Abstract
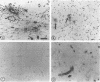
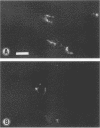
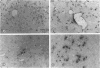
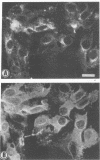
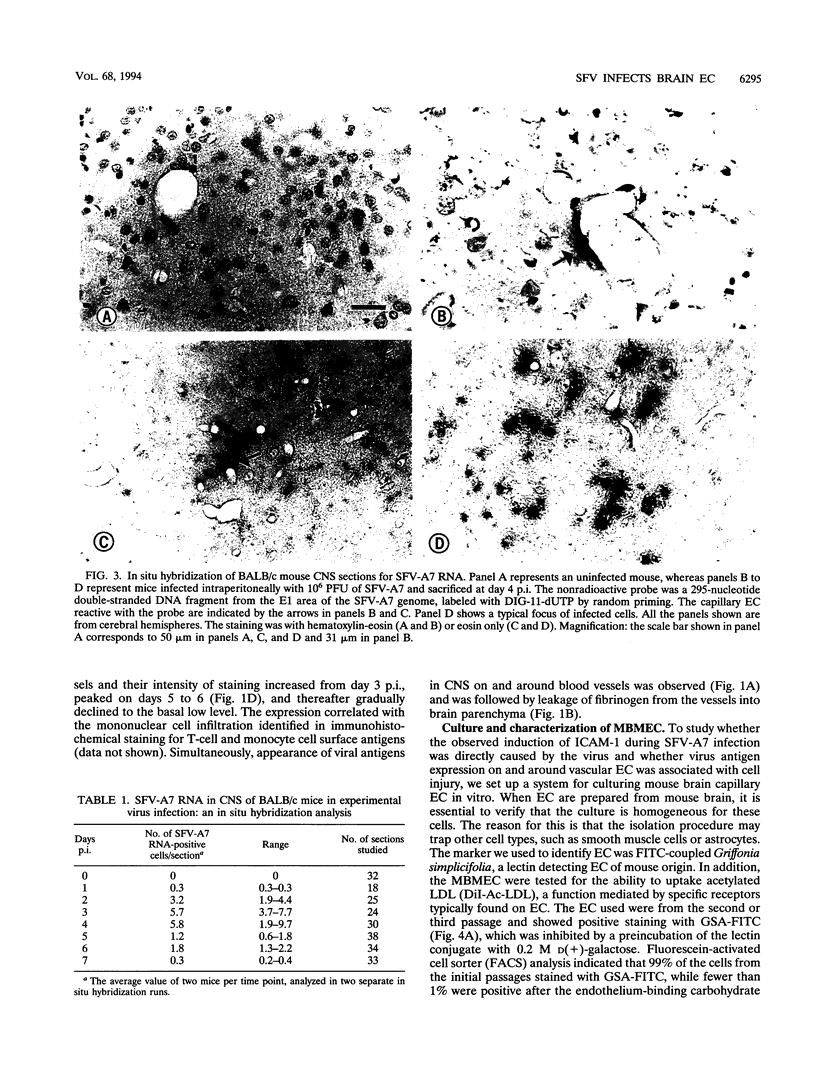
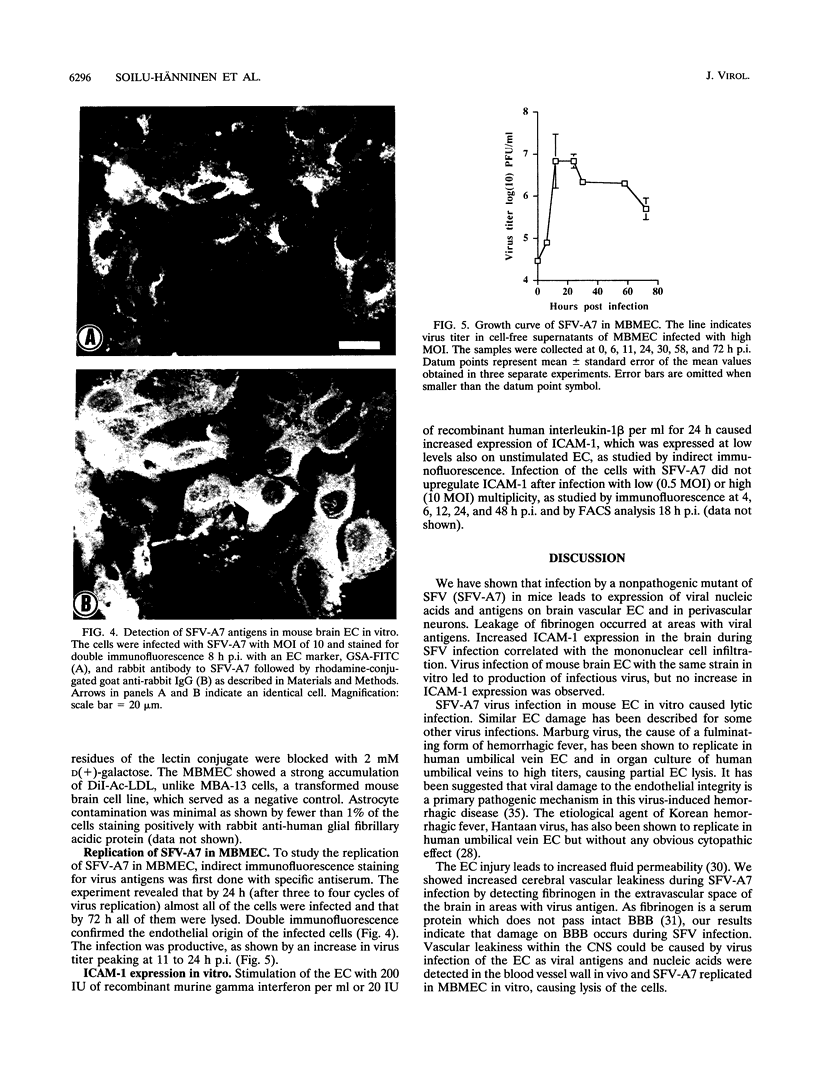
Induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is facilitated in a genetically resistant BALB/c mouse strain by a nonpathogenic strain of a neurotropic alphavirus, Semliki Forest virus (SFV-A7). One possible explanation for this enhancement is virus infection of endothelial cells (EC), causing increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier. We have now sought evidence for virus infection of EC in vivo by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization. SFV-A7 antigens and RNA were detected in vascular EC and perivascular neurons in cerebellar and spinal cord white matter. Expression of viral antigens was followed by fibrinogen leakage from the blood vessels into brain parenchyma. This was shown by immunoperoxidase staining detecting fibrinogen extravascularly in central nervous system sections of infected mice. Simultaneously, expression of ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) was induced on brain EC. SFV-A7 replicated in mouse brain microvascular EC in vitro and caused lysis of the cells. SFV-A7 did not induce ICAM-1 expression of mouse brain microvascular EC in vitro, while ICAM-1 was readily induced by gamma interferon and interleukin 1 beta. The observed increase of ICAM-1 expression on EC is immune mediated and not a direct effect of the virus infection. We conclude that SFV-A7 infection causes cerebral microvascular damage which contributes to the facilitation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in BALB/c mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades E. W., Hierholzer J. C., George V., Black J., Candal F. Viral susceptibility of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J Virol Methods. 1992 Sep;39(1-2):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90127-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen I., Brankin B. Pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis--the immune diathesis and the role of viruses. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Mar;52(2):95–105. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen O., Lygner P. E., Bergström T., Andersson M., Vahlne A. Viral infections trigger multiple sclerosis relapses: a prospective seroepidemiological study. J Neurol. 1993 Jul;240(7):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00867354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archelos J. J., Jung S., Mäurer M., Schmied M., Lassmann H., Tamatani T., Miyasaka M., Toyka K. V., Hartung H. P. Inhibition of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by an antibody to the intercellular adhesion molecule ICAM-1. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):145–154. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Barrett T., McDougall J. K. Viruses in the etiology of atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6386–6389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. L. Humoral and cell-mediated immune mechanisms in the production of pathology in avirulent Semliki Forest virus encephalitis. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.244-253.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradish C. J., Allner K., Maber H. B. The virulence of original and derived strains of Semliki forest virus for mice, guinea-pigs and rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1971 Aug;12(2):141–160. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-2-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1033–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannella B., Cross A. H., Raine C. S. Upregulation and coexpression of adhesion molecules correlate with relapsing autoimmune demyelination in the central nervous system. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1521–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgriff T. M. Viruses and hemostasis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11 (Suppl 4):S672–S688. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_4.s672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBault L. E., Kahn L. E., Frommes S. P., Cancilla P. A. Cerebral microvessels and derived cells in tissue culture: isolation and preliminary characterization. In Vitro. 1979 Jul;15(7):473–487. doi: 10.1007/BF02618149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabry Z., Waldschmidt M. M., Hendrickson D., Keiner J., Love-Homan L., Takei F., Hart M. N. Adhesion molecules on murine brain microvascular endothelial cells: expression and regulation of ICAM-1 and Lgp 55. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Jan;36(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90026-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Pathak S., Scallan M., Amor S., Dyson H. Replication of the A7(74) strain of Semliki Forest virus is restricted in neurons. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):627–637. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Macarak E. J., MacGregor R. R., Wolfe J., Kefalides N. A. Virus infection of endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):266–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D., Esiri M. Blood-brain barrier damage in acute multiple sclerosis plaques. An immunocytological study. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1B):557–572. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.1.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein G. W., Betz A. L., Bowman P. D. Use of isolated brain capillaries and cultured endothelial cells to study the blood-brain barrier. Fed Proc. 1984 Feb;43(2):191–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. E., Yunis E. J. Viral crystalline arrays in human coxsackie myocarditis. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):442–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. P., Mackenzie F., Tofts P., du Boulay E. P., McDonald W. I. Patterns of blood-brain barrier breakdown in inflammatory demyelination. Brain. 1991 Apr;114(Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.2.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen P., Arstila P., Lang H., Salmi A., Panelius M. Involvement of the central nervous system in acute, uncomplicated measles virus infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.610-613.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermode A. G., Tofts P. S., MacManus D. G., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., Moseley I. F., du Boulay E. P., McDonald W. I. Early lesion of multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1988 Nov 19;2(8621):1203–1204. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathey J. L., Wiley C. A., Verity M. A., Nelson J. A. Cultured human brain capillary endothelial cells are permissive for infection by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):266–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90252-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maples J. A. A method for the covalent attachment of cells to glass slides for use in immunohistochemical assays. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;83(3):356–363. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Wang L., Racke M. K., McFarlin D. E., Spatz M. Cytokine-regulated adhesion between encephalitogenic T lymphocytes and cerebrovascular endothelial cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Mar;43(1-2):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtarian F., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Adoptive transfer of myelin basic protein-sensitized T cells produces chronic relapsing demyelinating disease in mice. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):356–358. doi: 10.1038/309356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S., Webb H. E. Possible mechanisms for the transport of Semliki forest virus into and within mouse brain. An electron-microscopic study. J Neurol Sci. 1974 Oct;23(2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(74)90221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensiero M. N., Sharefkin J. B., Dieffenbach C. W., Hay J. Hantaan virus infection of human endothelial cells. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5929–5936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5929-5936.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petito C. K., Cash K. S. Blood-brain barrier abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: immunohistochemical localization of serum proteins in postmortem brain. Ann Neurol. 1992 Nov;32(5):658–666. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Cotran R. S. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation. 1990 Oct;50(4):537–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahagun G., Moore S. A., Fabry Z., Schelper R. L., Hart M. N. Purification of murine endothelial cell cultures by flow cytometry using fluorescein-labeled griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1227–1232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Vuorio E. Localization of types I, II, and III collagen mRNAs in developing human skeletal tissues by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasseville V. G., Newman W. A., Lackner A. A., Smith M. O., Lausen N. C., Beall D., Ringler D. J. Elevated vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in AIDS encephalitis induced by simian immunodeficiency virus. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1021–1030. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittler H. J., Mahner F., Drenckhahn D., Klenk H. D., Feldmann H. Replication of Marburg virus in human endothelial cells. A possible mechanism for the development of viral hemorrhagic disease. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1301–1309. doi: 10.1172/JCI116329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Noori M. A., Ciardi M., Cirelli A., Thompson E. J. Increased levels of circulating ICAM-1 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with active multiple sclerosis. Correlation with TNF-alpha and blood-brain barrier damage. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Mar;43(1-2):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90070-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley W. A., Bamford C. R., Clark K. Clinical viral infections and multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1985 Jun 8;1(8441):1313–1315. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(85)92801-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Mitchell M. E., Fondren G. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in cellular immune reactions in the human central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1309–1316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangel A. G., Temonen M., Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Vaheri A. Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in nephropathia epidemica and other viral diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Oct;90(1):13–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. M., O'Leary T. J., Baskin G. B., Benveniste R., Harris C. A., Nara P. L., Rhodes R. H. Immunohistochemical localization of human and simian immunodeficiency viral antigens in fixed tissue sections. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):199–205. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. X., Mäkelä M. J., Röyttä M., Salmi A. Effect of viral infection on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in mice. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 May;18(2):139–153. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. Theiler's virus infection in nude mice: viral RNA in vascular endothelial cells. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3589–3596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3589-3596.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]