Abstract
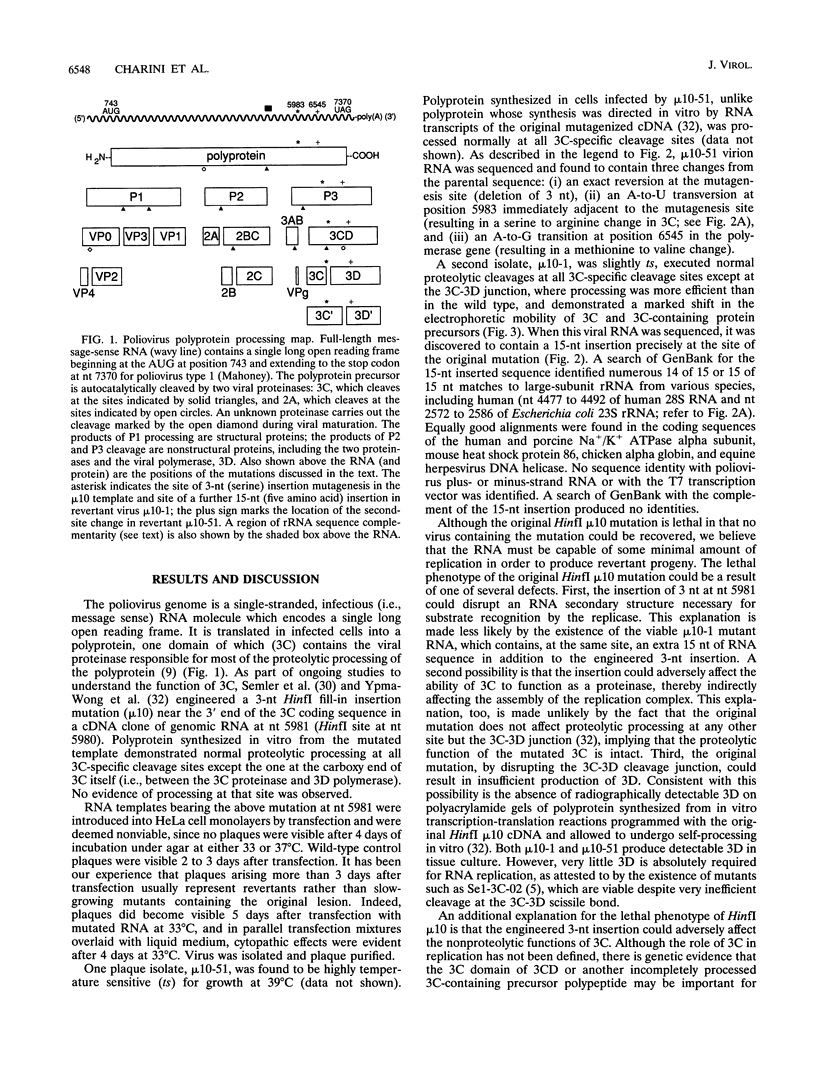
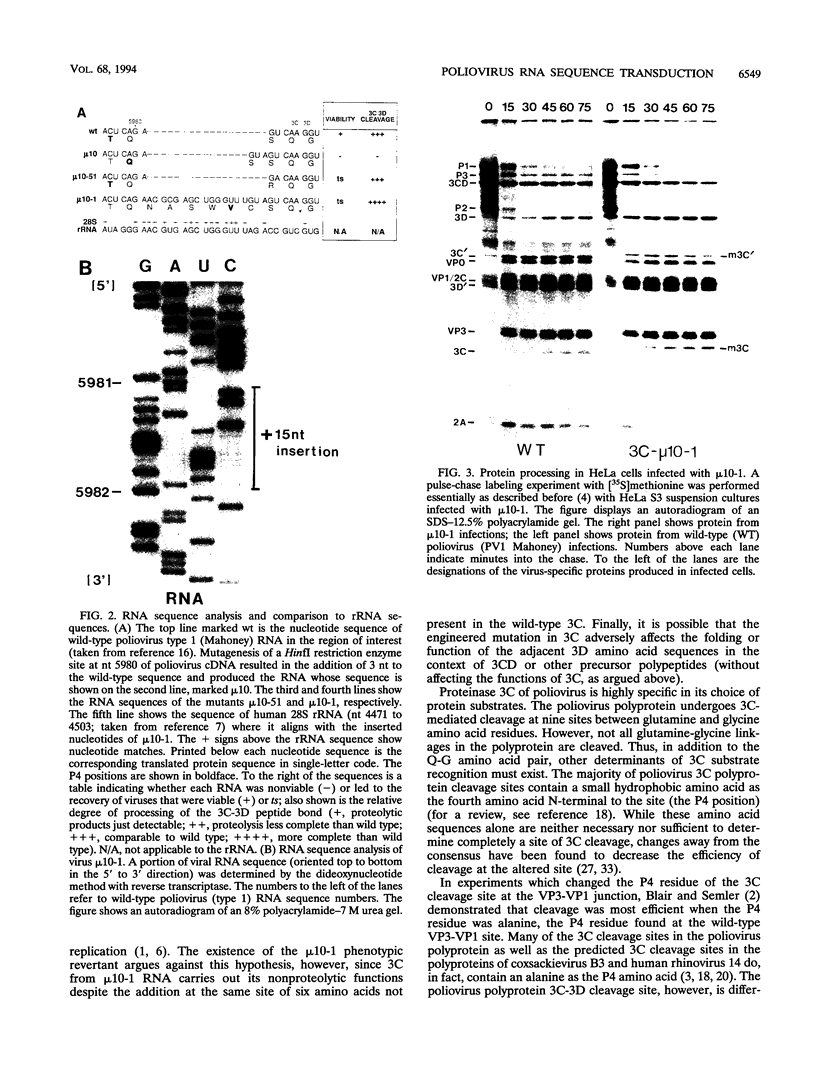
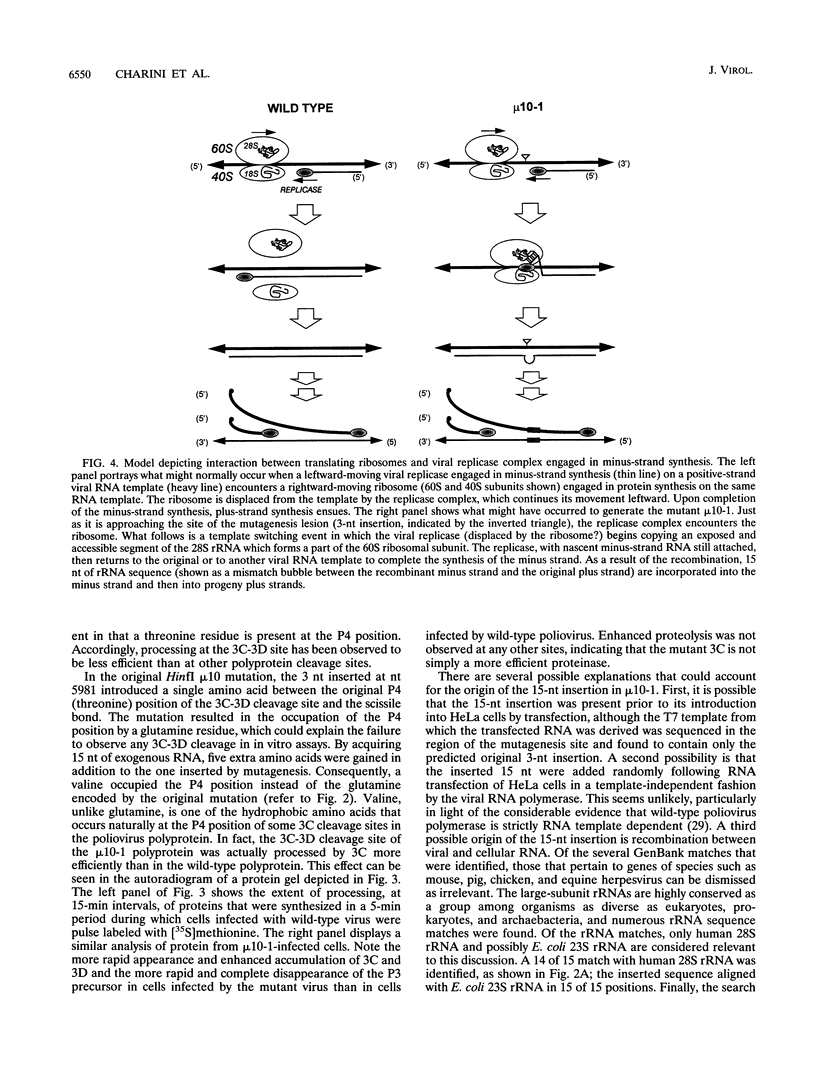
Cells infected with poliovirus express a virally encoded polyprotein which undergoes self-mediated cleavage into structural and nonstructural viral proteins. Most of these cleavages are catalyzed by the 3C proteolytic domain of the polyprotein. Polyprotein synthesized in vitro from an RNA template containing a three-nucleotide insertion in 3C underwent proteolytic processing at all but one of the 3C-dependent cleavage sites. When transfected into HeLa cells, this RNA template displayed a lethal phenotype. We report here the isolation of two pseudorevertant progeny strains with restored protein-processing phenotypes, one of which appears to have arisen by transduction of a stretch of nucleotides from human 28S rRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Achacoso P. L., Baltimore D. Poliovirus RNA synthesis utilizes an RNP complex formed around the 5'-end of viral RNA. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3587–3598. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair W. S., Semler B. L. Role for the P4 amino acid residue in substrate utilization by the poliovirus 3CD proteinase. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6111–6123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6111-6123.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan P. L., Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. Molecular cloning and complete sequence determination of RNA genome of human rhinovirus type 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charini W. A., Burns C. C., Ehrenfeld E., Semler B. L. trans rescue of a mutant poliovirus RNA polymerase function. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2655–2665. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2655-2665.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewalt P. G., Semler B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of proteinase 3C results in a poliovirus deficient in synthesis of viral RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2162–2170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2162-2170.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez I. L., Gorski J. L., Campen T. J., Dorney D. J., Erickson J. M., Sylvester J. E., Schmickel R. D. Variation among human 28S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRST G. K. Genetic recombination with Newcastle disease virus, polioviruses, and influenza. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:303–309. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller A. A., Semler B. L. Linker scanning mutagenesis of the internal ribosome entry site of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5075–5086. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5075-5086.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W. S., Temin H. M. Retroviral recombination and reverse transcription. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1227–1233. doi: 10.1126/science.1700865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Kirkegaard K. Poliovirus RNA recombination: mechanistic studies in the absence of selection. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3135–3145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatchikian D., Orlich M., Rott R. Increased viral pathogenicity after insertion of a 28S ribosomal RNA sequence into the haemagglutinin gene of an influenza virus. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):156–157. doi: 10.1038/340156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Baltimore D. The mechanism of RNA recombination in poliovirus. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):433–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90600-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. RNA recombination in animal and plant viruses. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):61–79. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.61-79.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Semler B. L. Picornavirus protein processing--enzymes, substrates, and genetic regulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:49–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. M., Stålhandske P. O., Pettersson U. Genome of coxsackievirus B3. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo M. A., Jolly C. A. The 5'-terminal sequence of potato leafroll virus RNA: evidence of recombination between virus and host RNA. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2591–2595. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. Poliovirus genome RNA hybridizes specifically to higher eukaryotic rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6797–6816. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Tautz N., Dubovi E. J., Thiel H. J. Viral cytopathogenicity correlated with integration of ubiquitin-coding sequences. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):602–616. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90074-L. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe S. S., Schlesinger S. RNAs from two independently isolated defective interfering particles of Sindbis virus contain a cellular tRNA sequence at their 5' ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3279–3283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munishkin A. V., Voronin L. A., Chetverin A. B. An in vivo recombinant RNA capable of autocatalytic synthesis by Q beta replicase. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):473–475. doi: 10.1038/333473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallai P. V., Burkhardt F., Skoog M., Schreiner K., Bax P., Cohen K. A., Hansen G., Palladino D. E., Harris K. S., Nicklin M. J. Cleavage of synthetic peptides by purified poliovirus 3C proteinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9738–9741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrault J. Origin and replication of defective interfering particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:151–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus RNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:89–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Dewalt P. G., Ypma-Wong M. F. Site-specific mutagenesis of cDNA clones expressing a poliovirus proteinase. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;33(1):39–51. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolskaya E. A., Romanova L. A., Kolesnikova M. S., Agol V. I. Intertypic recombination in poliovirus: genetic and biochemical studies. Virology. 1983 Jan 15;124(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Dewalt P. G., Johnson V. H., Lamb J. G., Semler B. L. Protein 3CD is the major poliovirus proteinase responsible for cleavage of the P1 capsid precursor. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Filman D. J., Hogle J. M., Semler B. L. Structural domains of the poliovirus polyprotein are major determinants for proteolytic cleavage at Gln-Gly pairs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17846–17856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]