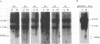Abstract
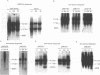
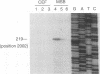
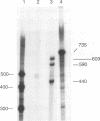
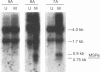
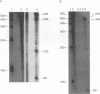
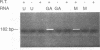
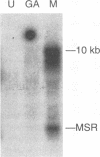
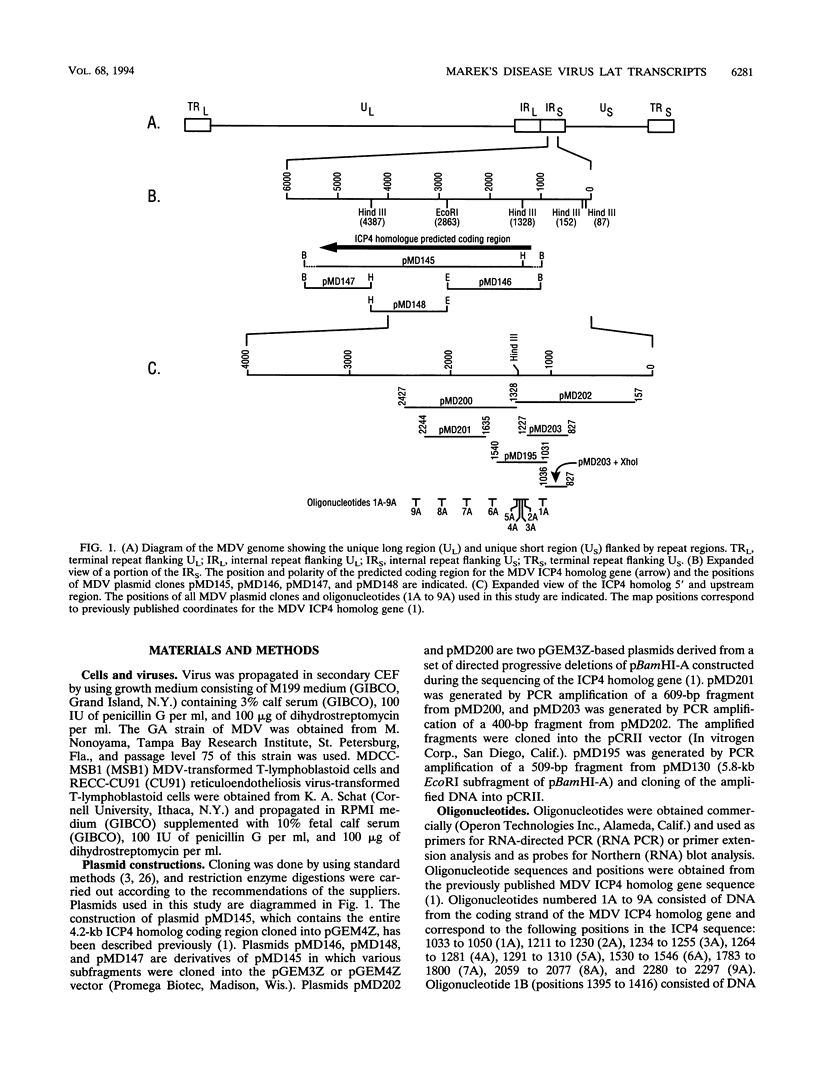
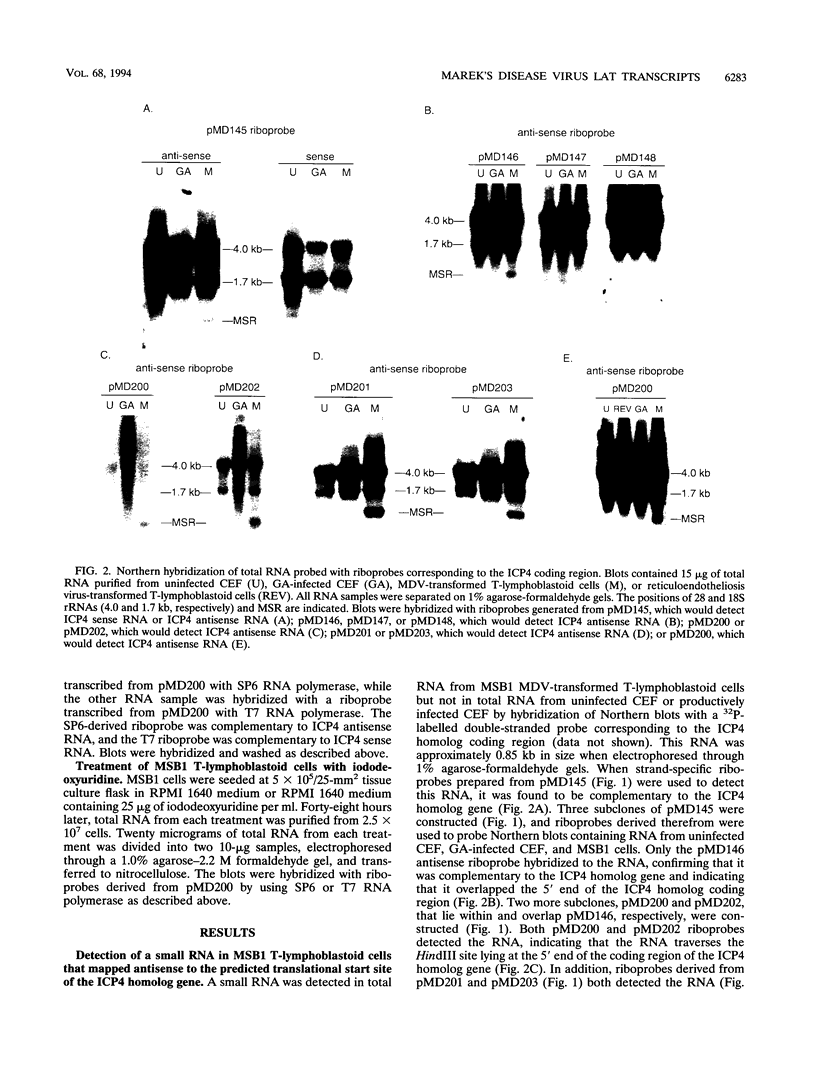
Two small RNAs (0.9 and 0.75 kb), named Marek's disease virus (MDV) small RNAs (MSRs) and a 10-kb RNA, all of which map antisense to the MDV ICP4 homolog gene, have been readily detected in MDCC-MSB1 MDV-transformed T-lymphoblastoid cells. These RNAs were not detectable in reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed T cells. When MDV was reactivated by treatment of lymphoblastoid cells with 25 micrograms of iododeoxyuridine per ml, the relative levels of the transcripts decreased. These RNAs were not detected by Northern (RNA) hybridization in productively infected chicken embryo fibroblasts 48 h postinfection; however, they were apparent 140 h postinfection. By using Northern hybridization, RNase protection assays, and primer extension analysis, the MSRs were determined to map antisense to the predicted translational start site of the ICP4 homolog gene. The conclusion most consistent with the data is that the two MSRs are overlapping, spliced RNAs. Both small RNAs contain a latency promoter binding factor consensus recognition sequence located toward their 5' ends as well as two potential ICP4 recognition consensus sequences, one in each orientation. The region contains a number of small open reading frames on each side and within the MSRs. Although the exact endpoints are unknown, the large 10-kb species spans the entire ICP4 homolog region. We believe that this group of RNAs, which map antisense to the ICP4 homolog gene, are latency-associated transcripts of MDV.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. S., Francesconi A., Morgan R. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Marek's disease virus ICP4 gene. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):657–667. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90589-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor A. H., O'Hare P. Regulation and cell-type-specific activity of a promoter located upstream of the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3269–3279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3269-3279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Adldinger H. K., Kahn D. E. Feather follicle epithelium: a source of enveloped and infectious cell-free herpesvirus from Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1970 May;14(2):219–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W., Shek W. R., Schat K. A. Spontaneous and induced herpesvirus genome expression in Marek's disease tumor cell lines. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.483-491.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. B., Sondermeijer P. J., Velicer L. F. Identification of a unique Marek's disease virus gene which encodes a 38-kilodalton phosphoprotein and is expressed in both lytically infected cells and latently infected lymphoblastoid tumor cells. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):85–94. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.85-94.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. Detection of pseudorabies virus transcripts in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected swine. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2908–2913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2908-2913.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Z. Z., Lee L. F., Liu J. L., Kung H. J. Structural analysis and transcriptional mapping of the Marek's disease virus gene encoding pp38, an antigen associated with transformed cells. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6509–6515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6509-6515.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K., Nazerian K. Induction of Marek's disease virus antigens by IdUrd in a chicken lymphoblastoid cell line. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):413–419. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Cullen B. R. Molecular basis of latency in pathogenic human viruses. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):815–820. doi: 10.1126/science.1658933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C., Delhon G., Bratanich A., Kutish G., Rock D. Analysis of the transcriptional promoter which regulates the latency-related transcript of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1164-1170.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D., Lee L., Liu J. L., Kung H. J., Tillotson J. K. Marek disease virus encodes a basic-leucine zipper gene resembling the fos/jun oncogenes that is highly expressed in lymphoblastoid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4042–4046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotanides H., Reich N. C. Requirement of tyrosine phosphorylation for rapid activation of a DNA binding factor by IL-4. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1265–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.7694370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maray T., Malkinson M., Becker Y. RNA transcripts of Marek's disease virus (MDV) serotype-1 in infected and transformed cells. Virus Genes. 1988 Oct;2(1):49–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00569736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. L., Holman R. P., Croen K. D., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Varicella-zoster virus transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):193–200. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazerian K., Witter R. L. Cell-free transmission and in vivo replication of Marek's disease virus. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):388–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.388-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. D., Cantello J., Morgan R. W., Schat K. A. Enhanced expression of the Marek's disease virus-specific phosphoproteins after stable transfection of MSB-1 cells with the Marek's disease virus homologue of ICP4. Virology. 1994 May 15;201(1):132–136. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Beam S. L., Mayfield J. E. Mapping bovine herpesvirus type 1 latency-related RNA in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected rabbits. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3827–3831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3827-3831.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Buckmaster A., Ross L. J. Partial transcription map of Marek's disease herpesvirus in lytically infected cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jul 15;44(1):101–109. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Transcription of the Marek's disease virus genome in a nonproductive chicken lymphoblastoid cell line. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts during latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3841–3847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3841-3847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Woods G. M., Fraser N. W. Identification of a novel latency-specific splice donor signal within the herpes simplex virus type 1 2.0-kilobase latency-associated transcript (LAT): translation inhibition of LAT open reading frames by the intron within the 2.0-kilobase LAT. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6800–6810. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6800-6810.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Human herpesviruses: a consideration of the latent state. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):318–332. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.318-332.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugaya K., Bradley G., Nonoyama M., Tanaka A. Latent transcripts of Marek's disease virus are clustered in the short and long repeat regions. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5773–5782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5773-5782.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L. T., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Identification of Marek's disease virus nuclear antigen in latently infected lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3764–3771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3764-3771.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth U. V., Vogt B., Schwyzer M. The three major immediate-early transcripts of bovine herpesvirus 1 arise from two divergent and spliced transcription units. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):195–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.195-205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaagstra J. C., Ghiasi H., Nesburn A. B., Wechsler S. L. Identification of a major regulatory sequence in the latency associated transcript (LAT) promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Virology. 1991 May;182(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90672-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]