Abstract
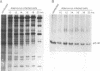
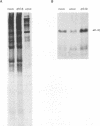
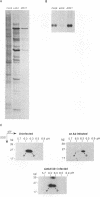
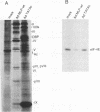
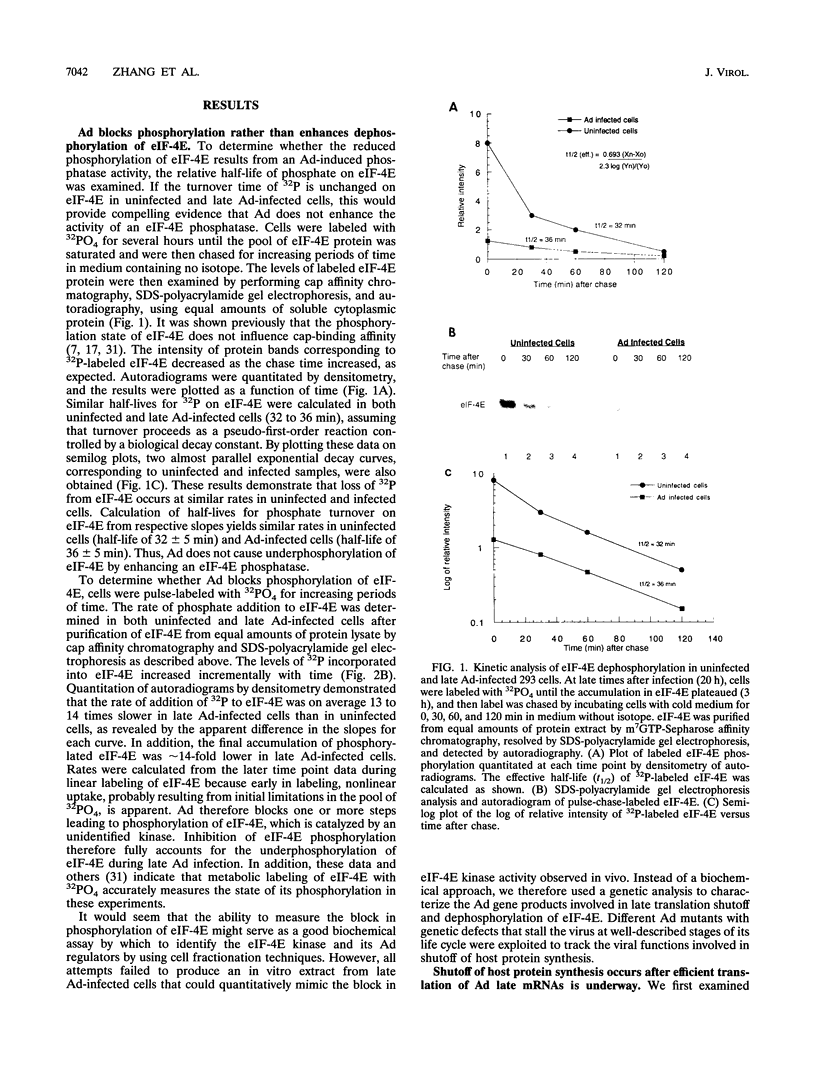
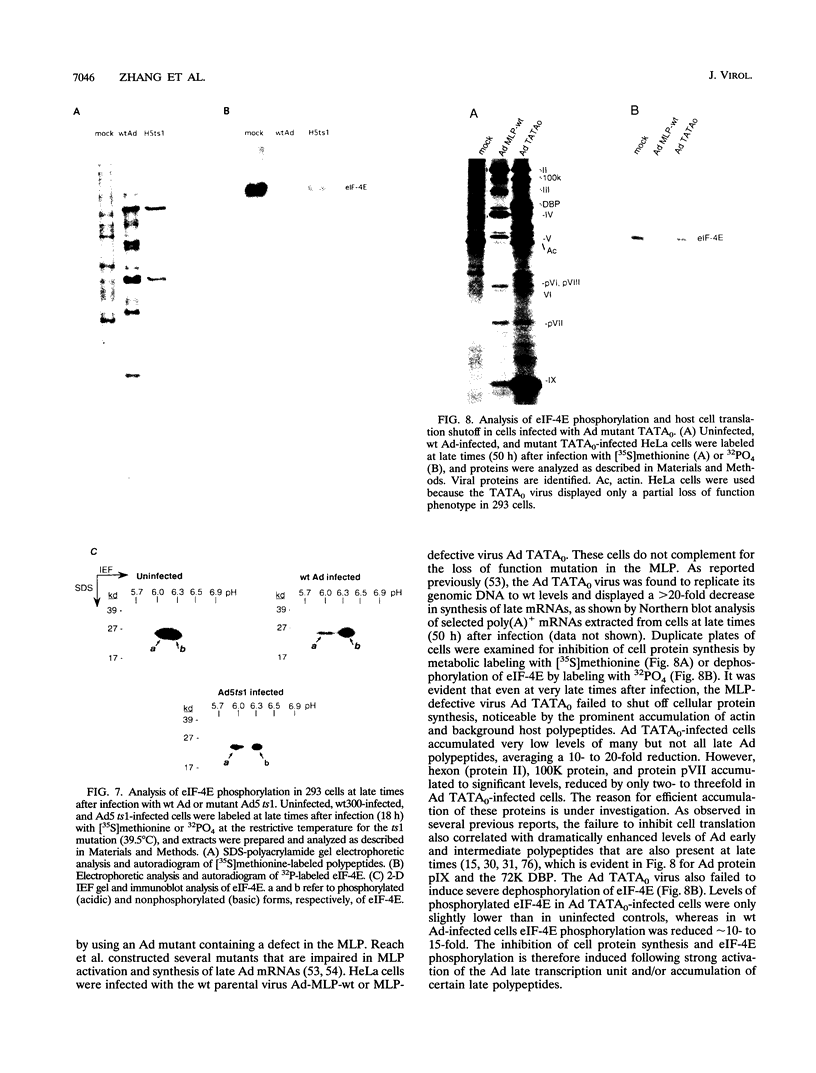
Adenovirus prevents host cell protein synthesis during its late phase of replication in large part by causing the underphosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-4E, a component of initiation factor eIF-4F (cap-binding protein complex). Late adenovirus mRNAs are preferentially translated because they possess a reduced requirement for eIF-4F. This study continues the characterization of the mechanism by which adenovirus inhibits cellular protein synthesis. First it is shown that adenovirus blocks the addition of phosphate to eIF-4E rather than enhancing its removal, establishing that the virus impairs a signalling pathway or protein kinase activity involved in eIF-4E phosphorylation. It is then shown that shutoff of cell protein synthesis and translation of late viral mRNAs are uncoupled, in that shutoff actually occurs a short time (1 to 3 h) after late adenovirus mRNAs are already undergoing translation. Finally, by using a variety of genetic mutants stalled at different stages in the viral life cycle, it was found that dephosphorylation of eIF-4E and inhibition of cell translation are not caused by early adenovirus gene products acting at late times or by events related to viral DNA replication. Instead, it is shown that inhibition of eIF-4E phosphorylation and cell translation are mediated upon activation of the viral major late transcription unit. These and other results presented indicate that the adenovirus signal which induces eIF-4E dephosphorylation and shutoff of cell protein synthesis is linked either to an activity of one or more late viral polypeptides, to double-stranded RNA produced by opposition of the early and late viral transcription units, or to both.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Dreyfuss G. Adenovirus proteins associated with mRNA and hnRNA in infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3276–3283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3276-3283.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. Translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: initiation factor 4E-dependent cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4467–4472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S. Adenovirus type 5 early region 1b gene product is required for efficient shutoff of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L., Sharp P. A. Effect of the tripartite leader on synthesis of a non-viral protein in an adenovirus 5 recombinant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):841–857. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti A. R., Weber J. Protease of adenovirus type 2: partial characterization. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Barber G. N., Katze M. G. Degradation of the interferon-induced 68,000-M(r) protein kinase by poliovirus requires RNA. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.791-800.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Involvement of the 24-kDa cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11134–11139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridge E., Ketner G. Redundant control of adenovirus late gene expression by early region 4. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):631–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.631-638.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll K., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Jagus R. Recombinant vaccinia virus K3L gene product prevents activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent, initiation factor 2 alpha-specific protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12837–12842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo J. L., Carrasco L. Adenovirus late protein synthesis is resistant to the inhibition of translation induced by poliovirus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7328–7334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. H., Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. The adenovirus L3 23-kilodalton proteinase cleaves the amino-terminal head domain from cytokeratin 18 and disrupts the cytokeratin network of HeLa cells. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3507–3514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3507-3514.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Chang H. W., Jacobs B. L., Kaufman R. J. The E3L and K3L vaccinia virus gene products stimulate translation through inhibition of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase by different mechanisms. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1688–1692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1688-1692.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Rhoads R. E. Overexpression of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor 4E in HeLa cells results in aberrant growth and morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8212–8216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Translation by the adenovirus tripartite leader: elements which determine independence from cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2669–2677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2669-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Racaniello V., Villamarin A., Palladino F., Schneider R. J. The adenovirus tripartite leader may eliminate the requirement for cap-binding protein complex during translation initiation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2059–2066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2059-2066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. W., Hagedorn C. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor or okadaic acid stimulates phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3162–3166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Selection and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of type 5 adenovirus. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):328–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.328-339.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenblum D., Schneider R. J. Modification of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F during infection by influenza virus. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3027–3035. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3027-3035.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher L., Corbin S. D., Browning K. S., Ravel J. M. The absence of a m7G cap on beta-globin mRNA and alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4 increases the amounts of initiation factor 4F required for translation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19582–19587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. M., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E is increased in Src-transformed cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2896–2900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. M., Mushynski W. E., Sonenberg N. Phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF-4E is induced in a ras-dependent manner during nerve growth factor-mediated PC12 cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1239–1247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Cutt J. R., Shenk T. Adenovirus early region 4 encodes functions required for efficient DNA replication, late gene expression, and host cell shutoff. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.250-257.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes B. W., Telling G. C., Myat M. M., Williams J. F., Flint S. J. The adenovirus L4 100-kilodalton protein is necessary for efficient translation of viral late mRNA species. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2732–2742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2732-2742.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis involves inactivation of cap-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90161-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis is prevented by the drug 2-aminopurine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7115–7119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi-Barve S., De Benedetti A., Rhoads R. E. Preferential translation of heat shock mRNAs in HeLa cells deficient in protein synthesis initiation factors eIF-4E and eIF-4 gamma. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21038–21043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judware R., Petryshyn R. Mechanism of action of a cellular inhibitor of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase from 3T3-F442A cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21685–21690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar R. L., Rychlik W., White M. W., Rhoads R. E., Morris D. R. Simultaneous cytoplasmic redistribution of ribosomal protein L32 mRNA and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E after mitogenic stimulation of Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Shenk T. An adenovirus mutant unable to express VAI RNA displays different growth responses and sensitivity to interferon in various host cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4493–4498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamphear B. J., Panniers R. Cap binding protein complex that restores protein synthesis in heat-shocked Ehrlich cell lysates contains highly phosphorylated eIF-4E. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5333–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Dodds J. T., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Betsch D. F., Weith H. L., Thach R. E. Influence of 5' proximal secondary structure on the translational efficiency of eukaryotic mRNAs and on their interaction with initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13979–13989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazaris-Karatzas A., Montine K. S., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5' cap. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):544–547. doi: 10.1038/345544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tang N., Thompson S., Miller J., Katze M. G. The 58,000-dalton cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) is a member of the tetratricopeptide repeat family of proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2331–2342. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Shenk T. Adenovirus tripartite leader sequence enhances translation of mRNAs late after infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Pfeffer L. M., Guidon P. T., Jr, Donner D. B. Tumor necrosis factor induces phosphorylation of a 28-kDa mRNA cap-binding protein in human cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8417–8421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Control of translation in adenovirus-infected cells. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):250–264. doi: 10.1159/000468763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Phorbol esters stimulate phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factors 3, 4B, and 4F. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2401–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundschau L. J., Faller D. V. Oncogenic ras induces an inhibitor of double-stranded RNA-dependent eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha-kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23092–23098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Stewart E. B., Merrick W. C., Henshaw E. C. Mechanism of inhibition of polypeptide chain initiation in heat-shocked Ehrlich cells involves reduction of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9648–9653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pause A., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of a DEAD box RNA helicase: the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2643–2654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05330.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilder S., Moore M., Logan J., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B-55K transforming polypeptide modulates transport or cytoplasmic stabilization of viral and host cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):470–476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Brendler T. G., Adya S., Daniels-McQueen S., Miller J. K., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Role of mRNA competition in regulating translation: further characterization of mRNA discriminatory initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reach M., Babiss L. E., Young C. S. The upstream factor-binding site is not essential for activation of transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5851–5860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5851-5860.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reach M., Xu L. X., Young C. S. Transcription from the adenovirus major late promoter uses redundant activating elements. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3439–3446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis by initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3017–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley D., Flint S. J. RNA-binding properties of a translational activator, the adenovirus L4 100-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3586–3595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3586-3595.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinker-Schaeffer C. W., Austin V., Zimmer S., Rhoads R. E. Ras transformation of cloned rat embryo fibroblasts results in increased rates of protein synthesis and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10659–10664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Rush J. S., Rhoads R. E., Waechter C. J. Increased rate of phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of the translational initiation factor eIF-4E correlates with the induction of protein and glycoprotein biosynthesis in activated B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19467–19471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Edery I., Gallo R., Sonenberg N. Preferential stimulation of rabbit alpha globin mRNA translation by a cap-binding protein complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 22;783(2):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Weinberger C., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA facilitates the initiation of translation in virus-infected cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Jaramillo M., Liu Y. L., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Kung H. F., Sonenberg N. Translation initiation factors induce DNA synthesis and transform NIH 3T3 cells. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):648–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI mediates a translational stimulation which is not restricted to the viral mRNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Dietlin T. A., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Worrilow L. M. Effect of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F on AUG selection in a bicistronic mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3594–3601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. A., Scheper G. C., Kleijn M., De Boer M., Voorma H. O. Dependence of the adenovirus tripartite leader on the p220 subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F during in vitro translation. Effect of p220 cleavage by foot-and-mouth-disease-virus L-protease on in vitro translation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Morley S. J., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Rhoads R. E., Traugh J. A. Association of initiation factor eIF-4E in a cap binding protein complex (eIF-4F) is critical for and enhances phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10617–10621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Ketner G. A cell line that supports the growth of a defective early region 4 deletion mutant of human adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5383–5386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh-Kai L., Akusjärvi G., Aleström P., Pettersson U., Tremblay M., Weber J. Genetic identification of an endoproteinase encoded by the adenovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata J. M., Maroto F. G., Sierra J. M. Inactivation of mRNA cap-binding protein complex in Drosophila melanogaster embryos under heat shock. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16007–16014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Dolph P. J., Schneider R. J. Secondary structure analysis of adenovirus tripartite leader. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10679–10684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cell translation facilitates release of virus particles and enhances degradation of the cytokeratin network. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2544–2555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2544-2555.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]