Abstract
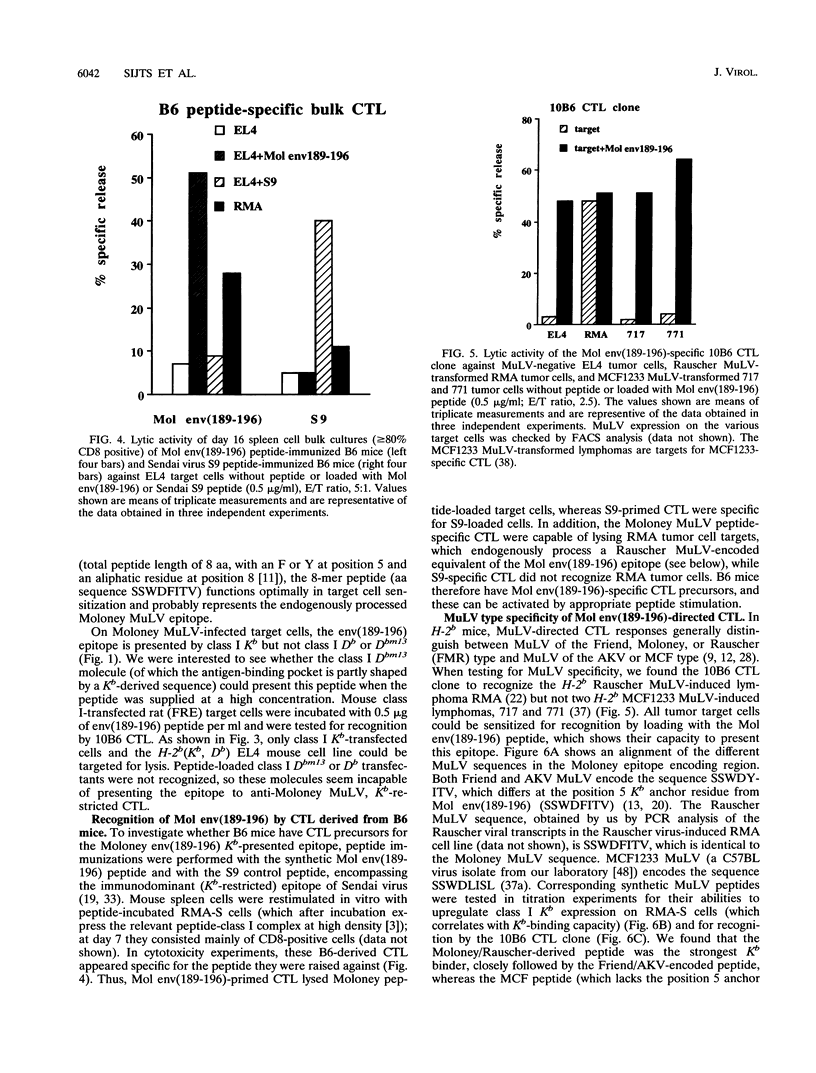
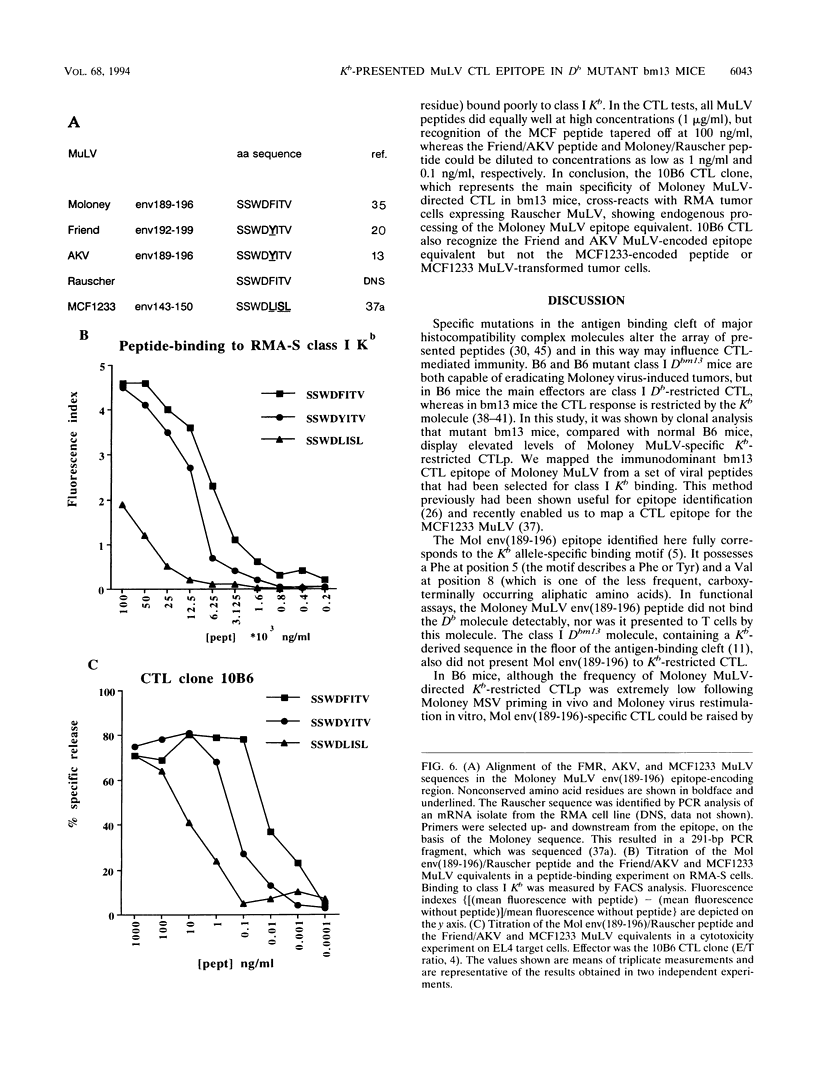
Upon infection with the Moloney murine sarcoma virus-murine leukemia virus (MuLV) complex, H-2b C57BL/6 (B6) mice respond with a class I Db-restricted cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response, which protects against virus-induced tumorigenesis. In the B6-derived Db mutant B6.CH-2bm13 (bm13) strain, part of the class I Db antigen-presenting groove is shaped by a class I Kb-encoded sequence. Like B6 mice, bm13 mice reject Moloney virus-induced tumors, but the protective CTL response is Kb restricted. In this study we show enhanced levels of Moloney MuLV-specific CTLp with a restriction for Kb in bm13 mice. Through the use of CTL clones from Moloney virus-immunized bm13 mice, the class I Kb-presented CTL epitope was identified. The epitope is located in the Moloney virus gp70 envelope protein region (Moloney envelope, amino acids 189 to 196 [Mol env (189-196)]), SSWDFITV and has the Kb allele-specific binding motif. The Dbm13 molecule does not present the env(189 to 196) epitope to Kb-restricted bm13 CTL. In B6 mice, Mol env(189-196)-specific CTL could be induced by peptide vaccination. B6 mice thus have CTL precursors specific for this epitope but at considerably lower levels than do bm13 mice. We hypothesize that additional positive selection of Kb-restricted CTL on the Dbm13 molecule in bm13 mice explains this difference in precursor frequencies. We examined related strains of MuLV for the presence of Mol env(189-196) sequence equivalents. Rauscher, Friend, and AKV MuLV-encoded Mol env(189-196) epitope equivalents were properly recognized in cytotoxicity assays, both as synthetic and as endogenously expressed (Rauscher MuLV) peptides. In contrast, the mink cell focus-forming virus MuLV-encoded epitope equivalent, lacking a Kb anchor residue, was not presented for CTL recognition and hence can be excluded as an important CTL epitope for mink cell focus-forming viruses.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Van Kaer L., Schumacher T. N., Ploegh H. L., Tonegawa S. Peptide contributes to the specificity of positive selection of CD8+ T cells in the thymus. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1041–1049. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90281-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruijn M. L., Schumacher T. N., Nieland J. D., Ploegh H. L., Kast W. M., Melief C. J. Peptide loading of empty major histocompatibility complex molecules on RMA-S cells allows the induction of primary cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):2963–2970. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flyer D. C., Burakoff S. J., Faller D. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte recognition of transfected cells expressing a cloned retroviral gene. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):815–818. doi: 10.1038/305815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORER P. A. Studies in antibody response of mice to tumour inoculation. Br J Cancer. 1950 Dec;4(4):372–379. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1950.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomard E., Levy J. P., Plata F., Henin Y., Duprez V., Bismuth A., Reme T. Studies on the nature of the cell surface antigen reacting with cytolytic T lymphocytes in murine oncornavirus-induced tumors. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Apr;8(4):228–236. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Geliebter J., Zeff R. A., Melvold R. W., Nathenson S. G. Three spontaneous H-2Db mutants are generated by genetic micro-recombination (gene conversion) events. Impact on the H-2-restricted immune responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2319–2335. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Aoki T., Nunn M., Lavrin D. H., Soares N., Gazdar A., Holden H., Chang K. S. Specificity of 51Cr-release cytotoxicity of lymphocytes immune to murine sarcoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Oct;53(4):1103–1111. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt C. A., Osorio K., Lilly F. Friend virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize both gag and env gene-encoded specificities. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):211–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs H., Von Boehmer H., Melief C. J., Berns A. Mutations in the major histocompatibility complex class I antigen-presenting groove affect both negative and positive selection of T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2333–2337. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Boog C. J., Roep B. O., Voordouw A. C., Melief C. J. Failure or success in the restoration of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response defects by dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3186–3193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Melief C. J. Fine peptide specificity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes directed against adenovirus-induced tumours and peptide-MHC binding. Int J Cancer Suppl. 1991;6:90–94. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Roux L., Curren J., Blom H. J., Voordouw A. C., Meloen R. H., Kolakofsky D., Melief C. J. Protection against lethal Sendai virus infection by in vivo priming of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with a free synthetic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., de Waal L. P., Melief C. J. Thymus dictates major histocompatibility complex (MHC) specificity and immune response gene phenotype of class II MHC-restricted T cells but not of class I MHC-restricted T cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1752–1766. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Hunsmann G., Friedrich R. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. P., Leclerc J. C. The murine sarcoma virus-induced tumor: exception or general model in tumor immunology? Adv Cancer Res. 1977;24:1–66. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)61012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Ohlén C., Höglund P., Franksson L., Kärre K. The RMA-S lymphoma mutant; consequences of a peptide loading defect on immunological recognition and graft rejection. Int J Cancer Suppl. 1991;6:38–44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J. A molecular model of MHC class-I-restricted antigen processing. Immunol Today. 1992 May;13(5):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90122-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolić-Zugić J., Bevan M. J. Role of self-peptides in positively selecting the T-cell repertoire. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):65–67. doi: 10.1038/344065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi P. S., Zinkernagel R. M., Leuscher I., Hengartner H., Pircher H. Enhanced positive selection of a transgenic TCR by a restriction element that does not permit negative selection. Int Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(2):131–138. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pamer E. G., Harty J. T., Bevan M. J. Precise prediction of a dominant class I MHC-restricted epitope of Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):852–855. doi: 10.1038/353852a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Gomard E., Leclerc J. C., Levy J. P. Further evidence for the involvement of thymus-processed lymphocytes in syngeneic tumor cell cytolysis. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):667–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plata F., Lilly F. Viral specificity of H-2-restricted T killer cells directed against syngeneic tumors induced by Gross, Friend, or Rauscher leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1174–1186. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F., Fowlkes B. J. Clonal deletion versus clonal anergy: the role of the thymus in inducing self tolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1342–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.1972593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohren E. M., Pease L. R., Ploegh H. L., Schumacher T. N. Polymorphisms in pockets of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules influence peptide preference. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1713–1721. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K. S., Lilly F. Identification of an epitope encoded in the env gene of Friend murine leukemia virus recognized by anti-Friend virus cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90473-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötzschke O., Falk K., Deres K., Schild H., Norda M., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Isolation and analysis of naturally processed viral peptides as recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):252–254. doi: 10.1038/348252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher T. N., De Bruijn M. L., Vernie L. N., Kast W. M., Melief C. J., Neefjes J. J., Ploegh H. L. Peptide selection by MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):703–706. doi: 10.1038/350703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha W. C., Nelson C. A., Newberry R. D., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R., Russell J. H., Loh D. Y. Positive selection of transgenic receptor-bearing thymocytes by Kb antigen is altered by Kb mutations that involve peptide binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6186–6190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijts A. J., De Bruijn M. L., Nieland J. D., Kast W. M., Melief C. J. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes against the antigen-processing-defective RMA-S tumor cell line. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1639–1642. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijts A. J., Ossendorp F., Mengedé E. A., van den Elsen P. J., Melief C. J. Immunodominant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia virus (MuLV)-encoded CTL epitope, identified by its MHC class I-binding motif, explains MuLV-type specificity of MCF-directed cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 1;152(1):106–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukart M. J., Boes J., Melief C. J. Recognition of H-2Kb mutant target cells by Moloney virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes from bm13 (H-2Db mutant) mice. I. Full recognition of Kbm11 by Kb-restricted CTL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukart M. J., Boes J., Melief C. J. Recognition of H-2Kb mutant target cells by Moloney virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes from bm13 (H-2Db-mutant) mice. II. Relationship of Kbm3 and Kbm11 in restriction specificities and allodeterminants. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukart M. J., Vos A., Melitef C. J. Cytotoxic T cell response against lymphoblasts infected with Moloney (Abelson) murine leukemia virus. Methodological aspects and H-2 requirements. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):251–257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C., MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C. Clonal analysis of cytolytic T lymphocyte specificity. I. Phenotypically distinct sets of clones as the cellular basis of cross-reactivity to alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1372–1385. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Zee R., Van Eden W., Meloen R. H., Noordzij A., Van Embden J. D. Efficient mapping and characterization of a T cell epitope by the simultaneous synthesis of multiple peptides. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasmel W. L., Zijlstra M., Radaszkiewicz T., Leupers C. J., de Goede R. E., Melief C. J. Major histocompatibility complex class II-regulated immunity to murine leukemia virus protects against early T- but not late B-cell lymphomas. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3156–3166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3156-3166.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Schoenmakers H. J., Schinkel A. H., Hesselink W. G., Portis J. L., Melief C. J. Naturally occurring leukemia viruses in H-2 congenic C57BL mice. III. Characterization of C-type viruses isolated from lymphomas induced by milk transmission of B-ecotropic virus. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal L. P., Kast W. M., Melvold R. W., Melief C. J. Regulation of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response against Sendai virus analyzed with H-2 mutants. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1090–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. The structure of the antigen-binding groove of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules determines specific selection of self-peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11032–11036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


