Abstract
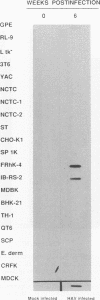
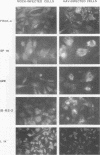
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) has been adapted to grow in primate cell cultures. We investigated replication of HAV in nonprimate cells by inoculating 20 cell lines from different species with the tissue culture-adapted HM175 strain. Slot blot hybridization and immunofluorescence analysis revealed that HAV replicated in GPE, SP 1K, and IB-RS-2 D10 cells of guinea pig, dolphin, and pig origin, respectively. Studies in IB-RS-2 D10 cells were discontinued because cultures were contaminated with classical swine fever virus. A growth curve showed that HAV grew poorly in GPE cells and intermediately in SP 1K cells compared with growth in FRhK-4 cells. Therefore, the cell surface receptor(s) and other host factor(s) required for HAV replication are present in nonprimate as well as primate cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. A., Ross B. C. Morphogenesis of hepatitis A virus: isolation and characterization of subviral particles. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5284–5289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5284-5289.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balayan M. S. Natural hosts of hepatitis A virus. Vaccine. 1992;10 (Suppl 1):S27–S31. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90537-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Cell type-specific proteins which interact with the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6716–6725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6716-6725.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Rosenblum B., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis A virus cDNA and its RNA transcripts are infectious in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3035-3039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day S. P., Murphy P., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Mutations within the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA which enhance replication in BS-C-1 cells. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6533–6540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6533-6540.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Huang Y. K., McRill C., Lewis M., Purcell R. H. Mutations in both the 2B and 2C genes of hepatitis A virus are involved in adaptation to growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):650–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.650-654.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Huang Y. K., Purcell R. H. 2B and 2C mutations are essential but mutations throughout the genome of HAV contribute to adaptation to cell culture. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):475–480. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., McRill C., Rosenblum B., Feinstone S., Purcell R. H. Mutations responsible for adaptation of hepatitis A virus to efficient growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4882–4886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4882-4886.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funkhouser A. W., Purcell R. H., D'Hondt E., Emerson S. U. Attenuated hepatitis A virus: genetic determinants of adaptation to growth in MRC-5 cells. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.148-157.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J., Normann A., Feinstone S. M., Flehmig B. Nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus GBM in comparison with two cell culture-adapted variants. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):548–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.548-554.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin D. M., Kocher T. D., Wilson A. C. Evolution of the cytochrome b gene of mammals. J Mol Evol. 1991 Feb;32(2):128–144. doi: 10.1007/BF02515385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Levy A., Racaniello V. R. Isolation and characterization of HeLa cell lines blocked at different steps in the poliovirus life cycle. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):43–51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.43-51.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N. Incomplete neutralization of hepatitis A virus in vitro due to lipid-associated virions. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2501–2505. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D. P., Zharkikh A., Graur D., VandeBerg J. L., Li W. H. Structure and evolution of opossum, guinea pig, and porcupine cytochrome b genes. J Mol Evol. 1993 Apr;36(4):327–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00182180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor A., Kornitschuk M., Hurrell J. G., Lehmann N. I., Coulepis A. G., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1237-1243.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes de Oca F., Macy M. L., Shannon J. E. Isoenzyme characterization of animal cell cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):462–469. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig R., Pott G., Seelig H. P., Liehr H., Metzger P., Waldherr R. Virus-binding activity of fibronectin: masking of hepatitis A virus. J Virol Methods. 1984 Jul;8(4):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedeschi V., Purcell R. H., Emerson S. U. Partial characterization of hepatitis A viruses from three intermediate passage levels of a series resulting in adaptation to growth in cell culture and attenuation of virulence. J Med Virol. 1993 Jan;39(1):16–22. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890390105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajac A. J., Amphlett E. M., Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V. Parameters influencing the attachment of hepatitis A virus to a variety of continuous cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1667–1675. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]