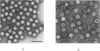
Abstract
VP60, the unique component of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus capsid, was expressed in the baculovirus system. The recombinant VP60, released in the supernatant of infected insect cells, assembled without the need of any other viral component to form viruslike particles (VLPs), structurally and immunologically indistinguishable from the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virion. Intramuscular vaccination of rabbits with the VLPs conferred complete protection in 15 days; this protection was found to be effective from the fifth day after VLP injection and was accompanied by a strong humoral response.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aponte C., Mattion N. M., Estes M. K., Charpilienne A., Cohen J. Expression of two bovine rotavirus non-structural proteins (NSP2, NSP3) in the baculovirus system and production of monoclonal antibodies directed against the expressed proteins. Arch Virol. 1993;133(1-2):85–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01309746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argüello Villares J. L. Viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits: vaccination and immune response. Rev Sci Tech. 1991 Jun;10(2):459–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beames B., Braunagel S., Summers M. D., Lanford R. E. Polyhedrin initiator codon altered to AUU yields unexpected fusion protein from a baculovirus vector. Biotechniques. 1991 Sep;11(3):378–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boga J. A., Marín M. S., Casais R., Prieto M., Parra F. In vitro translation of a subgenomic mRNA from purified virions of the Spanish field isolate AST/89 of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV). Virus Res. 1992 Oct;26(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90144-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Routledge E. G., Toms G. L. Monoclonal antibodies to feline calicivirus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2197–2200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J. R., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., McAuliffe V. J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Proteins of Norwalk virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.994-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Wang M., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Expression, self-assembly, and antigenicity of the Norwalk virus capsid protein. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6527–6532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6527-6532.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Wang M., Wang K., Estes M. K. Sequence and genomic organization of Norwalk virus. Virology. 1993 Jul;195(1):51–61. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Ayres M. D., Possee R. D. Linearization of baculovirus DNA enhances the recovery of recombinant virus expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5667–5672. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé M., Charpilienne A., Crawford S. E., Estes M. K., Cohen J. Expression of rotavirus VP2 produces empty corelike particles. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2946–2952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2946-2952.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow V. A., Summers M. D. High level expression of nonfused foreign genes with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90348-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López de Turiso J. A., Cortés E., Martínez C., Ruiz de Ybáez R., Simarro I., Vela C., Casal I. Recombinant vaccine for canine parvovirus in dogs. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2748–2753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2748-2753.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullough K. C., Butcher R. Monoclonal antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus 146S and 12S particles. Arch Virol. 1982;74(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01320777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Wirblich C., Thiel H. J. Genomic and subgenomic RNAs of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus are both protein-linked and packaged into particles. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):677–686. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90437-G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Wirblich C., Thiel H. J. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus--molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of a calicivirus genome. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):664–676. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90436-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill J. D. Nucleotide sequence of the capsid protein gene of two serotypes of San Miguel sea lion virus: identification of conserved and non-conserved amino acid sequences among calicivirus capsid proteins. Virus Res. 1992 Jul;24(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90008-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlinger V. F., Haas B., Meyers G., Weiland F., Thiel H. J. Identification and characterization of the virus causing rabbit hemorrhagic disease. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3331-3336.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra F., Boga J. A., Marin M. S., Casais R. The amino terminal sequence of VP60 from rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus supports its putative subgenomic origin. Virus Res. 1993 Mar;27(3):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90034-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra F., Prieto M. Purification and characterization of a calicivirus as the causative agent of a lethal hemorrhagic disease in rabbits. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4013–4015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4013-4015.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodák L., Granátová M., Valícek L., Smíd B., Veselý T., Nevoránková Z. Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus and their use in the diagnosis of infection. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2593–2598. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. L., Soergel M. E. Single major polypeptide of a calicivirus: characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stabilization of virions by cross-linking with dimethyl suberimidate. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):925–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.925-931.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakharia V. N., Snyder D. B., He J., Edwards G. H., Savage P. K., Mengel-Whereat S. A. Infectious bursal disease virus structural proteins expressed in a baculovirus recombinant confer protection in chickens. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):1201–1206. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valícek L., Smíd B., Rodák L., Kudrna J. Electron and immunoelectron microscopy of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV). Arch Virol. 1990;112(3-4):271–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01323171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vautherot J. F., Madelaine M. F., Boireau P., Laporte J. Bovine coronavirus peplomer glycoproteins: detailed antigenic analyses of S1, S2 and HE. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jul;73(Pt 7):1725–1737. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-7-1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Keus R. J. Baculovirus expression vector system for production of viral vaccines. Adv Biotechnol Processes. 1990;14:91–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. J., Chen W. X. Viral haemorrhagic disease in rabbits: a review. Vet Res Commun. 1989;13(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00142046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]