Abstract
Three infectious, attenuated molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac) were tested for viral and host determinants of protective immunity. The viruses differed in degree of virulence from highly attenuated to moderately attenuated to partially attenuated. Levels of immune stimulation and antiviral immunity were measured in rhesus macaques inoculated 2 years previously with these viruses. Monkeys infected with the highly attenuated or moderately attenuated viruses had minimal lymphoid hyperplasia, normal CD4/CD8 ratios, low levels of SIV-specific antibodies, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity against p55gag (Gag) or gp160env (Env). Monkeys infected with the partially attenuated virus had moderate to marked lymphoid hyperplasia, normal CD4/CD8 ratios, high levels of SIV-specific antibodies, and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity against both Gag and Env. After pathogenic virus challenge, monkeys immunized with the partially attenuated virus had 100- to 1,000-fold-lower viral load in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and lymph node mononuclear cells than naive control animals. One of four monkeys immunized with the highly attenuated virus and two of four monkeys immunized with the moderately attenuated virus developed similarly low viral loads after challenge. These three attenuated strains of SIV induced a spectrum of antiviral immunity that was inversely associated with their degree of attenuation. Only the least attenuated virus induced resistance to challenge infection in all immunized monkeys.
Full text
PDF


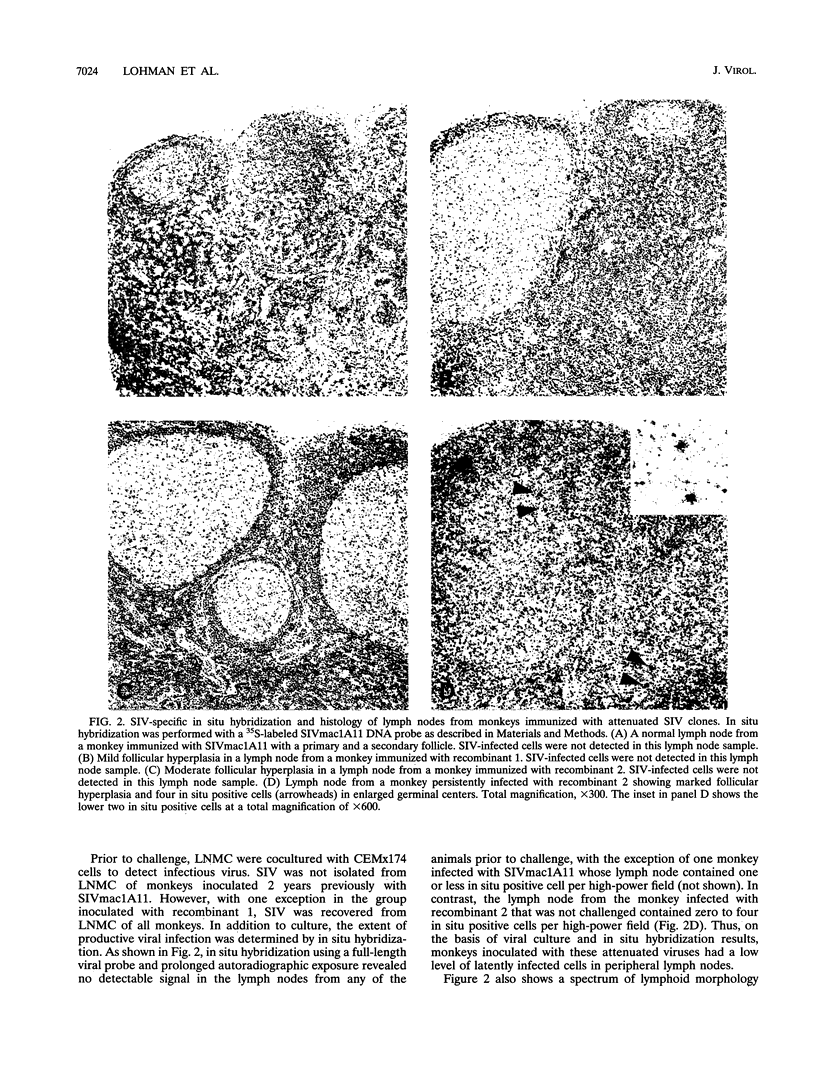
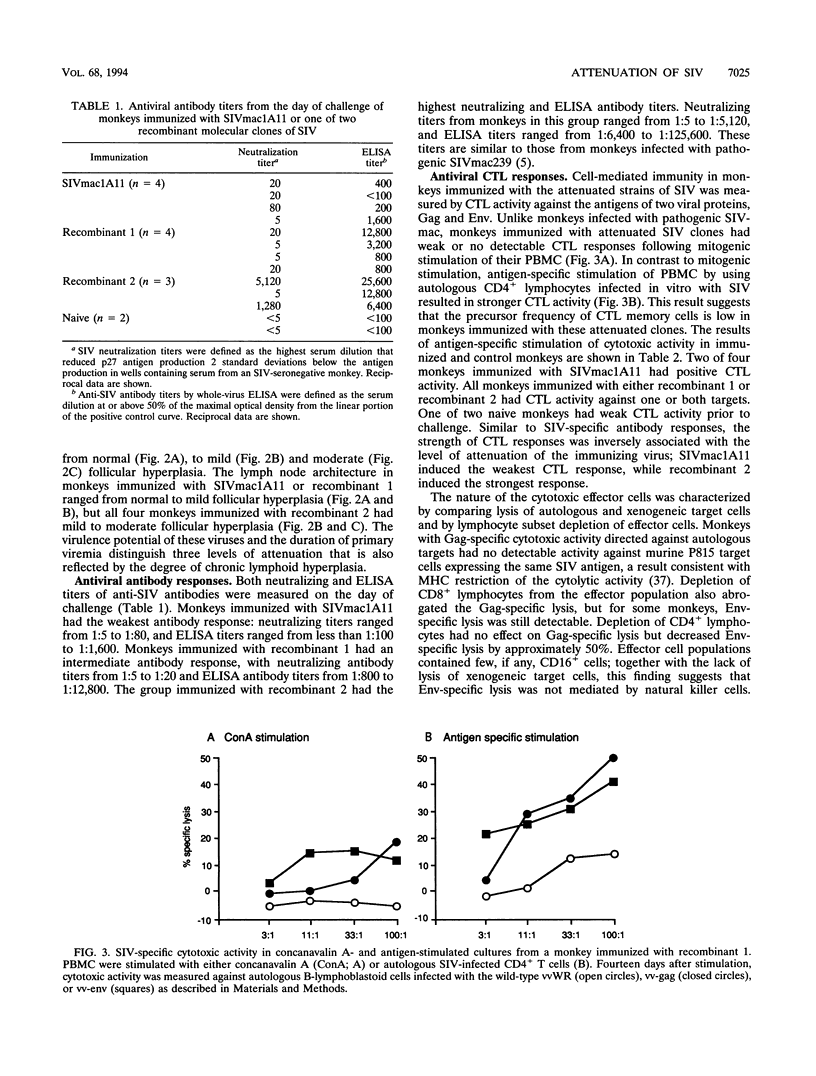
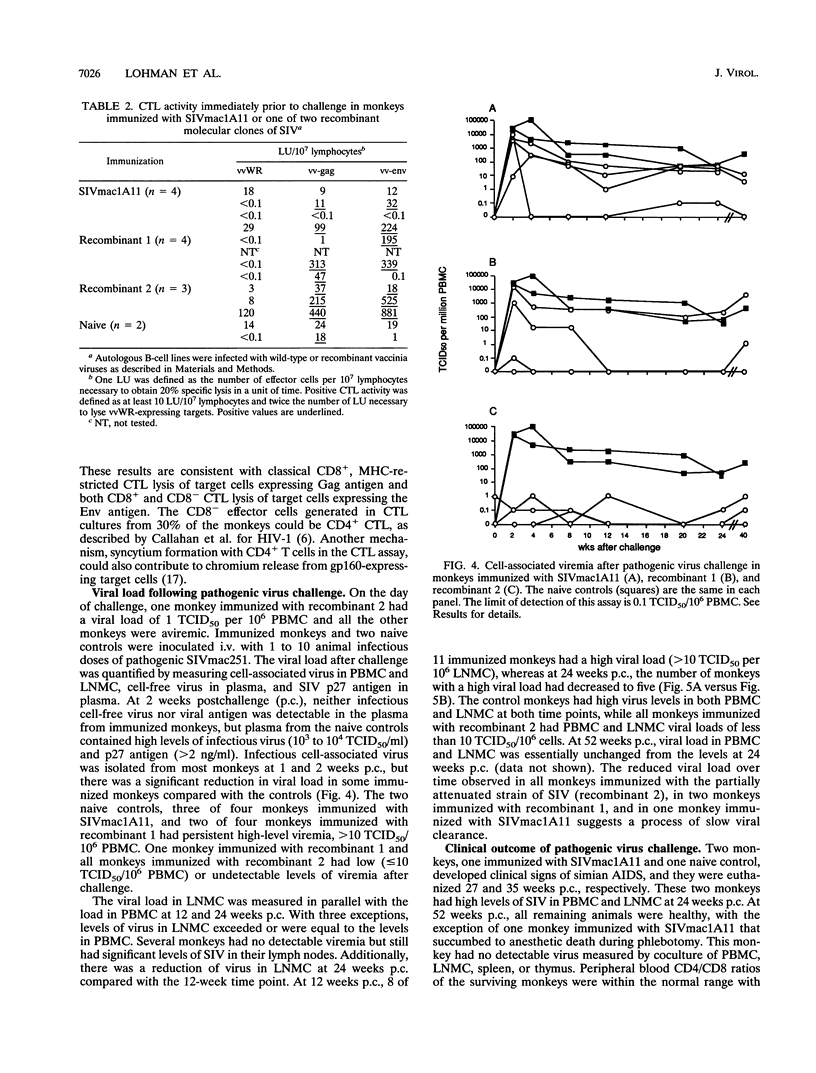
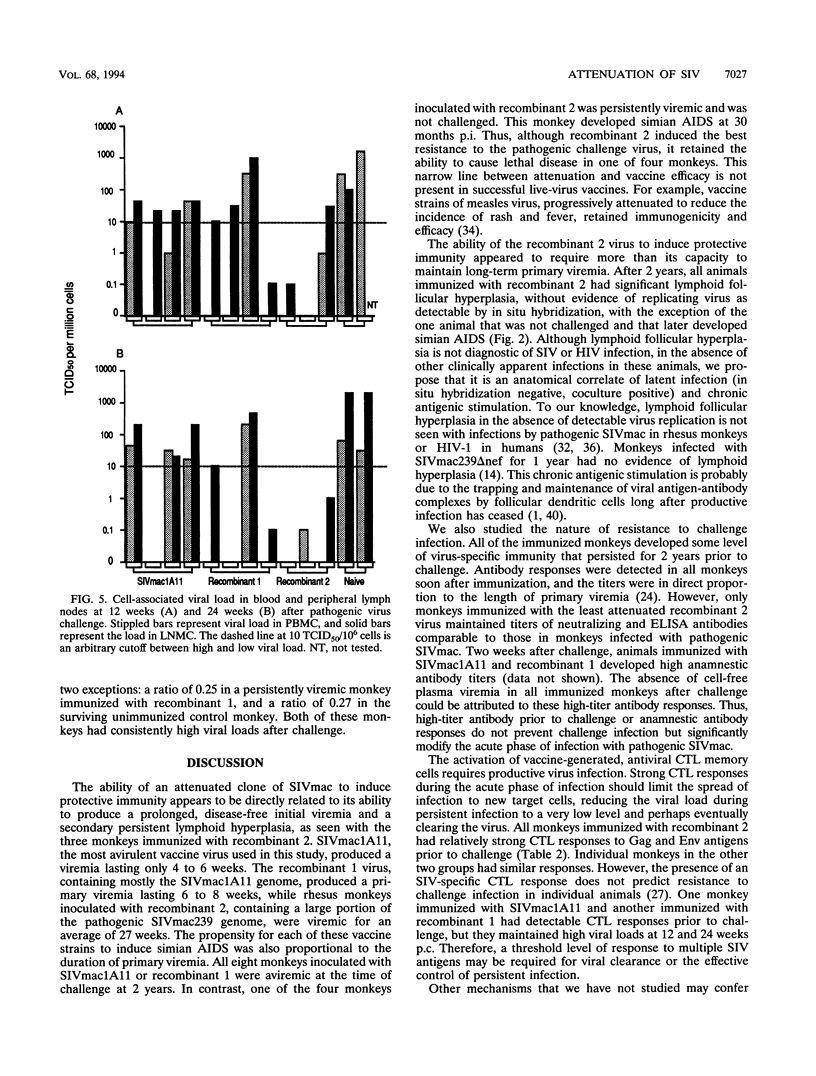


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad S., Lohman B., Marthas M., Giavedoni L., el-Amad Z., Haigwood N. L., Scandella C. J., Gardner M. B., Luciw P. A., Yilma T. Reduced virus load in rhesus macaques immunized with recombinant gp160 and challenged with simian immunodeficiency virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994 Feb;10(2):195–204. doi: 10.1089/aid.1994.10.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banapour B., Marthas M. L., Ramos R. A., Lohman B. L., Unger R. E., Gardner M. B., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A. Identification of viral determinants of macrophage tropism for simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5798–5805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5798-5805.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. P., Collignon C., Desrosiers R. C. Simian immunodeficiency virus mutants resistant to serum neutralization arise during persistent infection of rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4104–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4104-4113.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan K. M., Rowell J. F., Soloski M. J., Machamer C. E., Siliciano R. F. HIV-1 envelope protein is expressed on the surface of infected cells before its processing and presentation to class II-restricted T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):2928–2942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., McGuire T. C. The lentiviruses: maedi/visna, caprine arthritis-encephalitis, and equine infectious anemia. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:189–215. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Kirchhoff F., Czajak S. C., Sehgal P. K., Desrosiers R. C. Protective effects of a live attenuated SIV vaccine with a deletion in the nef gene. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1938–1941. doi: 10.1126/science.1470917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart A. R., Cloyd M. W. Interference patterns of human immunodeficiency viruses HIV-1 and HIV-2. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90454-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horohov D. W., Crim J. A., Smith P. L., Siegel J. P. IL-4 (B cell-stimulatory factor 1) regulates multiple aspects of influenza virus-specific cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Ringler D. J., Mori K., Panicali D. L., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90097-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H., Kodama T., Ringler D., Marthas M., Pedersen N., Lackner A., Regier D., Sehgal P., Daniel M., King N. Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.2160735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Hirsch V. M., Johnson P. R., Sawasdikosol S. Animal models for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:425–474. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner A. A., Smith M. O., Munn R. J., Martfeld D. J., Gardner M. B., Marx P. A., Dandekar S. Localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in the central nervous system of rhesus monkeys. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):609–621. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. G., Bellah S., McKinnon K., Yalley-Ogunro J., Zack P. M., Elkins W. R., Desrosiers R. C., Eddy G. A. Titration and characterization of two rhesus-derived SIVmac challenge stocks. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994 Feb;10(2):213–220. doi: 10.1089/aid.1994.10.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman B. L., Higgins J., Marthas M. L., Marx P. A., Pedersen N. C. Development of simian immunodeficiency virus isolation, titration, and neutralization assays which use whole blood from rhesus monkeys and an antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2187–2192. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2187-2192.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu W., Grassi F., Tourani J. M., Eme D., Israel-Biet D., Andrieu J. M. High concentration of peripheral blood mononuclear cells harboring infectious virus correlates with rapid progression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-related diseases. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1165–1168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Shaw K. E., Unger R. E., Planelles V., Stout M. W., Lackner J. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Leung N. J., Banapour B., Marthas M. L. Genetic and biological comparisons of pathogenic and nonpathogenic molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):395–402. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthas M. L., Banapour B., Sutjipto S., Siegel M. E., Marx P. A., Gardner M. B., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A. Rhesus macaques inoculated with molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus. J Med Primatol. 1989;18(3-4):311–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthas M. L., Miller C. J., Sutjipto S., Higgins J., Torten J., Lohman B. L., Unger R. E., Ramos R. A., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R. Efficacy of live-attenuated and whole-inactivated simian immunodeficiency virus vaccines against vaginal challenge with virulent SIV. J Med Primatol. 1992 Feb-May;21(2-3):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthas M. L., Ramos R. A., Lohman B. L., Van Rompay K. K., Unger R. E., Miller C. J., Banapour B., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A. Viral determinants of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) virulence in rhesus macaques assessed by using attenuated and pathogenic molecular clones of SIVmac. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6047–6055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6047-6055.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marthas M. L., Sutjipto S., Higgins J., Lohman B., Torten J., Luciw P. A., Marx P. A., Pedersen N. C. Immunization with a live, attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) prevents early disease but not infection in rhesus macaques challenged with pathogenic SIV. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3694–3700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3694-3700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Oldstone M. B. Virus-induced immunosuppression: infections with measles virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:335–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. D., Lord C. I., Stallard V., Mazzara G. P., Letvin N. L. The gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in rhesus monkeys infected with the simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):122–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Human immunodeficiency virus: an agent that defies vaccination. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1989;33:397–412. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039233-9.50016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C. Animal virus infections that defy vaccination: equine infectious anemia, caprine arthritis-encephalitis, maedi-visna, and feline infectious peritonitis. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1989;33:413–428. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-039233-9.50017-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringler D. J., Wyand M. S., Walsh D. G., MacKey J. J., Chalifoux L. V., Popovic M., Minassian A. A., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Cellular localization of simian immunodeficiency virus in lymphoid tissues. I. Immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere Y., Tanneau-Salvadori F., Regnault A., Lopez O., Sansonetti P., Guy B., Kieny M. P., Fournel J. J., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic responses of seropositive individuals: distinct types of effector cells mediate killing of targets expressing gag and env proteins. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2270–2277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2270-2277.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Howell D. N., Cresswell P. Genes regulating HLA class I antigen expression in T-B lymphoblast hybrids. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(3):235–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00375376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Greenhouse J. J., Psallidopoulos M. C., Baseler M., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S., Lane H. C. Increasing viral burden in CD4+ T cells from patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection reflects rapidly progressive immunosuppression and clinical disease. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 15;113(6):438–443. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-6-438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew J. G., Mandel T. E. Prolonged antigen half-life in the lymphoid follicles of specifically immunized mice. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):69–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rompay K. K., Marthas M. L., Ramos R. A., Mandell C. P., McGowan E. K., Joye S. M., Pedersen N. C. Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection of infant rhesus macaques as a model to test antiretroviral drug prophylaxis and therapy: oral 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine prevents SIV infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2381–2386. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




