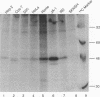
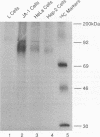
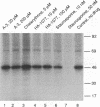
Abstract
The human receptors for poliovirus (hPVR) are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Whereas the two membrane-bound isoforms, hPVR alpha and hPVR delta, share identical three-domain extracellular portions, their C-terminal cytoplasmic parts differ considerably. This feature is well conserved in the corresponding monkey proteins AGM alpha 1, AGM delta 1, and AGM alpha 2. The cellular function of these proteins is presently unknown. In this short communication we report that hPVR alpha and possibly also AGM alpha 1 and AGM alpha 2, but not the delta isoforms, are phosphoproteins. The phosphorylation occurs at a serine in the cytoplasmic tails of these receptors. We further present evidence suggesting that the kinase responsible for the phosphorylation is calcium/calmodulin kinase II.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt G., Bibb J. A., Bradley J., Wimmer E. Molecular characterization of the cellular receptor for poliovirus. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):105–113. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb J. A., Witherell G., Bernhardt G., Wimmer E. Interaction of poliovirus with its cell surface binding site. Virology. 1994 May 15;201(1):107–115. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. H., Jr, Johnson D., Ogonowski M., Weiner H. L. Type 1 human poliovirus binds to human synaptosomes. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jan;21(1):64–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Valtorta F., Czernik A. J., Benfenati F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.8430330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. I., Schulman H. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:559–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Virus receptors: binding, adhesion strengthening, and changes in viral structure. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.1-5.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Seban E., Maffrand J. P. Characterization of specific binding sites for [3H]-staurosporine on various protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):189–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyoto I., Yamamoto S., Aizu E., Kato R. Staurosporine, a potent protein kinase C inhibitor, fails to inhibit 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-caused ornithine decarboxylase induction in isolated mouse epidermal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):740–746. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90938-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Nomoto A. Functional domains of the poliovirus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Sato Y., Yonekawa H., Gotoh O., Nomoto A. A second gene for the African green monkey poliovirus receptor that has no putative N-glycosylation site in the functional N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7059–7066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7059-7066.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Johnson B., Lionetti K. A., Nobis P., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Transformation of a human poliovirus receptor gene into mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. E., Racaniello V. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a murine homolog of the human poliovirus receptor gene. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2807–2813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2807-2813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:62–81. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringer D. P. Separation of phosphotyrosine, phosphoserine, and phosphothreonine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:3–10. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01003-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schächtele C., Seifert R., Osswald H. Stimulus-dependent inhibition of platelet aggregation by the protein kinase C inhibitors polymyxin B, H-7 and staurosporine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90628-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. A chimeric poliovirus/CD4 receptor confers susceptibility to poliovirus on mouse cells. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2523–2526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2523-2526.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus can enter and infect mammalian cells by way of an intercellular adhesion molecule 1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3598–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Integrins as virus receptors. Curr Biol. 1993 Sep 1;3(9):596–599. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90007-B. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara N., Tachikawa E., Izumi F., Yasugawa S., Yamamoto H., Miyamoto E. Staurosporine: an effective inhibitor for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Neurochem. 1991 Jan;56(1):294–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]