Abstract
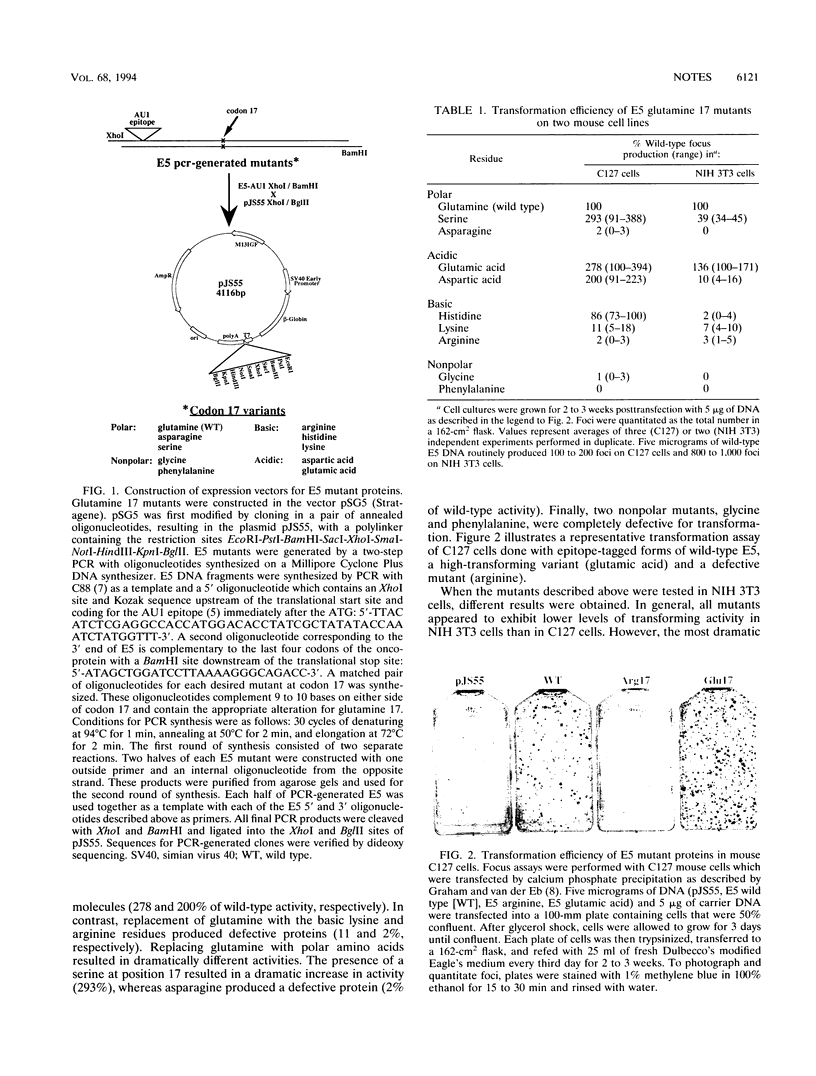
The E5 transforming protein of bovine papillomavirus type 1 is a 44-amino-acid, hydrophobic protein which localizes predominantly to Golgi membranes. The E5 transmembrane domain contains a highly conserved glutamine residue at position 17 which, from previous limited mutagenic analysis, appeared essential for transforming activity. In order to determine the specific amino acid requirements at this position, we constructed a series of substitution mutants, representing all classes of amino acids, employing a vector which expressed E5 independently of other bovine papillomavirus gene products. All of the expressed E5 mutant proteins were stable, dimerized normally, and localized to the Golgi. Our results obtained with C127 mouse cells demonstrated that acidic amino acids (and serine) increased E5 transforming activity, whereas basic amino acids greatly inhibited E5 activity. Nonpolar amino acid substitutions were also defective. Interestingly, the relative transforming activities of these E5 mutant proteins changed dramatically when assayed with NIH 3T3 cells, suggesting that an auxiliary cellular protein(s) may modulate E5 transformation or that there are additional or different mechanisms of E5 transformation which are utilized in these two cell lines.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burkhardt A., DiMaio D., Schlegel R. Genetic and biochemical definition of the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2381–2385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Guralski D., Schiller J. T. Translation of open reading frame E5 of bovine papillomavirus is required for its transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Andresson T., Sparkowski J. J., Schlegel R. The BPV-1 E5 protein, the 16 kDa membrane pore-forming protein and the PDGF receptor exist in a complex that is dependent on hydrophobic transmembrane interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4851–4859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Kulke R., Dimaio D., Schlegel R. A glutamine residue in the membrane-associating domain of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E5 oncoprotein mediates its binding to a transmembrane component of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):405–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.405-413.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Schlegel R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus binds to a 16 kd cellular protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):137–145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groff D. E., Lancaster W. D. Genetic analysis of the 3' early region transformation and replication functions of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Burkhardt A. L., Schlegel R., DiMaio D. 44-amino-acid E5 transforming protein of bovine papillomavirus requires a hydrophobic core and specific carboxyl-terminal amino acids. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4071–4078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Weinstat D. L., DiMaio D. Transforming activity of a 16-amino-acid segment of the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein linked to random sequences of hydrophobic amino acids. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4515–4519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4515-4519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Shook D. R., Maynell L. A. Evidence that the deep keratin filament systems of the Xenopus embryo act to ensure normal gastrulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8736–8740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulke R., Horwitz B. H., Zibello T., DiMaio D. The central hydrophobic domain of the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein can be functionally replaced by many hydrophobic amino acid sequences containing a glutamine. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.505-511.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor can mediate tumorigenic transformation by the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4137–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):845–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Vousden K. H., Lowy D. R. E5 open reading frame of bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes a transforming gene. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.1-6.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade-Glass M., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small, hydrophobic polypeptide. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.3014660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]