Abstract
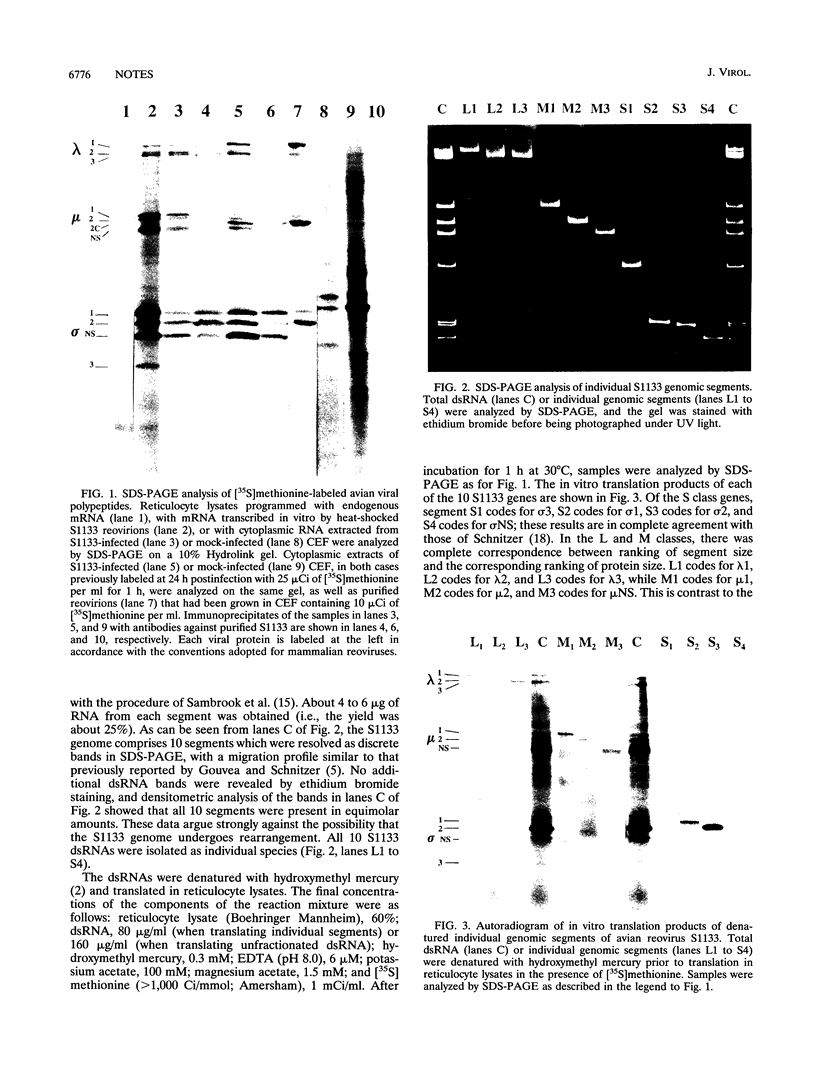
Avian reovirus S1133 encodes 10 primary translation products, 8 of which are structural components of the viral particle and 2 of which are nonstructural proteins. The identity of the gene that codes for each of these polypeptides was determined by in vitro translation of denatured individual genome segments.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benavente J., Shatkin A. J. Avian reovirus mRNAs are nonfunctional in infected mouse cells: translational basis for virus host-range restriction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. R., Zarbl H., Millward S. Reovirus guanylyltransferase is L2 gene product lambda 2. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):307–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.307-311.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo J. E., Shatkin A. J. Translation of bicistronic viral mRNA in transfected cells: regulation at the level of elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass S. E., Naqi S. A., Hall C. F., Kerr K. M. Isolation and characterization of a virus associated with arthritis of chickens. Avian Dis. 1973 Apr-Jun;17(2):415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouvea V. S., Schnitzer T. J. Polymorphism of the genomic RNAs among the avian reoviruses. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):87–91. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C., Blobel G. Post-translational cleavage of presecretory proteins with an extract of rough microsomes from dog pancreas containing signal peptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Analysis of ribosome binding sites from the s1 message of reovirus. Initiation at the first and second AUG codons. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):807–820. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni Y., Ramig R. F., Kemp M. C. Identification of proteins encoded by avian reoviruses and evidence for post-translational modification. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):466–469. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nick H., Cursiefen D., Becht H. Structural and growth characteristics of two avian reoviruses. Arch Virol. 1975;48(3):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01317969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J. Protein coding assignment of the S genes of the avian reovirus S1133. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer T. J., Ramos T., Gouvea V. Avian reovirus polypeptides: analysis of intracellular virus-specified products, virions, top component, and cores. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1006-1014.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Physical and chemical characterization of an avian reovirus. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):968–976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.968-976.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe R., Meanger J., Enriquez C. E., Wilcox G. E. Avian reovirus proteins associated with neutralization of virus infectivity. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):688–696. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]