Abstract
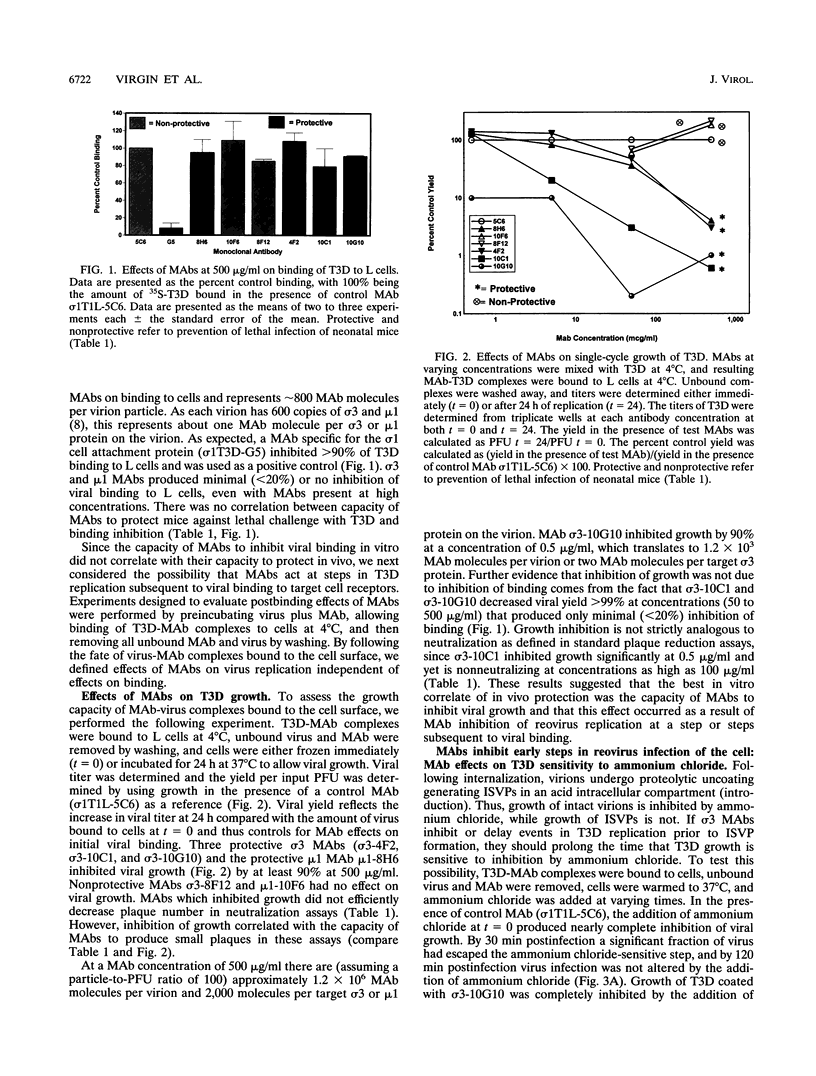
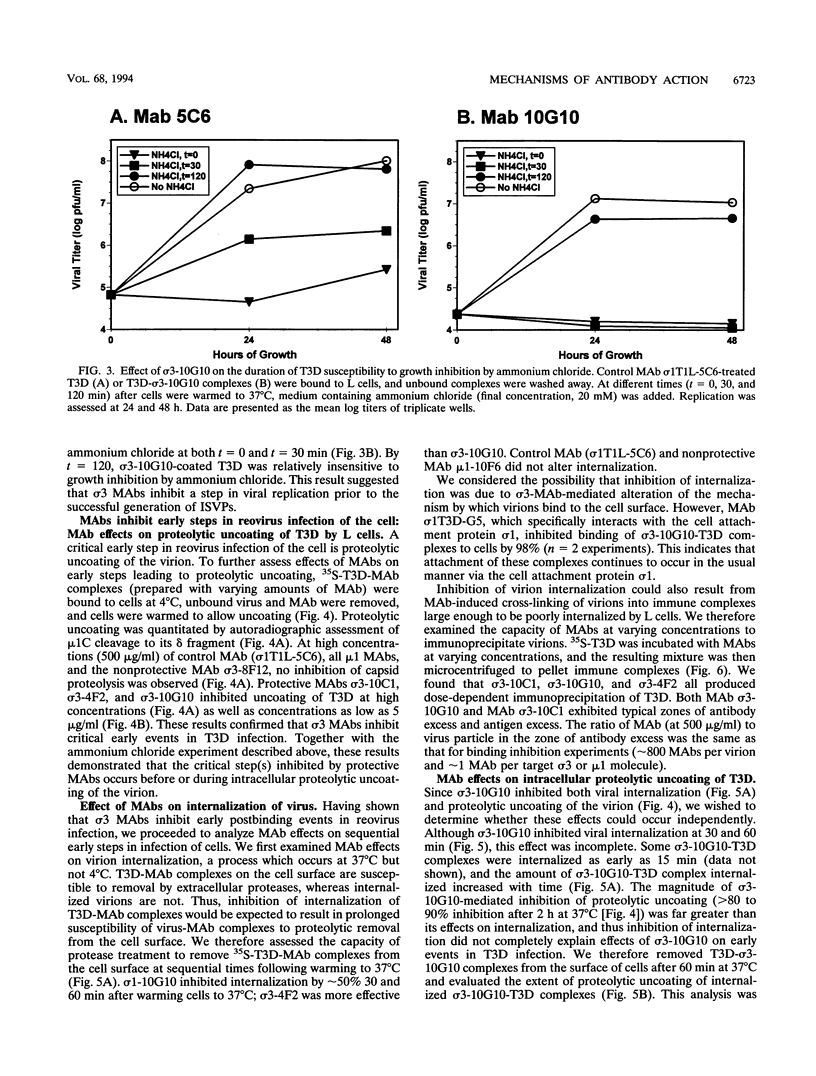
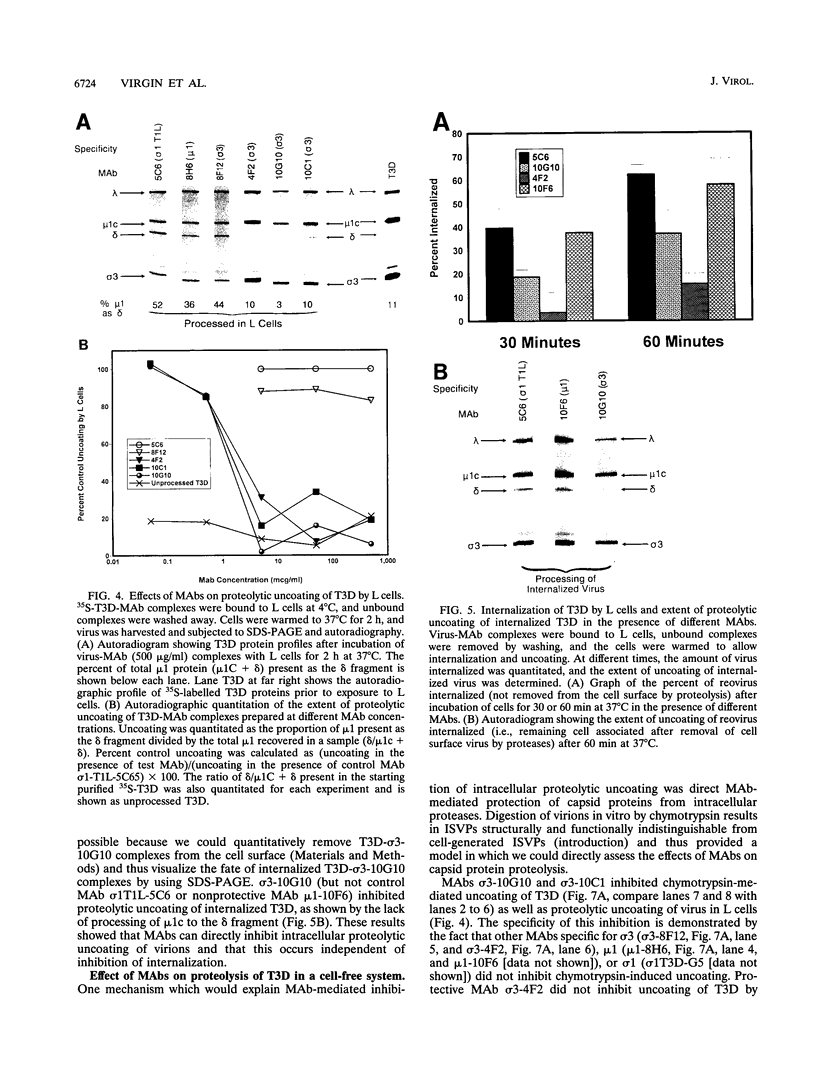
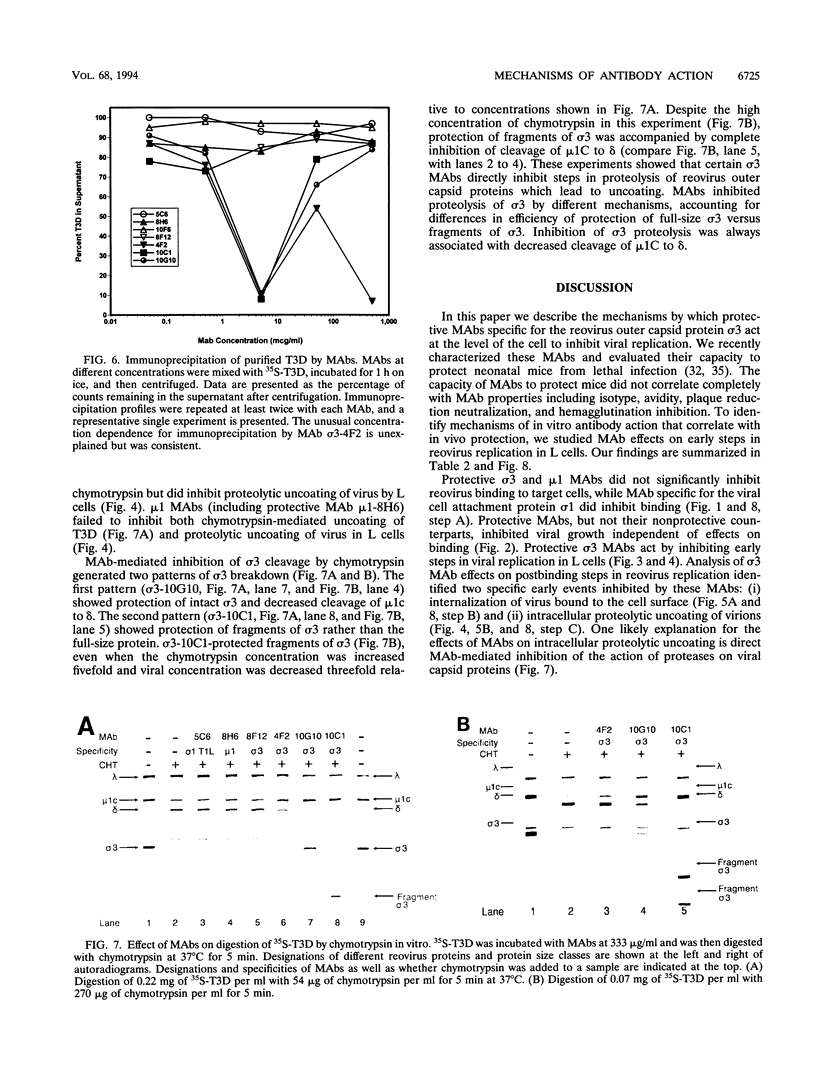
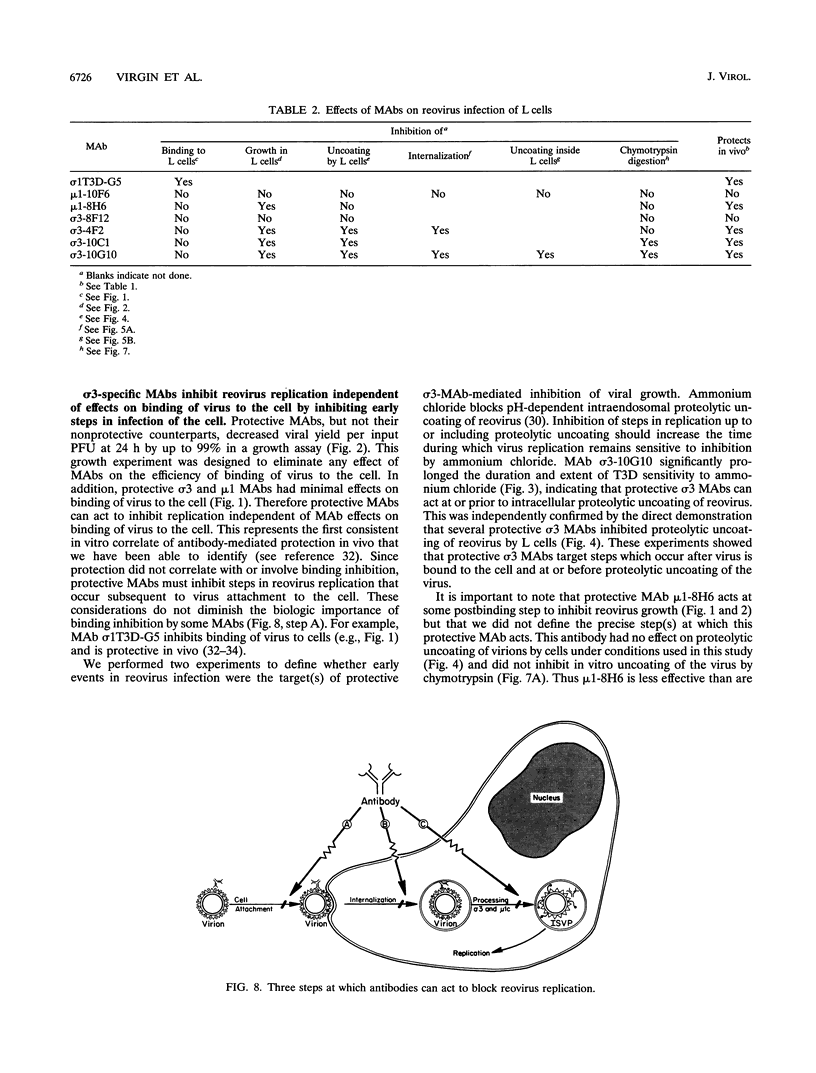
We identified in vitro correlates of in vivo protection mediated by nonneutralizing antibodies specific for reovirus capsid proteins. We defined mechanisms of antibody action by analyzing monoclonal antibody (MAb) effects at sequential steps in reovirus serotype 3 strain Dearing (T3D) infection of L cells. Two types of experiments showed that protective MAbs specific for the outer capsid proteins sigma 3 or mu 1 inhibited T3D infection independent of effects on binding. First, MAbs which had no effect on T3D binding inhibited T3D growth. Second, MAb-coated T3D attached to L cells did not replicate as efficiently as T3D without bound antibody. We therefore defined sigma 3-specific MAb effects on postbinding steps in T3D infection. T3D coated with MAb sigma 3-10G10 exhibited prolonged sensitivity to growth inhibition by ammonium chloride. Since ammonium chloride inhibits endosomal acidification and proteolytic processing of the T3D capsid, this suggested that MAbs inhibit early steps in T3D infection. This was confirmed by direct demonstration that several sigma 3-specific MAbs inhibited proteolytic uncoating of virions by fibroblasts. We identified two mechanisms for antibody-mediated inhibition of virion uncoating: (i) inhibition of internalization of T3D-MAb complexes bound to the cell surface, and (ii) inhibition of intracellular proteolysis of the T3D capsid. Studies using a cell-free system confirmed that sigma 3-specific MAbs directly block proteolytic uncoating of the T3D virion. In addition, we found that sigma 3-specific MAbs block (and therefore define) two distinct steps in proteolytic uncoating of the reovirion. We conclude that antibodies which are protective in vivo inhibit postbinding events in reovirus infection of permissive cells. Protective antibodies act by inhibiting internalization and intracellular proteolytic uncoating of the virion. Analysis of postbinding mechanisms of MAb action may identify targets for vaccine development and antiviral therapy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong S. J., Dimmock N. J. Neutralization of influenza virus by low concentrations of hemagglutinin-specific polymeric immunoglobulin A inhibits viral fusion activity, but activation of the ribonucleoprotein is also inhibited. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3823–3832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3823-3832.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Bodkin D., Dambrauskas R., Trier J. S., Fields B. N., Wolf J. L. Intraluminal proteolytic activation plays an important role in replication of type 1 reovirus in the intestines of neonatal mice. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1830–1833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1830-1833.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodkin D. K., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Proteolytic digestion of reovirus in the intestinal lumens of neonatal mice. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4676–4681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4676-4681.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Copps T. P., Sargent M. D., Long D. G., Chapman J. D. New intermediate subviral particles in the in vitro uncoating of reovirus virions by chymotrypsin. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):552–564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.552-564.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Sargent M. D., Lievaart P. A., Copps T. P. Reovirus: evidence for a second step in the intracellular uncoating and transcriptase activation process. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90664-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning W. M., Fields B. N. Ammonium chloride prevents lytic growth of reovirus and helps to establish persistent infection in mouse L cells. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):987–988. doi: 10.1126/science.6297010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fields B. N. Genetic studies on the mechanism of chemical and physical inactivation of reovirus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden K. A., Wang G., Yeager M., Nibert M. L., Coombs K. M., Furlong D. B., Fields B. N., Baker T. S. Early steps in reovirus infection are associated with dramatic changes in supramolecular structure and protein conformation: analysis of virions and subviral particles by cryoelectron microscopy and image reconstruction. J Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;122(5):1023–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.5.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Kao S. Y., Lewis A. J., Crainic R., Wimmer E. Functional basis of poliovirus neutralization determined with monospecific neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.466-474.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Ostapchuk P., Wimmer E. Bivalent attachment of antibody onto poliovirus leads to conformational alteration and neutralization. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):547–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.547-550.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Raux H., Gaudin Y., Ruigrok R. W. Mechanisms of rabies virus neutralization. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):302–313. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollins S. W., Porterfield J. S. A new mechanism for the neutralization of enveloped viruses by antiviral antibody. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):244–246. doi: 10.1038/321244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Virus receptors: binding, adhesion strengthening, and changes in viral structure. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.1-5.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J., Shiwen H., Duke G., Gilbert S., Rueckert R., Anderegg J. Neutralization of poliovirus by a monoclonal antibody: kinetics and stoichiometry. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):412–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Protein sigma 1 is the reovirus cell attachment protein. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucia-Jandris P., Hooper J. W., Fields B. N. Reovirus M2 gene is associated with chromium release from mouse L cells. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5339–5345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5339-5345.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratos-Flier E., Goodman M. J., Murray A. H., Kahn C. R. Ammonium inhibits processing and cytotoxicity of reovirus, a nonenveloped virus. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):1003–1007. doi: 10.1172/JCI112653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. A carboxy-terminal fragment of protein mu 1/mu 1C is present in infectious subvirion particles of mammalian reoviruses and is proposed to have a role in penetration. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6408–6418. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6408-6418.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M. L., Furlong D. B., Fields B. N. Mechanisms of viral pathogenesis. Distinct forms of reoviruses and their roles during replication in cells and host. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):727–734. doi: 10.1172/JCI115369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outlaw M. C., Dimmock N. J. Insights into neutralization of animal viruses gained from study of influenza virus. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Apr;106(2):205–220. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800048354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacitti A. F., Gentsch J. R. Inhibition of reovirus type 3 binding to host cells by sialylated glycoproteins is mediated through the viral attachment protein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1407–1415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1407-1415.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R. W., Choi A. H., Lee P. W. The alpha-anomeric form of sialic acid is the minimal receptor determinant recognized by reovirus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):382–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Li X. Y., Tyler K. L., Cullen J. M., Virgin H. W., 4th Lymphocytes protect against and are not required for reovirus-induced myocarditis. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6119–6124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6119-6124.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Kaye K., Fields B. N. Topological analysis of the reovirus type 3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. E., Tang D., Lee P. W. Evidence that the epidermal growth factor receptor on host cells confers reovirus infection efficiency. Virology. 1993 Nov;197(1):405–411. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturzenbecker L. J., Nibert M., Furlong D., Fields B. N. Intracellular digestion of reovirus particles requires a low pH and is an essential step in the viral infectious cycle. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2351–2361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2351-2361.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosteson M. T., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Ion channels induced in lipid bilayers by subvirion particles of the nonenveloped mammalian reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10549–10552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., Mann M. A., Fields B. N., Virgin H. W., 4th Protective anti-reovirus monoclonal antibodies and their effects on viral pathogenesis. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3446–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3446-3453.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler K. L., Virgin H. W., 4th, Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N. Antibody inhibits defined stages in the pathogenesis of reovirus serotype 3 infection of the central nervous system. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):887–900. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Bassel-Duby R., Fields B. N., Tyler K. L. Antibody protects against lethal infection with the neurally spreading reovirus type 3 (Dearing). J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4594–4604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4594-4604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virgin H. W., 4th, Mann M. A., Fields B. N., Tyler K. L. Monoclonal antibodies to reovirus reveal structure/function relationships between capsid proteins and genetics of susceptibility to antibody action. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6772–6781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6772-6781.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrijsen R., Mosser A., Boeyé A. Postabsorption neutralization of poliovirus. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3126–3133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3126-3133.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Fields B. N. Neutralization of reovirus: the gene responsible for the neutralization antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1305–1310. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Ramig R. F., Mustoe T. A., Fields B. N. Identification of the gene coding for the hemagglutinin of reovirus. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):581–584. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham T. J., Mathias P., Cheresh D. A., Nemerow G. R. Integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90231-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]