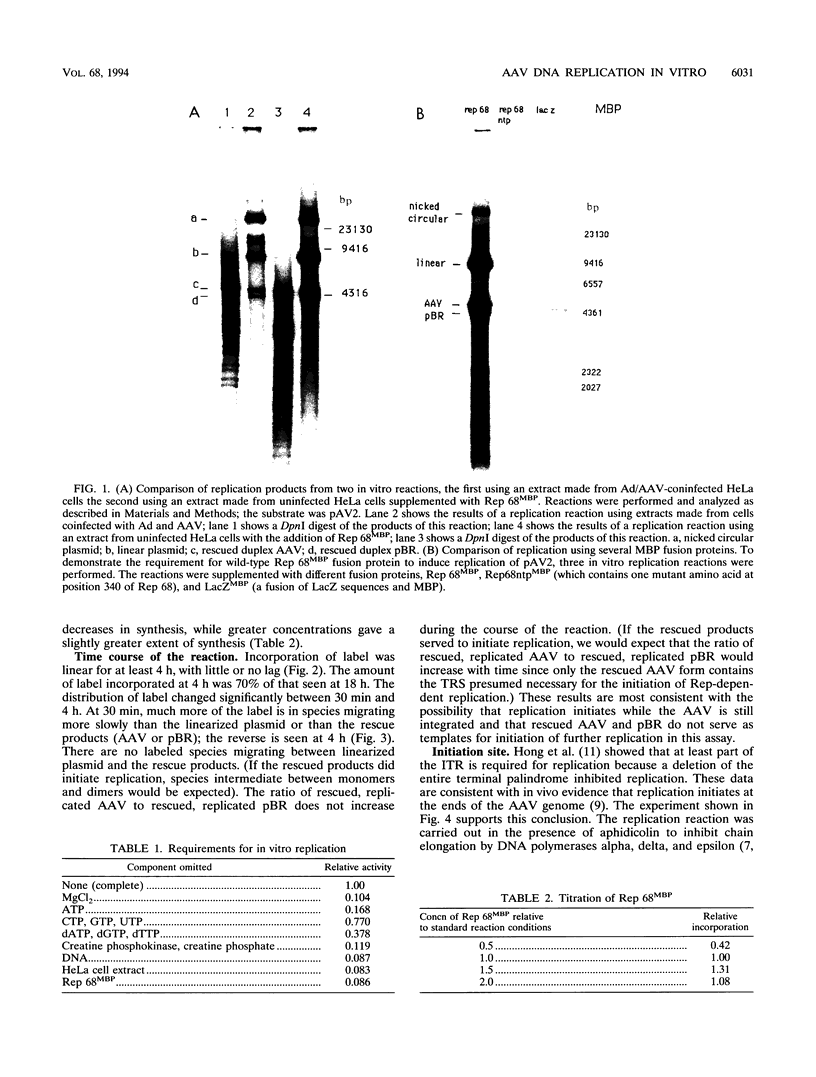
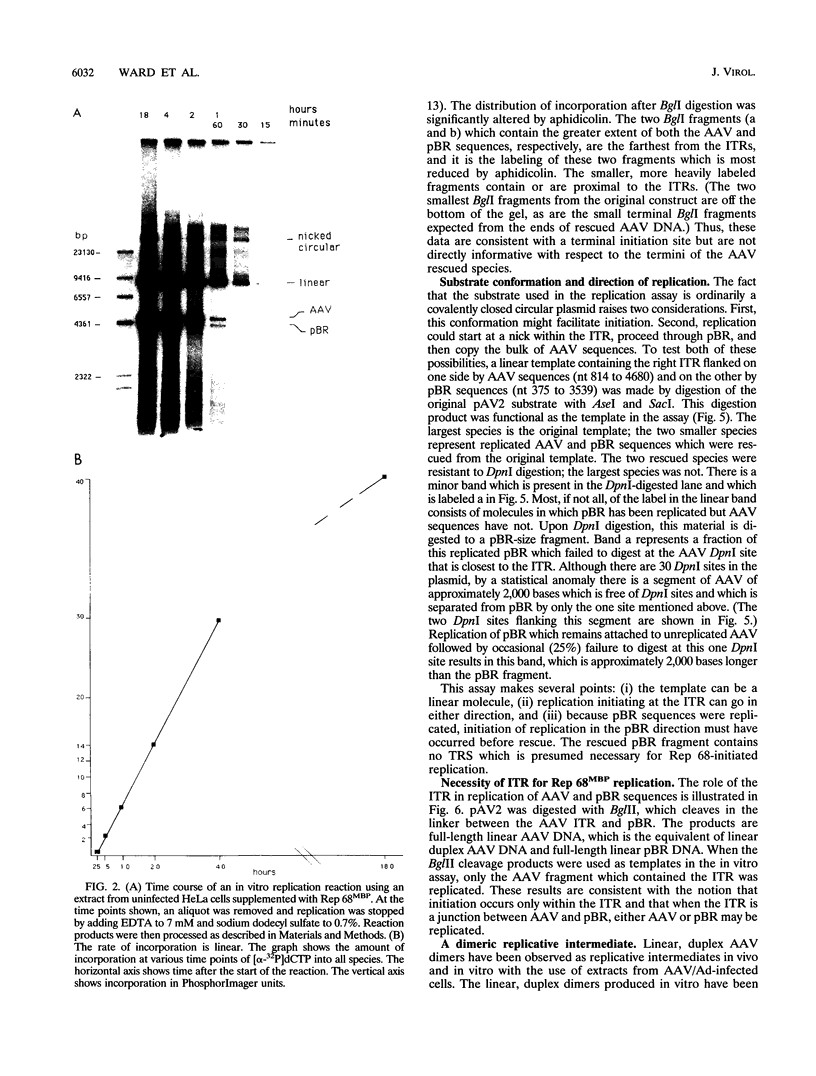
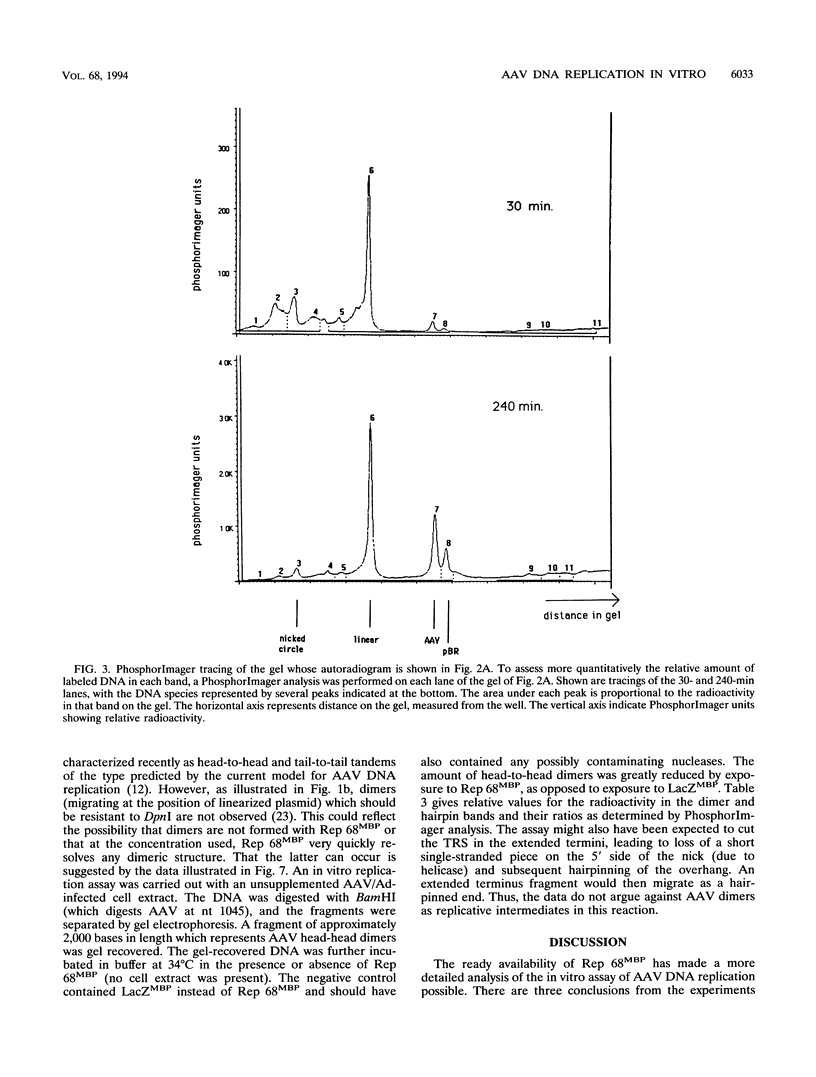
Abstract
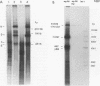
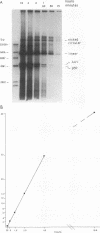
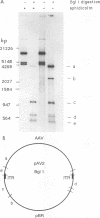
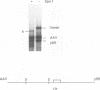
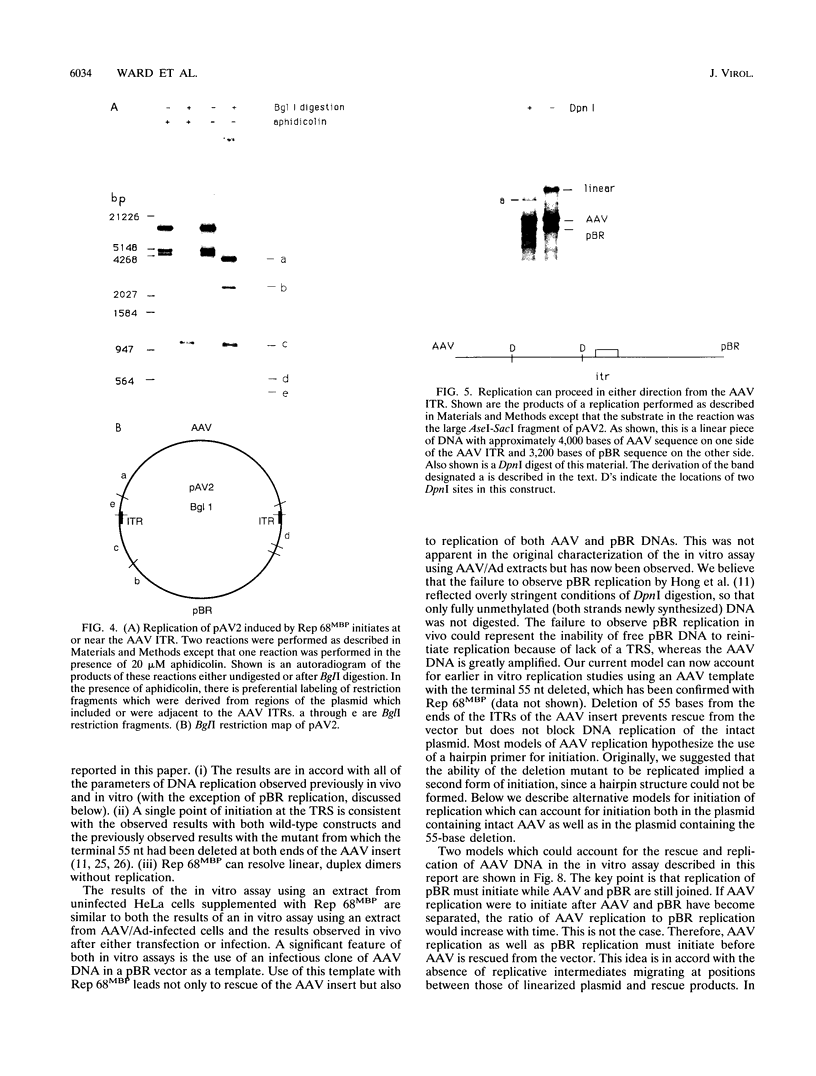
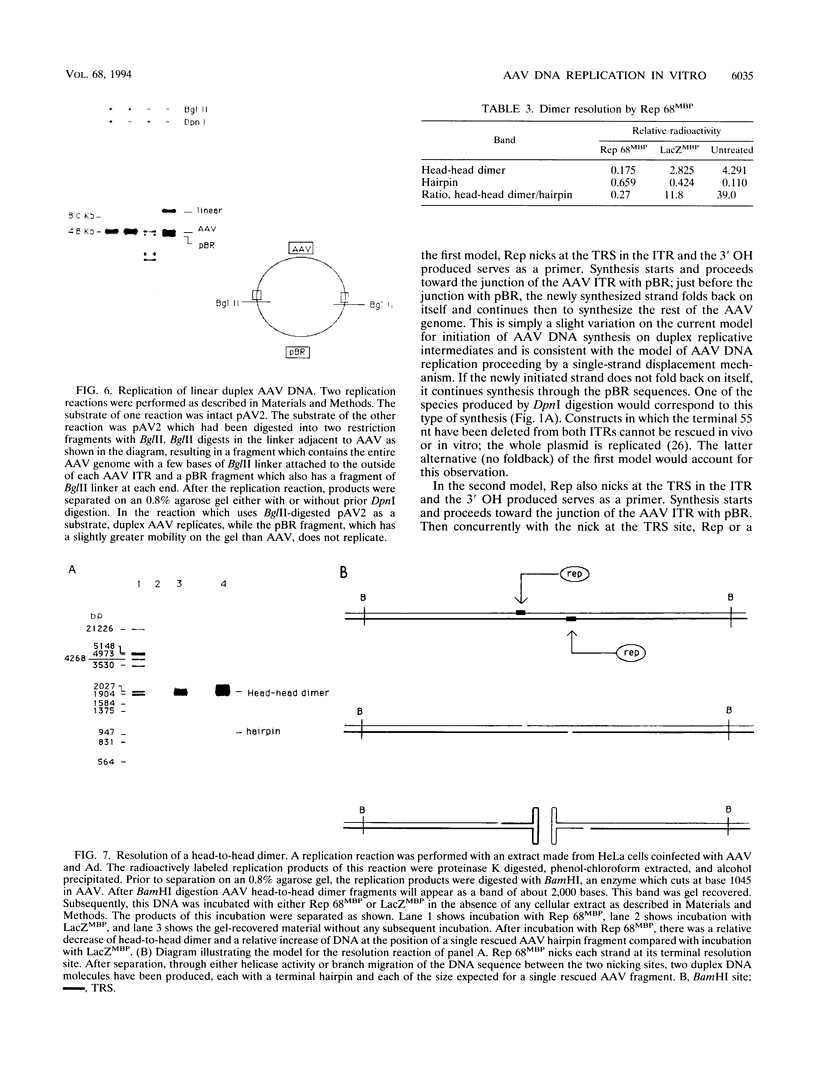
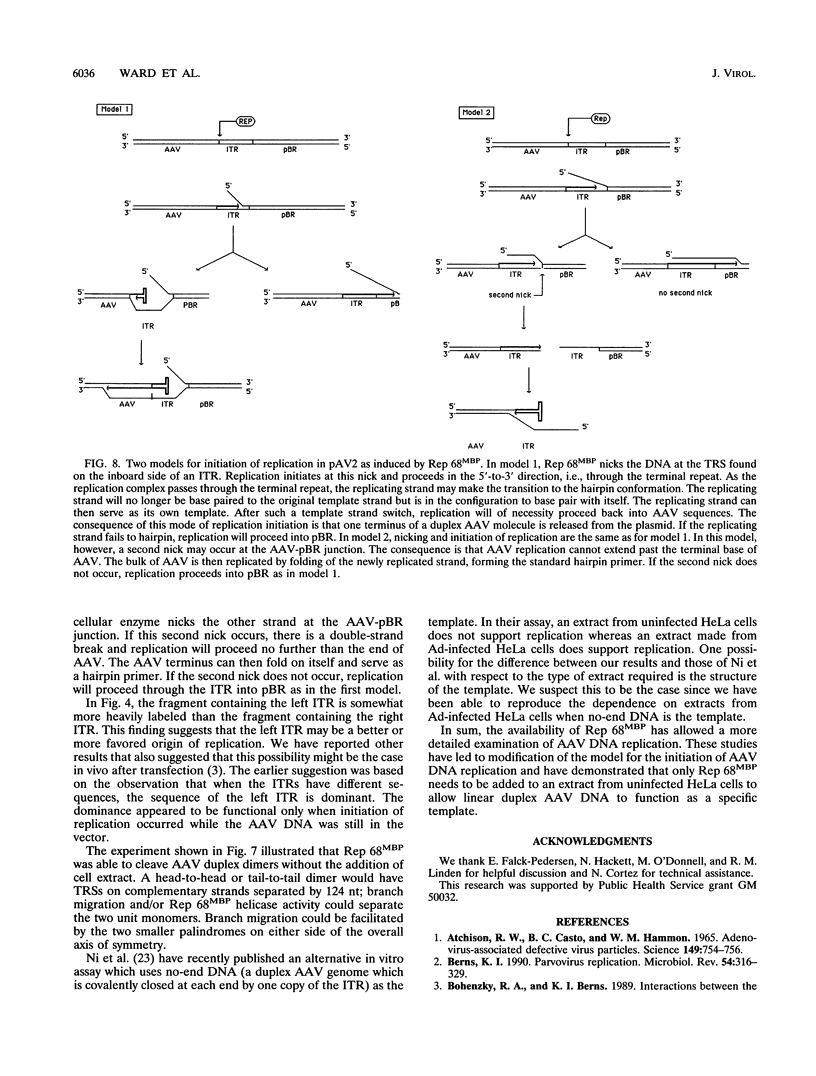
The adeno-associated virus (AAV) nonstructural protein Rep 68 is required for viral DNA replication. An in vitro assay has been developed in which addition of Rep 68 to an extract from uninfected HeLa cells supports AAV DNA replication. In this paper, we report characterization of the replication process when a fusion of the maltose binding protein and Rep 68, expressed in Escherichia coli, was used in the assay. Replication was observed when the template was either linear double-stranded AAV DNA or a plasmid construct containing intact AAV DNA. When the recombinant plasmid construct was used as the template, there was replication of pBR322 DNA as well as the AAV DNA; however, linear pBR322 DNA was not replicated. When the plasmid construct was the template, replication appeared to initiate on the intact plasmid and led to separation of the AAV sequences from those of the vector, a process which has been termed rescue. There was no evidence that replication could initiate on the products of rescue. Rep 68 can make a site-specific nick 124 nucleotides from the 3' end of AAV DNA; the site of the nick has been called the terminal resolution site. Our data are most consistent with initiation occurring at the terminal resolution site and proceeding toward the 3' terminus. When the template was the plasmid construct, either elongation continued past the junction into pBR322 sequences or the newly synthesized sequence hairpinned, switched template strands, and replicated the AAV DNA. Replication was linear for 4 h, during which time 70% of the maximal synthesis took place. An additional finding was that the Rep fusion could resolve AAV dimer length duplex intermediates into monomer duplexes without DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATCHISON R. W., CASTO B. C., HAMMON W. M. ADENOVIRUS-ASSOCIATED DEFECTIVE VIRUS PARTICLES. Science. 1965 Aug 13;149(3685):754–756. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3685.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I. Parvovirus replication. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):316–329. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.316-329.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohenzky R. A., Berns K. I. Interactions between the termini of adeno-associated virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 5;206(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90526-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Janik J. E., Sebring E. D., Rose J. A. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 completely help adenovirus-associated virus replication. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):241–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.241-247.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Mutation of a consensus purine nucleotide binding site in the adeno-associated virus rep gene generates a dominant negative phenotype for DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1764–1770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1764-1770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiorini J. A., Weitzman M. D., Owens R. A., Urcelay E., Safer B., Kotin R. M. Biologically active Rep proteins of adeno-associated virus type 2 produced as fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):797–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.797-804.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goscin L. P., Byrnes J. J. DNA polymerase delta: one polypeptide, two activities. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2513–2518. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J., Muzyczka N. In vitro excision of adeno-associated virus DNA from recombinant plasmids: isolation of an enzyme fraction from HeLa cells that cleaves DNA at poly(G) sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2513–2522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Origin and termination of adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):488–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G., Ward P., Berns K. I. In vitro replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4673–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G., Ward P., Berns K. I. Intermediates of adeno-associated virus DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):2011–2015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.2011-2015.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90526-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Linden R. M., Berns K. I. Characterization of a preferred site on human chromosome 19q for integration of adeno-associated virus DNA by non-homologous recombination. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5071–5078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Menninger J. C., Ward D. C., Berns K. I. Mapping and direct visualization of a region-specific viral DNA integration site on chromosome 19q13-qter. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):831–834. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90470-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotin R. M., Siniscalco M., Samulski R. J., Zhu X. D., Hunter L., Laughlin C. A., McLaughlin S., Muzyczka N., Rocchi M., Berns K. I. Site-specific integration by adeno-associated virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlin C. A., Tratschin J. D., Coon H., Carter B. J. Cloning of infectious adeno-associated virus genomes in bacterial plasmids. Gene. 1983 Jul;23(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. J., Berns K. I. Cloning, expression, and partial purification of Rep78: an adeno-associated virus replication protein. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):566–573. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusby E., Fife K. H., Berns K. I. Nucleotide sequence of the inverted terminal repetition in adeno-associated virus DNA. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):402–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.402-409.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Mayor H. D., Smith K. O., Rapp F. Association of 20-Millimicron Particles with Adenoviruses. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.271-274.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson E., Trempe J. P., Carter B. J. Identification of the trans-acting Rep proteins of adeno-associated virus by antibodies to a synthetic oligopeptide. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):823–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.823-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni T. H., Zhou X., McCarty D. M., Zolotukhin I., Muzyczka N. In vitro replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1128–1138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1128-1138.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. A., Carter B. J. In vitro resolution of adeno-associated virus DNA hairpin termini by wild-type Rep protein is inhibited by a dominant-negative mutant of rep. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1236–1240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1236-1240.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Berns K. I., Tan M., Muzyczka N. Cloning of adeno-associated virus into pBR322: rescue of intact virus from the recombinant plasmid in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Zhu X., Xiao X., Brook J. D., Housman D. E., Epstein N., Hunter L. A. Targeted integration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) into human chromosome 19. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3941–3950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Lusby E. W., Berns K. I. Nucleotide sequence and organization of the adeno-associated virus 2 genome. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):555–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.555-564.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P., Berns K. I. In vitro rescue of an integrated hybrid adeno-associated virus/simian virus 40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 20;218(4):791–804. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90267-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wobbe C. R., Dean F., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. In vitro replication of duplex circular DNA containing the simian virus 40 DNA origin site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]