or when all deoxynucleoside triphosphates were present in the reaction. Results from kinetic and stoichiometric analyses suggest that the reaction is catalytic and shows substrate and enzyme dependence. The 3'-terminal 13 nt of poliovirus minus-strand RNA also served as an acceptor for TATase activity, raising the possibility that this activity functions in poliovirus RNA replication. The efficiency of utilization and the nature of the products formed during the reaction were dependent on the acceptor RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Achacoso P. L., Baltimore D. Poliovirus RNA synthesis utilizes an RNP complex formed around the 5'-end of viral RNA. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3587–3598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Trono D., Baltimore D. Substitutions in the protease (3Cpro) gene of poliovirus can suppress a mutation in the 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.607-612.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Baltimore D. Purification of a terminal uridylyltransferase that acts as host factor in the in vitro poliovirus replicase reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):221–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. C., Levin D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase stimulation by terminal uridylyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7628–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Purification and properties of poliovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Infectious replicative intermediate of poliovirus: purification and characterization. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Purification and characterization of poliovirus-induced infectious double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1736–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Dorson J. W., Bollum F. J. Terminal riboadenylate transferase: a poly A polymerase in purified vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.203-208.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns C. C., Lawson M. A., Semler B. L., Ehrenfeld E. Effects of mutations in poliovirus 3Dpol on RNA polymerase activity and on polyprotein cleavage. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4866–4874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4866-4874.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns C. C., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Temperature-sensitive polioviruses containing mutations in RNA polymerase. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):568–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90580-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Mosser A. G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. W., Richards O. C., Dmitrieva T. M., Agol V., Ehrenfeld E. RNA duplex unwinding activity of poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3Dpol. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3010–3018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3010-3018.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Baltimore D. Genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus is present as free VPg and VPg-pUpU in poliovirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7452–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti C., Semler B. L. Role of a viral membrane polypeptide in strand-specific initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2647–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2647-2654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M. In vitro synthesis of poliovirus ribonucleic acid: role of the replicative intermediate. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.376-384.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grun J. B., Brinton M. A. Characterization of West Nile virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and cellular terminal adenylyl and uridylyl transferases in cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1113–1124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1113-1124.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon S. A., Richards O. C., Summers D. F., Ehrenfeld E. The 5'-terminal nucleotides of hepatitis A virus RNA, but not poliovirus RNA, are required for infectivity. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2757–2760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2757-2760.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi N., Haruna I., Watanabe I., Mikoshiba K., Tsukada Y. Poly(U) polymerase in rat brain. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):337–339. doi: 10.1038/256337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irurzun A., Perez L., Carrasco L. Involvement of membrane traffic in the replication of poliovirus genomes: effects of brefeldin A. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):166–175. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90178-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klump W. M., Bergmann I., Müller B. C., Ameis D., Kandolf R. Complete nucleotide sequence of infectious Coxsackievirus B3 cDNA: two initial 5' uridine residues are regained during plus-strand RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1573–1583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1573-1583.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Dorner A. J., Harris T. J., Wimmer E. The structure of poliovirus replicative form. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1217–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubinski J. M., Ransone L. J., Dasgupta A. Primer-dependent synthesis of covalently linked dimeric RNA molecules by poliovirus replicase. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2997–3003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2997-3003.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTAGNIER L., SANDERS F. K. REPLICATIVE FORM OF ENCEPHALOMYOCARDITIS VIRUS RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Nature. 1963 Aug 17;199:664–667. doi: 10.1038/199664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Navab M., Peterson C., Hocko J., Dasgupta A. Antibody to poliovirus genome-linked protein (VPg) precipitates in vitro synthesized RNA attached to VPg-precursor polypeptide(s). Virus Res. 1984;1(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld K. L., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Purification, characterization, and comparison of poliovirus RNA polymerase from native and recombinant sources. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24212–24219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G. Picornavirus nonstructural proteins: emerging roles in virus replication and inhibition of host cell functions. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):6917–6921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.6917-6921.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. R., Goff S. P. Linker insertion mutagenesis of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase expressed in bacteria: definition of the minimal polymerase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3104–3108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuer Q., Kuhn R. J., Wimmer E. Characterization of poliovirus clones containing lethal and nonlethal mutations in the genome-linked protein VPg. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2967–2975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2967-2975.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Heterogeneity of the 3' end of minus-strand RNA in the poliovirus replicative form. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.387-394.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus RNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:89–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ivanoff L. A., Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Butt B., Petteway S. R., Jr, Rothstein M. A., Ehrenfeld E. Formation of poliovirus RNA polymerase 3D in Escherichia coli by cleavage of fusion proteins expressed from cloned viral cDNA. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Martin S. C., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Structure of poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. Electron microscope analysis of RNA cross-linked in vivo with psoralen derivative. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):325–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Yu P., Neufeld K. L., Ehrenfeld E. Nucleotide binding by the poliovirus RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17141–17146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E. 3'-Terminal addition to HeLa cell nuclear and cytoplasmic poly (A). J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA IV. Poly(U) in replicative intermediate and double-stranded RNA. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):498–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90450-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. III. In vitro addition of polyadenylic acid to poliovirus RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1432–1439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1432-1439.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Yang C. F., Kuhn R. J., Wimmer E. Uridylylation of the genome-linked protein of poliovirus in vitro is dependent upon an endogenous RNA template. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Goff S. P. Domain structure of the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: mutational analysis and separate expression of the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Yang C. F., Takeda N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Analysis of RNA synthesis of type 1 poliovirus by using an in vitro molecular genetic approach. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2816–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2816-2822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuschall D. M., Hiebert E., Flanegan J. B. Poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase synthesizes full-length copies of poliovirion RNA, cellular mRNA, and several plant virus RNAs in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):209–216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.209-216.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. III. Polyuridylic acid and polyadenylic acid as components of the purified poliovirus replicative intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel P., Dorssers L., Wernars K., Van Kammen A. Terminal uridylyl transferase of Vigna unguiculata: purification and characterization of an enzyme catalyzing the addition of a single UMP residue to the 3'-end of an RNA primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2433–2453. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]