Abstract
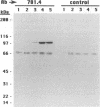
An antigen expressed by astrocytes in human brain tissue and by various human astrocytoma cell lines was shown to cross-react with a monoclonal antibody generated against amino acids (aa) 584 to 609 of the transmembrane protein gp41 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). This region is an immunodominant segment of gp41, and high levels of antibodies against this epitope have been detected in both serum and cerebrospinal fluid of HIV-infected individuals at all stages of HIV infection. Immunohistochemistry with this monoclonal antibody demonstrated the presence of a cross-reactive antigen in human brain tissue, with an increased frequency and intensity of staining in HIV-positive individuals when compared with HIV-negative controls. By using a panel of HIV-positive and -negative sera, we show that antibodies in HIV-positive serum specifically bound to the surfaces of human astrocytoma cells. HIV-positive sera depleted of antibodies recognizing gp41 aa 584 to 609 showed a significant diminution in cell surface binding. Conversely, the serum antibodies that bound to and were eluted from the aa 584 to 609 peptide also bound to the astrocyte cell surface. To identify the target antigen, the immunoreactivity of three astrocytoma cell lines was examined. By immunoprecipitation of metabolically labeled cell lysates and Western blot (immunoblot) analysis, we identified a protein of approximately 100 kDa as the target antigen. Cross-reactive antibodies between HIV proteins and astrocyte epitopes, such as this 100-kDa protein and others previously reported, suggests that an autoimmune response against these target antigens may disrupt the normal functions of astrocytes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achim C. L., Morey M. K., Wiley C. A. Expression of major histocompatibility complex and HIV antigens within the brains of AIDS patients. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):535–541. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronstein W. S., Lewis S. A., Norden A. P., Dalton J. P., Strand M. Molecular identity of a major antigen of Schistosoma mansoni which cross-reacts with Trichinella spiralis and Fasciola hepatica. Parasitology. 1986 Feb;92(Pt 1):133–151. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000063502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budka H., Costanzi G., Cristina S., Lechi A., Parravicini C., Trabattoni R., Vago L. Brain pathology induced by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A histological, immunocytochemical, and electron microscopical study of 100 autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;75(2):185–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00687080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianfriglia M., Armellini D., Massone A., Mariani M. Simple immunization protocol for high frequency production of soluble antigen-specific hybridomas. Hybridoma. 1983;2(4):451–457. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciardi A., Sinclair E., Scaravilli F., Harcourt-Webster N. J., Lucas S. The involvement of the cerebral cortex in human immunodeficiency virus encephalopathy: a morphological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00662637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Mattiace L. A., Kure K., Hutchins K., Lyman W. D., Brosnan C. F. Microglia in human disease, with an emphasis on acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Lab Invest. 1991 Feb;64(2):135–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer E. B., Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):364–367. doi: 10.1126/science.2326646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddleston M., de La Torre J. C., Xu J. Y., Dorfman N., Notkins A., Zolla-Pazner S., Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry accompanying HIV-1 infection: human monoclonal antibodies that bind to gp41 and to astrocytes. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Oct;9(10):939–944. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry as a mechanism for virus-induced autoimmunity. Immunol Res. 1989;8(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02918552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Ho D. D., de la Monte S. M., Hirsch M. S., Rota T. R., Sobel R. A. Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol. 1986 Sep;20(3):289–295. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genis P., Jett M., Bernton E. W., Boyle T., Gelbard H. A., Dzenko K., Keane R. W., Resnick L., Mizrachi Y., Volsky D. J. Cytokines and arachidonic metabolites produced during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected macrophage-astroglia interactions: implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV disease. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1703–1718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Vaca K., Noonan C. A. Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1593–1596. doi: 10.1126/science.2148832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. Fine mapping of an immunodominant domain in the transmembrane glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2639–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2639-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyes M. P., Brew B. J., Saito K., Quearry B. J., Price R. W., Lee K., Bhalla R. B., Der M., Markey S. P. Inter-relationships between quinolinic acid, neuroactive kynurenines, neopterin and beta 2-microglobulin in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of HIV-1-infected patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Sep;40(1):71–80. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow R. A., Ostrow D. G., Detels R., Phair J. P., Polk B. F., Rinaldo C. R., Jr The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study: rationale, organization, and selected characteristics of the participants. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Aug;126(2):310–318. doi: 10.1093/aje/126.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman A. P., Pitha P. M., Shin H. S., Shin M. L. Production of tumor necrosis factor and other cytokines by astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide or a neurotropic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolli F., Colao M. G., De Maio E., Di Pietro M., Galli E., Grippo A., Mazzotta F., Pinto F. Intrathecal synthesis of anti-HIV antibodies in AIDS patients. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Nov;99(2-3):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90162-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariuzza R., Strand M. Chemical basis for diversity in antibody specificity analysed by hapten binding to monoclonal anti-4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenacetyl (NP) immunoglobulins. Mol Immunol. 1981 Sep;18(9):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Chen I. S. HIV-1, macrophages, glial cells, and cytokines in AIDS nervous system disease. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2391–2397. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monell C. R., Hoover D. R., Odaka N., He X., Saah A. J., Strand M. Assessment of the antibody response to the immunosuppressive/immunodominant region of HIV gp41 in a 5-year longitudinal study. J Med Virol. 1993 Feb;39(2):125–130. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890390208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. P., Strand M. Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium, and S. japonicum: identification of genus-, species-, and gender-specific antigenic worm glycoproteins. Exp Parasitol. 1984 Feb;57(1):110–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(84)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cash K. S. Blood-brain barrier abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: immunohistochemical localization of serum proteins in postmortem brain. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):658–666. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick L., diMarzo-Veronese F., Schüpbach J., Tourtellotte W. W., Ho D. D., Müller F., Shapshak P., Vogt M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D. Intra-blood-brain-barrier synthesis of HTLV-III-specific IgG in patients with neurologic symptoms associated with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1498–1504. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg C. L., Monell C. R., Strand M. Inhibition of lymphoproliferation by a synthetic peptide with sequence identity to gp41 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3257–3260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3257-3260.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg C. L., Strand M. A synthetic peptide with sequence identity to the transmembrane protein GP41 of HIV-1 inhibits distinct lymphocyte activation pathways dependent on protein kinase C and intracellular calcium influx. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90051-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg C. L., Strand M. Inhibition of protein kinase C and anti-CD3-induced Ca2+ influx in Jurkat T cells by a synthetic peptide with sequence identity to HIV-1 gp41. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3928–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatier J. M., Vives E., Mabrouk K., Benjouad A., Rochat H., Duval A., Hue B., Bahraoui E. Evidence for neurotoxic activity of tat from human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):961–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.961-967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Gnann J. W., Jr, Langlois A. J., Shriver K., Nelson J. A., Oldstone M. B. B- and T-lymphocyte responses to an immunodominant epitope of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2531–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2531-2536.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Näher H., Stroehmann I. Phenotypic heterogeneity of cerebrospinal fluid-derived HIV-specific and HLA-restricted cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):178–181. doi: 10.1038/335178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharer L. R. Pathology of HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. A review. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):3–11. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., McMillan A., Pan X. Schistosoma mansoni: reactivity with infected human sera and monoclonal antibody characterization of a glycoprotein in different developmental stages. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Oct;54(2):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90121-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo J. R., McLane M. F., Lee T. H., Essex M. Molecular mimicry between the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 V3 loop and human brain proteins. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7711–7715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7711-7715.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselingh S. L., Power C., Glass J. D., Tyor W. R., McArthur J. C., Farber J. M., Griffin J. W., Griffin D. E. Intracerebral cytokine messenger RNA expression in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome dementia. Ann Neurol. 1993 Jun;33(6):576–582. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Zurbriggen A., Oldstone M. B., Fujinami R. S. Common immunologic determinant between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 and astrocytes. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1370–1376. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1370-1376.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]