Abstract
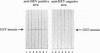
A synthetic gene encoding an artificial polypeptide composed of antigenic epitopes of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) proteins was constructed from short oligodeoxyribonucleotides by using PCR. The polypeptide comprises a mosaic of three antigenically active dominant regions from the protein encoded by open reading frame 2 (ORF2), one antigenically active region from the protein encoded by ORF3 of the Burmese HEV strain, and one antigenically active region from the protein encoded by ORF3 of the Mexican HEV strain. The mosaic protein was expressed in Escherichia coli as a chimera with glutathione S-transferase or beta-galactosidase. Guinea pig sera containing antibodies to the corresponding HEV synthetic peptides were used to demonstrate by Western immunoblot analysis and enzyme immunoassay the presence and accessibility of all HEV-specific antigenic epitopes introduced into the mosaic protein. Both the glutathione S-transferase and beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins were analyzed by using a panel of human anti-HEV-positive and -negative sera. The data obtained strongly indicate a diagnostic potential for the mosaic protein.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aichele P., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M., Schulz M. Antiviral cytotoxic T cell response induced by in vivo priming with a free synthetic peptide. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1815–1820. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aye T. T., Uchida T., Ma X., Iida F., Shikata T., Ichikawa M., Rikihisa T., Win K. M. Sequence and gene structure of the hepatitis E virus isolated from Myanmar. Virus Genes. 1993 Feb;7(1):95–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01702352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau K. H., Dawson G. J., Bile K. M., Magnius L. O., Sjogren M. H., Mushahwar I. K. Detection of IgA class antibody to hepatitis E virus in serum samples from patients with hepatitis E virus infection. J Med Virol. 1993 Aug;40(4):334–338. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890400414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien D. Y., Choo Q. L., Tabrizi A., Kuo C., McFarland J., Berger K., Lee C., Shuster J. R., Nguyen T., Moyer D. L. Diagnosis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection using an immunodominant chimeric polyprotein to capture circulating antibodies: reevaluation of the role of HCV in liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10011–10015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coursaget P., Buisson Y., Depril N., le Cann P., Chabaud M., Molinié C., Roue R. Mapping of linear B cell epitopes on open reading frames 2- and 3-encoded proteins of hepatitis E virus using synthetic peptides. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 May 15;109(2-3):251–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson G. J., Chau K. H., Cabal C. M., Yarbough P. O., Reyes G. R., Mushahwar I. K. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for hepatitis E virus IgG and IgM antibodies utilizing recombinant antigens and synthetic peptides. J Virol Methods. 1992 Jul;38(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(92)90180-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favorov M. O., Fields H. A., Purdy M. A., Yashina T. L., Aleksandrov A. G., Alter M. J., Yarasheva D. M., Bradley D. W., Margolis H. S. Serologic identification of hepatitis E virus infections in epidemic and endemic settings. J Med Virol. 1992 Apr;36(4):246–250. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890360403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favorov M. O., Khudyakov Y. E., Fields H. A., Khudyakova N. S., Padhye N., Alter M. J., Mast E., Polish L., Yashina T. L., Yarasheva D. M. Enzyme immunoassay for the detection of antibody to hepatitis E virus based on synthetic peptides. J Virol Methods. 1994 Feb;46(2):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(94)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry as a mechanism for virus-induced autoimmunity. Immunol Res. 1989;8(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02918552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R., Ghosh H. P. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gB in the nuclear envelope of infected cells. Virus Res. 1993 Jun;28(3):217–231. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(93)90023-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith R., Yarbough P. O., Reyes G. R., Fry K. E., Gabor K. A., Kamel M., Zakaria S., Amer S., Gaffar Y. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of acute sporadic hepatitis E in Egyptian children. Lancet. 1992 Feb 8;339(8789):328–331. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91647-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Tam A. W., Yarbough P. O., Reyes G. R., Carl M. Expression and diagnostic utility of hepatitis E virus putative structural proteins expressed in insect cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Aug;31(8):2167–2173. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.8.2167-2173.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. C., Nguyen D., Fernandez J., Yun K. Y., Fry K. E., Bradley D. W., Tam A. W., Reyes G. R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the Mexico isolate of hepatitis E virus (HEV). Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):550–558. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90230-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa M., Araki M., Rikihisa T., Uchida T., Shikata T., Mizuno K. Cloning and expression of cDNAs from enterically-transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis virus. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(7):535–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur M., Hyams K. C., Purdy M. A., Krawczynski K., Ching W. M., Fry K. E., Reyes G. R., Bradley D. W., Carl M. Human linear B-cell epitopes encoded by the hepatitis E virus include determinants in the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3855–3858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khudyakov YuE, Favorov M. O., Jue D. L., Hine T. K., Fields H. A. Immunodominant antigenic regions in a structural protein of the hepatitis E virus. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):390–393. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khudyakov YuE, Khudyakova N. S., Jue D. L., Wells T. W., Padhya N., Fields H. A. Comparative characterization of antigenic epitopes in the immunodominant region of the protein encoded by open reading frame 3 in Burmese and Mexican strains of hepatitis E virus. J Gen Virol. 1994 Mar;75(Pt 3):641–646. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-3-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khudyakov Y. E., Khudyakova N. S., Fields H. A., Jue D., Starling C., Favorov M. O., Krawczynski K., Polish L., Mast E., Margolis H. Epitope mapping in proteins of hepatitis E virus. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):89–96. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V., Gorbalenya A. E., Purdy M. A., Rozanov M. N., Reyes G. R., Bradley D. W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8259–8263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Bansal V. J., Rao K. V., Jameel S. Hepatitis B virus envelope epitopes: gene assembly and expression in Escherichia coli of an immunologically reactive novel multiple-epitope polypeptide 1 (MEP-1). Gene. 1992 Jan 15;110(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90640-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok A. S., Kwan W. K., Moeckli R., Yarbough P. O., Chan R. T., Reyes G. R., Lai C. L., Chung H. T., Lai T. S. Seroepidemiological survey of hepatitis E in Hong Kong by recombinant-based enzyme immunoassays. Lancet. 1992 Nov 14;340(8829):1205–1208. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92901-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manivel V., Ramesh R., Panda S. K., Rao K. V. A synthetic peptide spontaneously self-assembles to reconstruct a group-specific, conformational determinant of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):4006–4011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Smith G. P. Antibody-selectable filamentous fd phage vectors: affinity purification of target genes. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):305–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90495-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy M. A., McCaustland K. A., Krawczynski K., Tam A., Beach M. J., Tassopoulos N. C., Reyes G. R., Bradley D. W. Expression of a hepatitis E virus (HEV)-trpE fusion protein containing epitopes recognized by antibodies in sera from human cases and experimentally infected primates. Arch Virol. 1992;123(3-4):335–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01317268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., Yarbough P. O., Tam A. W., Purdy M. A., Huang C. C., Kim J. S., Bradley D. W., Fry K. E. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): the novel agent responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991 Jul;26 (Suppl 3):142–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02779285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore S. J., Yarbough P. O., Gabor K. A., Reyes G. R. Hepatitis E virus: the cause of a waterbourne hepatitis outbreak. J Med Virol. 1992 May;37(1):58–60. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasappa J., Saegusa J., Prabhakar B. S., Gentry M. K., Buchmeier M. J., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H., Oldstone M. B., Notkins A. L. Molecular mimicry: frequency of reactivity of monoclonal antiviral antibodies with normal tissues. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.397-401.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam A. W., Smith M. M., Guerra M. E., Huang C. C., Bradley D. W., Fry K. E., Reyes G. R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90760-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo J. R., McLane M. F., Lee T. H., Essex M. Molecular mimicry between the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 V3 loop and human brain proteins. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7711–7715. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7711-7715.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsarev S. A., Emerson S. U., Reyes G. R., Tsareva T. S., Legters L. J., Malik I. A., Iqbal M., Purcell R. H. Characterization of a prototype strain of hepatitis E virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):559–563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsarev S. A., Tsareva T. S., Emerson S. U., Kapikian A. Z., Ticehurst J., London W., Purcell R. H. ELISA for antibody to hepatitis E virus (HEV) based on complete open-reading frame-2 protein expressed in insect cells: identification of HEV infection in primates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;168(2):369–378. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbough P. O., Tam A. W., Fry K. E., Krawczynski K., McCaustland K. A., Bradley D. W., Reyes G. R. Hepatitis E virus: identification of type-common epitopes. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5790–5797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5790-5797.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann R. N., Kerr J. M., Siani M. A., Banville S. C., Santi D. V. Identification of highest-affinity ligands by affinity selection from equimolar peptide mixtures generated by robotic synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4505–4509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]