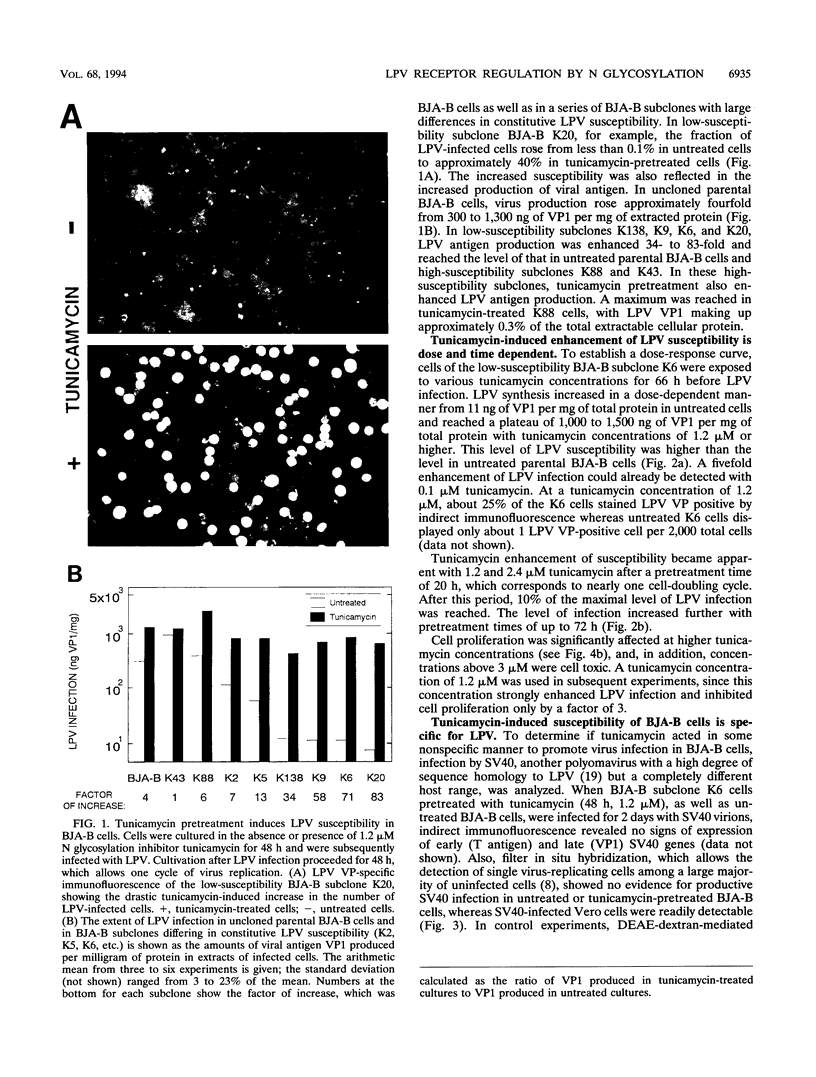
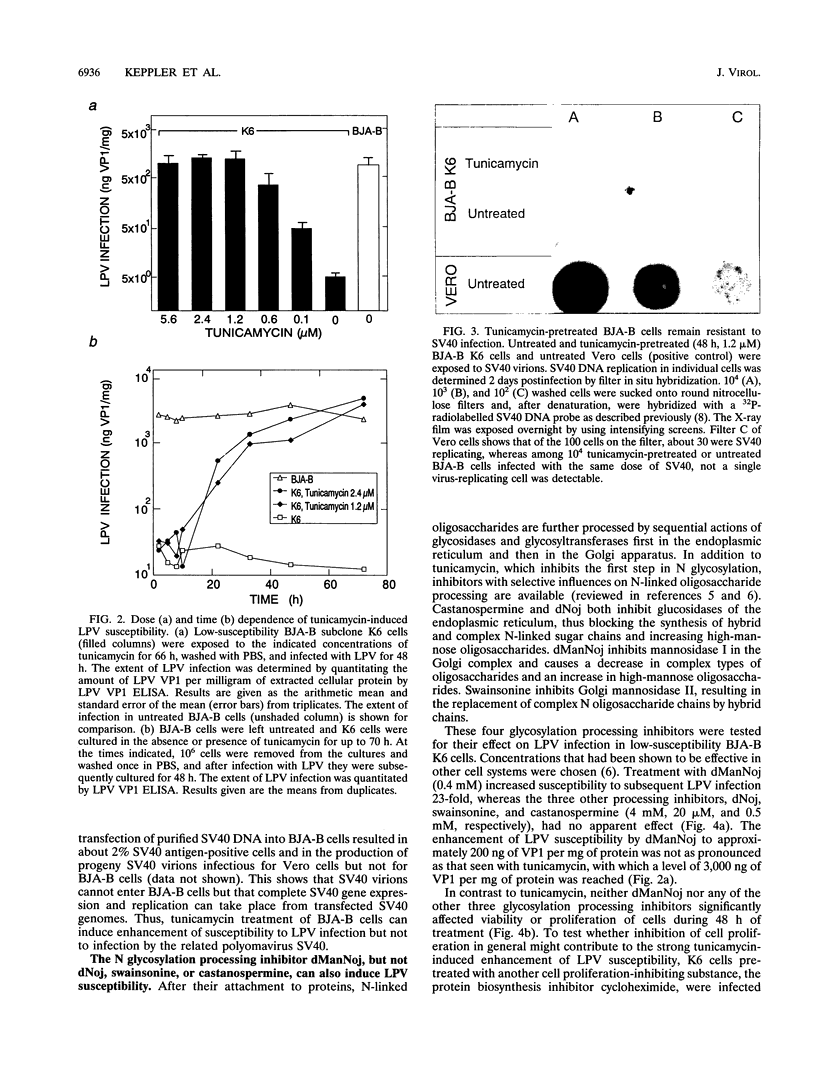
Abstract
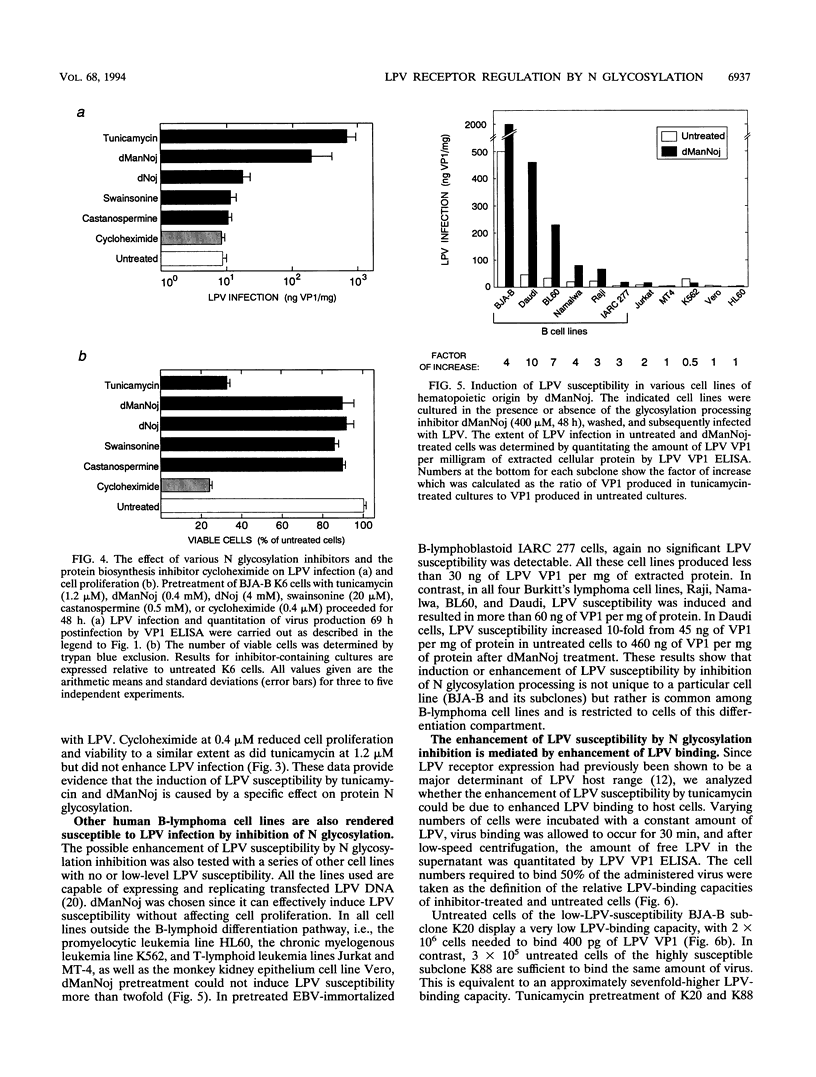
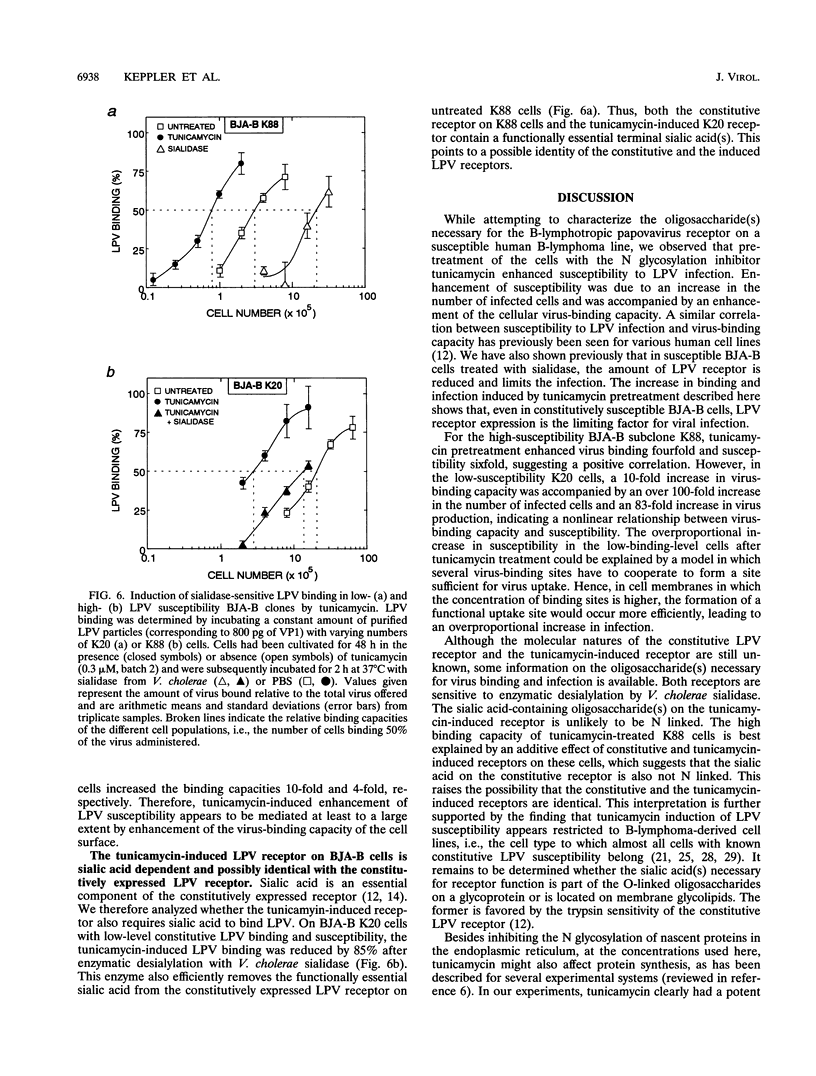
The host range of the B-lymphotropic papovavirus (LPV) in cultured human cells is limited to a few B-lymphoma-derived cell lines. The constitutively expressed cell surface receptor for the virus is a major determinant restricting the LPV host range (G. Haun, O. T. Keppler, C. T. Bock, M. Herrmann, H. Zentgraf, and M. Pawlita, J. Virol. 67:7482-7492, 1993). Here we show that human B-lymphoma cells with low-level susceptibility are rendered highly susceptible to LPV infection by pretreatment with the N glycosylation inhibitor tunicamycin but remain nonsusceptible to infection by the related polyomavirus simian virus 40. Among the selective N glycosylation processing inhibitors, deoxymannojirimycin, but not deoxynojirimycin, swainsonine, or castanospermine, could mimic the effect of tunicamycin. Tunicamycin treatment also induced a drastic enhancement of the cells' LPV-binding capacity, indicating that the induction of LPV susceptibility might be mediated by an increase in the number of functional cell surface receptors and/or by increased receptor affinity. Sialidase sensitivity of the tunicamycin-induced LPV receptor showed that oligosaccharides carrying terminal sialic acids are necessary for binding and are likely to be O linked. The constitutive LPV receptor is also sialic acid dependent, which points to a possible identity with the sialic acid-dependent tunicamycin-induced LPV receptor. We conclude that removal or modification of certain N-linked oligosaccharides in human B-lymphoma cells can enhance expression or functional activity of the sialylated LPV receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwell G., Morell A. G. The role of surface carbohydrates in the hepatic recognition and transport of circulating glycoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1974;41(0):99–128. doi: 10.1002/9780470122860.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas B., Gelfi J., L'Haridon R., Vogel L. K., Sjöström H., Norén O., Laude H. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):417–420. doi: 10.1038/357417a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden M. V., Farrell K., Wilson C. A. Glycosylation-dependent inactivation of the ecotropic murine leukemia virus receptor. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):626–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.626-631.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Glycosylation inhibitors for N-linked glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:661–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D. Inhibitors of the biosynthesis and processing of N-linked oligosaccharide chains. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:497–534. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes B., Gissmann L., Pawlita M. Detection of individual virus-infected cells by filter in situ hybridization. Mol Cell Probes. 1988 Sep;2(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(88)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Carlsson S. R. Leukosialin, a major sialoglycoprotein on human leukocytes as differentiation antigens. Med Biol. 1986;64(6):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haun G., Keppler O. T., Bock C. T., Herrmann M., Zentgraf H., Pawlita M. The cell surface receptor is a major determinant restricting the host range of the B-lymphotropic papovavirus. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7482–7492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7482-7492.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Interplay between carbohydrate in the stalk and the length of the connecting peptide determines the cleavability of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3296–3300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3296-3300.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Bonnardel C. The use of lymphomatous and lymphoblastoid cell lines in the study of Burkitt's lymphoma. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;(60):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur H., Walter G. Monoclonal antibodies specific for the carboxy terminus of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.483-491.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlita M., Clad A., zur Hausen H. Complete DNA sequence of lymphotropic papovavirus: prototype of a new species of the polyomavirus genus. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):196–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piller F., Piller V., Fox R. I., Fukuda M. Human T-lymphocyte activation is associated with changes in O-glycan biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15146–15150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Furuno A., Kato K., Yoshiike K. Biological and biochemical studies of African green monkey lymphotropic papovavirus. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):502–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.502-509.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. A., Eiden M. V. Viral and cellular factors governing hamster cell infection by murine and gibbon ape leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5975–5982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5975-5982.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Gissmann L. Lymphotropic papovaviruses isolated from African green monkey and human cells. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1979 Aug;167(3):137–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02121180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]