Abstract
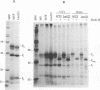
Membrane fusion caused by measles virus (MV) is a function of the fusion (F) protein. This process is essential for penetration into the host cell and subsequent initiation of the virus replicative cycle. The biological activity of the MV F protein is generated by endoproteolytic cleavage of a precursor protein (F0) into a large F1 subunit and a smaller F2 subunit held together by disulfide bonds. The cleavage site consists of a cluster of five basic amino acids (amino acids 108 to 112) within the predicted primary structure of the F protein. To investigate the role of the arginine residue at the carboxy terminus of the F2 subunit (arginine 112), site-directed mutagenesis was used to construct a cleavage mutant of the MV F protein in which this arginine residue was changed to a leucine residue. The mutated F gene, encoding four out of the five basic amino acids at the cleavage site, was inserted into the genome of vaccinia virus. The resulting recombinant virus was used to study expression of the mutant F protein in infected cells. Analysis of the Leu-112 mutant protein made in infected cells demonstrated that this single-amino-acid substitution resulted in a reduced rate of transport of the mutant protein to the cell surface, despite its efficient cleavage to yield F1 and F2 subunits. However, the electrophoretic mobilities of the Leu-112 polypeptides suggested that the protein was cleaved incorrectly. This aberrant cleavage appears to have abolished the ability of the F protein to cause syncytium formation. The data indicate that the arginine 112 residue is critical for the correct proteolytic cleavage that is required for the membrane fusion activity of the MV F protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. High-level eucaryotic in vivo expression of biologically active measles virus hemagglutinin by using an adenovirus type 5 helper-free vector system. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2718–2727. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2718-2727.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Richardson C., Shen S. H. Intracellular processing, glycosylation, and cell-surface expression of the measles virus fusion protein (F) encoded by a recombinant adenovirus. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhatib G., Shen S. H., Briedis D., Richardson C., Massie B., Weinberg R., Smith D., Taylor J., Paoletti E., Roder J. Functional analysis of N-linked glycosylation mutants of the measles virus fusion protein synthesized by recombinant vaccinia virus vectors. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1522–1531. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1522-1531.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch M. L., Earl P. L., Fargnoli K., Picciafuoco S., Giombini F., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G. Identification of the fusion peptide of primate immunodeficiency viruses. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.2541505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Scarano F., Waxham M. N., Ross A. M., Hoxie J. A. Sequence similarities between human immunodeficiency virus gp41 and paramyxovirus fusion proteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):245–252. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H. G., Veronese F. M., Tschachler E., Pal R., Kalyanaraman V. S., Gallo R. C., Reitz M. S., Jr Characterization of an HIV-1 point mutant blocked in envelope glycoprotein cleavage. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., McQuain C., Sergel T., McGinnes L., Reitter J. The role of the amino terminus of F1 of the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein in cleavage and fusion. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):997–1000. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Ability of the hydrophobic fusion-related external domain of a paramyxovirus F protein to act as a membrane anchor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Shaughnessy M. A., Lamb R. A. Analysis of the relationship between cleavability of a paramyxovirus fusion protein and length of the connecting peptide. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1293–1301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1293-1301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffy K. R., Kraus G., Looney D. J., Wong-Staal F. Role of the fusogenic peptide sequence in syncytium induction and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4532–4535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4532-4535.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Pincus S., Tartaglia J., Richardson C., Alkhatib G., Briedis D., Appel M., Norton E., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus recombinants expressing either the measles virus fusion or hemagglutinin glycoprotein protect dogs against canine distemper virus challenge. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4263–4274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4263-4274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsanyi T. M., Jörnvall H., Norrby E. Isolation and characterization of the measles virus F1 polypeptide: comparison with other paramyxovirus fusion proteins. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsanyi T. M., Utter G., Norrby E. Purification, morphology and antigenic characterization of measles virus envelope components. J Gen Virol. 1984 Feb;65(Pt 2):355–366. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-2-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialard J., Lalumière M., Vernet T., Briedis D., Alkhatib G., Henning D., Levin D., Richardson C. Synthesis of the membrane fusion and hemagglutinin proteins of measles virus, using a novel baculovirus vector containing the beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):37–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.37-50.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]